Fort Wayne (Detroit) facts for kids
|
Fort Wayne
|
|

Original barracks at Fort Wayne
|
|
| Location | 6053 West Jefferson Avenue Detroit, Michigan |
|---|---|
| Area | 96 acres (39 ha) |
| Built | 1842–51 |
| Architect | Montgomery C. Meigs |
| NRHP reference No. | 71000425 |
Quick facts for kids Significant dates |
|
| Added to NRHP | May 6, 1971 |
Fort Wayne is a historic fort located in Detroit, Michigan. It sits right on the Detroit River, very close to the Canadian border. This old fort has many original buildings, like the barracks from 1848 and the fort itself, built in 1845.
The fort covers about 96 acres (39 hectares). Most of it, including the original fort and many buildings, has been managed by the city of Detroit since the 1970s. The rest is used by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers as a boatyard. Fort Wayne became a Michigan State Historic Site in 1958 and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1971.
Contents
Why Was Fort Wayne Built?
Fort Wayne is the third fort built in Detroit. The first was Fort Pontchartrain du Detroit, built by the French in 1701. The British took it over in 1760 during the French and Indian War. They then built Fort Lernoult, which the United States took control of in 1796 and renamed Fort Shelby. This fort was later torn down in 1826.
The area where Fort Wayne stands was once a high sand mound with fresh springs. Native American burial mounds were also found here. One large mound was located where the fort was built. Archaeologists found pottery there, which they named "Wayne Ware."
In the early 1700s, the Potawatomi people had a trading village near this site. This shows the area was important long before the fort was built.
Early History of the Fort Site
The War of 1812 began near the future fort site. American soldiers fired on a Canadian town in 1812. Later, British General Isaac Brock landed here before taking Detroit. American General William Hull surrendered Fort Shelby without a fight.
After the war, in 1815, the Treaty of Springwells was signed at this site. This treaty ended fighting between the U.S. government and Native American tribes who had sided with the British. Important leaders like Governor Lewis Cass and General William Henry Harrison were there.
In the late 1830s, small rebellions happened in Canada. The U.S. government realized it needed better defenses along its northern border. In 1841, Congress decided to build new forts, including one in Detroit.
Building the Fort
The Army sent Lieutenant Montgomery C. Meigs to Detroit. He bought land along the Detroit River, where it was closest to Canada. Construction of Fort Wayne began in 1842. The fort was finished in 1851 and cost $150,000. It was named after General "Mad" Anthony Wayne, a hero from the Revolutionary War. He had taken control of Detroit from the British in 1796.
How Fort Wayne Was Designed
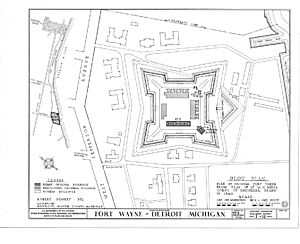
The original fort is shaped like a rectangle with strong walls. These walls were made of earth and covered with cedar. Inside the walls were brick rooms with openings for cannons. The design was based on ideas from Sebastian Vauban, a French military engineer from the 1600s.
The fort has a dry moat around it and a special half-moon shaped defense called a demilune facing the river. Cannons were meant to be placed on top of the walls, but they were never installed.
Changes to the Fort Over Time
Even though the fort looks much like it did originally, some changes have been made. Starting in 1863, the cedar walls were replaced with brick. This made the fort even stronger. A new gate for vehicles was added in 1938 to allow trucks to enter.
Inside the fort, there is a large limestone building that served as barracks for soldiers. It had rooms for sleeping, eating, and kitchens. A limestone powder magazine, used to store gunpowder, was also built. Other buildings, like officer's housing, were built inside but have since been removed.
Many other buildings were constructed outside the main fort walls. These included wooden Victorian-style homes for officers in the 1880s. These homes were later covered in brick. A guardhouse from the Spanish-American War era (1889) is also on the grounds. A hospital was built in 1890, and new barracks for soldiers were added around 1905.
Fort Wayne's Role in History
After it was built, Fort Wayne was not immediately used for defense. The U.S. and Britain settled their differences peacefully. For about ten years, only a single watchman guarded the fort. Some believe the fort was a stop on the Underground Railroad during this time. A local farmer reportedly used his ferry to help people escape to Canada.
The Civil War and Beyond
In 1861, the American Civil War made Fort Wayne important again. Fears of an attack from Canada led to the fort's walls being strengthened. The Michigan 1st Volunteer Infantry Regiment started their service at Fort Wayne. Throughout the Civil War, the fort was a place where Michigan troops gathered and where wounded soldiers recovered.
After the Civil War, until 1920, Fort Wayne was a place where soldiers rested after serving on the western frontier. In 1875, the city of Detroit grew and took over the land around the fort.
During the Spanish–American War, troops from the fort went to Cuba and the Philippines. The fort's guardhouse also had the first telephone exchange in that part of Detroit.
World Wars and Modern Use
After World War I, the fort was used to hold people accused of being communists. During the Great Depression, it provided shelter for homeless families and housed the Civilian Conservation Corps.
Fort Wayne became very important during World War II. It was the largest motor supply depot in the world. Every tank, truck, jeep, tire, or spare part sent from Detroit factories to the war fronts passed through Fort Wayne. Over 2,000 workers, mostly civilian women, worked there. Italian prisoners of war were also held at the fort and worked as servants and cooks. Many of them chose to stay in Detroit after the war.
After World War II, parts of the fort were given to the City of Detroit. In 1948, the original fort and barracks became a military museum. During the Cold War, Fort Wayne was a place where thousands of new soldiers were sworn into service for the Korean War and Vietnam War. The fort also provided housing for families displaced by the 1967 12th Street Riot until 1971. The last part of the fort was given to the city in 1976.
Fort Wayne Today
Since 2006, the Detroit Recreation Department has managed Fort Wayne, with help from the Historic Fort Wayne Coalition and the Detroit Historical Society.
Today, the fort hosts many events, including historic reenactments and soccer matches. You can also rent areas for special events. The grounds are home to the ancient Native American burial mound and the Tuskegee Airmen National Historical Museum.
Detroit City Football Club (DCFC) played their first game at Fort Wayne in 2012. Their adult soccer league still plays on the fields there.
There are discussions about making Fort Wayne part of the national park system, especially with the new Gordie Howe International Bridge being built nearby. The National Park Service has helped explore ways to preserve the fort and attract more visitors.
In 2019, Fort Wayne was the finish line for the 31st season of the TV show The Amazing Race.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Fort Wayne (Detroit) para niños
In Spanish: Fort Wayne (Detroit) para niños