History of American comics facts for kids
The history of American comics started a long time ago, in the 1800s. Back then, comics were mostly found in newspapers and were part of sensational news that tried to grab attention. In the 1900s, comics became their own special art medium and a big part of American culture.
Contents
How American Comics Started

American comics began in 1842 with a book called The Adventures of Mr. Obadiah Oldbuck by Rodolphe Töpffer. But comics really grew popular as comic strips in daily newspapers. These early comic strips created many things we still see today, like speech balloons (the bubbles where characters talk). They also started popular types of stories, like family adventures. Comic characters became famous across the country! Newspapers even competed to get the most popular artists.
The first true comic book, separate from newspapers, appeared in 1934. At first, these comic books just reprinted newspaper strips. But soon, they started having new stories. The first appearance of Superman in 1938 kicked off the Golden Age of Comic Books. During World War II, superheroes and talking animals were super popular. New types of stories also appeared, like westerns, romance, and science fiction. This made even more people read comics.
In the early 1950s, comic book sales started to drop. Some people also worried that comics were bad for children. To protect their image, comic book companies created the Comics Code Authority (CCA). This group set rules for what could be in comics. Because of these rules, many crime and horror comics stopped being published.
The Silver Age of Comic Books began in 1956. This was when superheroes became popular again. Sales of non-superhero comics went down, and many publishers closed. Marvel Comics introduced new and exciting superheroes. This made Marvel the top comic publisher during the Bronze Age of Comic Books, which lasted from the early 1970s to 1985. Unlike earlier ages, the Bronze Age didn't start with one big event. Superheroes were still very popular, but underground comics also appeared. These comics had new art styles and were sold in different ways.
After the Bronze Age came the Modern Age of Comic Books. At first, it seemed like a new "golden age." Writers and artists gave classic characters fresh looks. They also started new series that brought in many readers. Important comics like Maus showed how powerful comic stories could be. However, the comic industry soon faced money problems. It took years for things to get better.
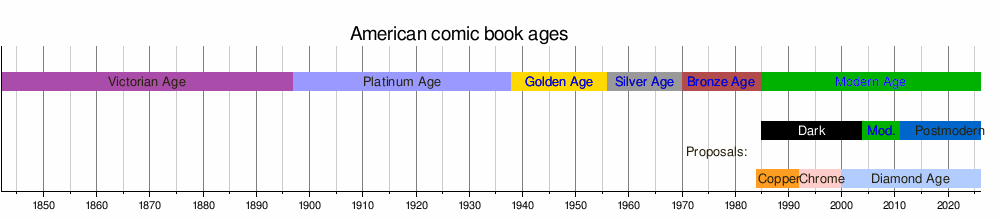
Comic Book Ages: A Timeline
Historians often divide the history of American comics into different "ages."
- Golden Age (around 1938 to 1956): This era began with Superman's first appearance. It ended when DC Comics introduced a new version of The Flash.
- Silver Age (around 1956 to 1970): This period saw superheroes become popular again.
- Bronze Age (around 1970 to 1985): This age followed the Silver Age.
- Modern Age (around 1985 to today): This is the current period of comics.
These dates can change a little depending on who you ask. The terms "Golden Age" and "Silver Age" were first used by comic fans in the 1960s.
Other Ways to Divide Comic History
Some people, like Steve Geppi, also include comic strips when talking about comic history. He adds two periods before the Golden Age:
- Victorian Age (1828 to 1882)
- Platinum Age (1882 to 1938)
There are also other names for later periods, like the Copper Age or the Dark Age of Comic Books. The "Dark Age" name comes from the popularity of comics with more serious and gritty stories, like Batman: The Dark Knight Returns and Watchmen.
Timeline of Comic Ages
Victorian Age (1842–1897)
Comics in the United States were inspired by early European works. In 1842, a book by Rodolphe Töpffer called Les amours de Mr. Vieux Bois was published in the U.S. It was called The Adventures of Mr. Obadiah Oldbuck. This was an unauthorized copy, meaning it was printed without Töpffer's permission. His comics were reprinted often until the late 1870s. This gave American artists ideas to make their own similar works. In 1849, Journey to the Gold Diggins by Jeremiah Saddlebags by James A. and Donald F. Read became the first American comic.
At first, not many comics were made in the U.S. Then, funny magazines like Puck, Judge, and Life started publishing drawings and humorous stories. They also had picture stories and silent comics. Artists like Arthur Burdett Frost created very new and interesting stories. However, these magazines were only for rich and educated people.
Comics really took off when new technology made it easy and cheap to print pictures. Newspaper owners like William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer were in a big competition. They decided to publish cartoons in their newspapers to attract more readers.
Platinum Age (1897–1938)

