Elephant seal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Elephant sealTemporal range: Pleistocene - Recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male and female Northern Elephant Seals | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Mirounga
|
| Species | |
|
|
The Elephant Seal is a giant type of seal. These amazing animals belong to the genus Mirounga. There are two main kinds, or species, of elephant seals. One lives in the northern part of the world, and the other lives in the south.
The southern elephant seal makes its home in the cold Antarctic waters. The northern elephant seal prefers the islands off the coasts of California and Mexico. Elephant seals are the largest animals that can live both on land and in the water. Male elephant seals, called bulls, have a very big nose. They can weigh around 750 pounds and be 8 feet long when they are grown up. Some older males can even reach 11 feet in length and weigh 1,375 pounds!
Contents
What Makes Elephant Seals Special?
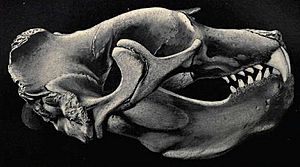
Elephant seals get their name from the male's large nose, called a proboscis. This nose looks a lot like an elephant's trunk. Male elephant seals use this big nose to make incredibly loud roaring sounds. They do this especially during the time when they look for mates.
More importantly, the nose helps them save water. It has special spaces that help them get moisture back from the air they breathe out. This is very important during mating season. At this time, the seals stay on the beach and do not go into the ocean to eat. They need to save every bit of body moisture they can.
Elephant seals are much bigger than other seals. Southern elephant seal males are usually about 16 feet long. They can weigh around 6,600 pounds. They are much larger than the females, called cows. Some very big males can even be 20 feet long and weigh 8,800 pounds! Females are typically about 10 feet long and weigh around 2,000 pounds. Northern elephant seal males are usually 14 to 16 feet long. The heaviest ones weigh about 5,500 pounds.
How Elephant Seals Live and Survive
Elephant seals spend most of their lives, over 80%, in the ocean. They can hold their breath for more than 100 minutes. This is longer than any other mammal that is not a whale or dolphin. Elephant seals can dive very deep, sometimes as far as 5,085 feet (1,550 meters) below the ocean's surface. The deepest recorded dive was by a southern elephant seal, going down 7,835 feet (2,388 meters)!
On average, their dives are about 1,000 to 2,000 feet deep. Females usually dive for about 20 minutes, and males for about 60 minutes. They dive to find their favorite foods. These include skates, rays, squid, octopi, eels, small sharks, and large fish. Sometimes, their stomachs also contain gastroliths, which are small stones. Even though they are excellent swimmers, they can also move quickly on land.
Elephant seals have a thick layer of blubber (fat) under their skin. This blubber protects them from the extreme cold, even more than their fur does. Their hair and outer skin layers come off in large patches. This process is called molting. New skin grows back from blood vessels that reach through the blubber. When a seal is molting, it can get cold easily. So, it must stay on land in a safe place called a "haul out" area. Northern male and young adult seals molt during June and July. Northern females and younger seals molt during April and May.
Elephant seals have a very large amount of blood. This allows them to carry a lot of oxygen, which they need for their long dives. They have large spaces in their bellies to hold blood. They can also store oxygen in their muscles. This is because their muscles have more myoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen. They also have more oxygen-carrying red blood cells. These special features help elephant seals dive so deep and stay underwater for up to two hours.
The milk that elephant seals produce is very high in fat. After starting with a lower fat content, it can become over 50% fat. For comparison, human milk is about 4% fat, and cow milk is about 3.5% fat.
Life Cycle of Elephant Seals
Northern elephant seals usually live for about 9 years. Southern elephant seals live longer, typically 20 to 22 years. Male seals become ready to breed at five to six years old. However, they usually don't become dominant males until they are eight. Their best breeding years are between ages 9 and 12. The oldest known male northern elephant seal lived for about 14 years.
Female elephant seals start having pups when they are 3 to 6 years old, usually around age 4. They have one pup each time they breed. Once they start breeding, about 79% of adult females have a pup every year. First-time mothers are not as successful at breeding as experienced mothers. This means having a pup for the first time is harder for them. Experienced breeding females have an 83% chance of surviving each year. But first-time breeders only have a 66% chance. This shows that having a first pup takes a lot of energy from the mother. In years when the ocean water is warmer in the northeastern Pacific, more male pups are born than female pups.
Elephant Seal Behavior
Life on Land
When it's not breeding season, elephant seals only come ashore to shed their skin. This process is called moulting. In late summer, hundreds of seals gather on beaches. They often roll around in muddy pools of water. They lie close together as they slowly shed patches of hair and skin. After their old skin is replaced by a new, smooth coat of fur, the seals return to the ocean.
Before mating, male elephant seals often fight each other. They throw their huge bodies against one another. The winners of these fights get to mate with the females.
Diving for Food
Elephant seals dive very deep, up to 5,085 feet (1,550 meters), to find their favorite foods. Their diet includes skates, rays, squid, octopus, eels, and small sharks. Southern elephant seals also eat penguins. Their stomachs often contain gastroliths, which are stones they swallow.
Even though they spend most of their time in the water, elephant seals are surprisingly good on land. They can even move faster than humans when crossing sand dunes!
How Elephant Seals Are Doing Today
The IUCN says that both types of elephant seals are of least concern. This means their populations are stable and not currently at high risk. However, they still face some dangers. These include getting tangled in trash in the ocean, problems with fishing gear, and collisions with boats.
It's hard to count all elephant seals because they are not all on land at the same time. But the latest count of the California breeding group was about 124,000 seals. In the United States, elephant seals are protected by the Marine Mammal Protection Act. This law was passed in 1972. It makes it illegal to hunt, kill, capture, or bother these animals.
Images for kids
-
Northern elephant seals on Piedras Blancas beach, near San Simeon, California
-
Beachmasters, the dominant southern elephant seal bulls fighting at Macquarie Island
-
Northern elephant seals at Piedras Blancas, California
See also
 In Spanish: Elefantes marinos para niños
In Spanish: Elefantes marinos para niños