The late 1800s, called the "Platinum Age," slowly brought in the main parts of American mass comics. Funny comics were found in the humor sections of newspapers. They were printed in the Sunday paper to keep people buying it. Newspapers were known for their opinions and non-news pages, where pictures were very important. These pages were called comic supplements.
In 1892, William Randolph Hearst published cartoons in his newspaper, The San Francisco Examiner. James Swinnerton drew the first pictures of humanized animals in a series called Little Bears and Tykes. Still, most drawings in newspapers were single funny cartoons on a full page. Stories told through a sequence of pictures slowly became more common.
In 1894, Joseph Pulitzer printed the first color comic strip in the New York World. It was drawn by Walt McDougall. This showed that color printing was possible for comics. Artists began to create characters that appeared regularly. In 1894, Richard F. Outcault introduced Hogan's Alley in the New York World. This series showed street kids, one of whom wore a yellow nightgown. Soon, this little character became very popular, and readers called him Yellow Kid.

On October 25, 1896, the Yellow Kid spoke his first words in a speech balloon. Before this, his words were written on his shirt. Outcault had used speech balloons before, but this date is often seen as the birth of modern comics in the United States.
The Yellow Kid's success helped the New York World sell more papers. This made Hearst want the artist, Outcault. In 1896, Hearst and Pulitzer had a big fight over Outcault. Pulitzer kept publishing Hogan's Alley with a new artist, and Hearst published the series under a different name. Richard Outcault chose the title The Yellow Kid. In 1897, the Yellow Kid magazine was published. It collected the comic strips that had appeared in newspapers. This was the first magazine of its kind.
From 1903 to 1905, Gustave Verbeek created his comic series "The UpsideDowns of Old Man Muffaroo and Little Lady Lovekins." These comics were special because you could read the 6-panel comic, then flip the book upside down and keep reading a new story! He made 64 of these unique comics.
Golden Age (1938–1956)
The Golden Age of Comic Books was a time for American comics from 1938 to 1956. During this period, modern comic books were first published and quickly became very popular. The superhero idea was created, and many famous characters appeared. These included Superman, Batman, Captain Marvel, Captain America, and Wonder Woman.
Silver Age (1956 – c. 1969)
The Silver Age of Comic Books began when DC Comics published Showcase #4 in October 1956. This comic introduced the modern version of Flash. At that time, only three superheroes—Superman, Batman, and Wonder Woman—still had their own comic books. The Comics Code was very powerful during the Silver Age. The Code stopped many topics from being in stories. This meant certain types of comics, like crime and horror, couldn't be sold in most comic shops. It also helped superheroes stay popular. The underground comix movement started at the end of the Silver Age. These comics were a response to the Code's rules and were part of the bigger counterculture of the 1960s.
Bronze Age (c. 1970 – c. 1985)
The Bronze Age of Comic Books is a common name for a period in the history of American superhero comic books. It usually runs from 1970 to 1985. It came after the Silver Age of Comic Books and before the Modern Age of Comic Books.
Modern Age (c. 1985 – present)
The Modern Age of Comic Books is a period in the history of American superhero comic books that generally started in 1985 and continues today. For about the first 15 years of this time, many comic book characters were redesigned. Artists and writers became more famous in the industry. Independent comics grew, and bigger comic companies became more focused on business.
Another name for the time after the mid-1980s is the Dark Age of Comic Books. This name comes from the popularity of serious comics like Batman: The Dark Knight Returns and Watchmen. Some writers say the Dark Age lasted from 1985 to 2004. They say the Modern Age of Comic Books began in 2004 with Marvel's "Avengers Disassembled" and DC Comics' "Infinite Crisis" in 2005. Some even suggest a "Postmodern Age" starting in 2011 with the first appearance of Miles Morales.
The Copper Age of Comic Books is another suggested period. It might have started in 1984 with Marvel's Secret Wars series and ended in 1991 with Jim Lee's X-Men series. In 1992, a group of Marvel artists, including Jim Lee, left to form Image Comics. This company allowed creators to own their characters. Some people see this as the true start of the "Modern Age of Comics" that continues today. Another name, the "Diamond Age," has been suggested for the period starting with Marvel's Ultimate line in 2000.

