Culture of the United States facts for kids
The culture of the United States is a mix of many different behaviors, traditions, and ideas found across the United States. This includes how people speak, what they read, the music they listen to, the art they create, the food they eat, the sports they play, and their beliefs. American culture has been shaped by its long history, its geography, and many people moving to and within the country.
America's culture started with ideas from Western countries, especially England. But it also has strong influences from French, German, Greek, Irish, Italian, Jewish, Polish, Scandinavian, and Spanish traditions. Over time, influences from African, Native American, and more recently, Asian cultures have also become a big part of American life. Since the U.S. was founded in 1776, many waves of immigrants have arrived. This mix of cultures is often called a "melting pot" and is a special part of American society.
Americans have created or greatly improved many types of music, like heavy metal, rhythm and blues, jazz, gospel, country, hip hop, and rock 'n' roll. The four most popular team sports are American football, baseball, basketball, and ice hockey. Most Americans are Protestant or Catholic, though more people are now saying they don't follow a religion. Popular American foods include hot dogs, milkshakes, and barbecue. The main language spoken is English, but the U.S. does not have an official language for the whole country.
American culture values liberty, individualism, and limited government. It also strongly supports free speech and the right to use the Internet. American culture can be different depending on the region, race, age, or how many people live in an area. The United States has a big cultural influence around the world and is often called a "cultural superpower."
Contents
History of American Culture
American culture began with settlers from England and Spain in colonial North America. English people were the largest group in the 17th century and helped shape the main ideas and attitudes that became the American character. Later, many immigrants from Germany and Ireland added to and changed this culture.

A key American idea was Jeffersonian democracy, which is still important today. Thomas Jefferson wrote about American culture, defending it against European ideas that thought America was not as good.
Over time, different groups of immigrants brought their own cultures. German, Irish, and Italian influences are strong in the Northeast. Latin American culture is very noticeable in areas that were once Spanish, and Asian American cultures are strong on the West Coast. Caribbean culture has also grown in many cities.
Native American cultures remain strong in areas with large populations, especially on Indian reservations in the West. While many native languages have been lost, some, like Hawaiian and Navajo, are still spoken.
American culture includes both traditional and modern ideas, and it values taking risks and expressing oneself freely. Because the U.S. is so large and has so many different people, its culture has many different ways of showing itself. The U.S. has the largest immigrant population in the world, and this mix of cultures has led to its global influence, sometimes called Americanization.
Regions of the United States

The United States has several distinct cultural regions. These include New England, the Mid-Atlantic, the South, the Midwest, the Southwest, and the West.
The West Coast (California, Oregon, and Washington state) is often called the "Left Coast" because it tends to have more liberal political views.
The South is sometimes called the "Bible Belt" because many people there are evangelical Protestants and have traditional social views. Church attendance is generally higher in the South. This is different from the Northeast and Midwest, which have more diverse religions, or the West, which tends to be less religious.
Strong cultural differences have always been a part of the U.S. For example, the differences between the Northern and Southern states over slavery led to the American Civil War.
Language in the U.S.

The United States does not have an official language at the federal level. However, 28 states have made English their official language, and it is the main language spoken across the country. Most Americans (over 97%) can speak English well, and for many, it's the only language they speak at home.
The English spoken in the U.S. is called American English. It has many regional accents, but it also has features that make it different from British English. There are four main accent regions: the North, the Midland, the South, and the West. Some people believe there's a "General American" accent that doesn't sound like any specific region, often linked to the Midwest. American Sign Language, used by deaf people, also comes from the United States.
More than 300 other languages are spoken in the U.S., some by Native American peoples (about 150 living languages) and others brought by immigrants. Spanish is spoken by nearly 30 million people and is an official language in Puerto Rico and New Mexico. People who speak both English and Spanish sometimes mix them, a practice called Spanglish.
Native languages include Navajo, Yupik, Dakota, and Apache, spoken on Indian reservations. Hawaiian is an official language in Hawaii, and Chamorro and Carolinian are official in the Northern Mariana Islands.
| Language | Percentage of the total population |
|---|---|
| English only | 78.2% |
| Spanish | 13.4% |
| Chinese | 1.1% |
| Other | 7.3% |
American Customs and Traditions
Food and Cooking
American food is very diverse because the country is huge, has a large population, and many different cultures have influenced it. Traditional American cooking uses ingredients like turkey, potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, squash, and maple syrup. These foods were used by Native Americans and early European settlers.

Famous American dishes like apple pie, donuts, fried chicken, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs come from immigrant recipes and new ideas developed in the U.S. Foods like French fries, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos, and Italian-inspired pasta dishes are also very popular.
The types of food eaten at home vary a lot by region and family background. Recent immigrants often eat foods from their home countries, and over time, American versions of these foods appear, like Chinese American or Italian American food. German food has also had a big impact, especially in the Midwest, with dishes like hamburgers and pot roast.

Different regions have their own cooking styles. Louisiana and Mississippi are famous for Cajun and Creole cooking, which mix French, Acadian, and Haitian influences. Examples include Crawfish Étouffée, Red beans and rice, and gumbo.
Soul food, which developed from African American cooking in the South, is popular there and among many African Americans elsewhere.
Americans usually prefer coffee over tea. Many people drink at least one cup of coffee daily. Orange juice and milk are common breakfast drinks. The American fast food industry is the world's first and largest, with companies like McDonald's and Burger King having restaurants all over the globe.
- Some representative American foods
-
Traditional Thanksgiving dinner with turkey, dressing, sweet potatoes, and cranberry sauce
-
A cream-based New England chowder, traditionally made with clams and potatoes
-
Fried chicken, a southern dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and deep fried
-
Creole Jambalaya with shrimp, ham, tomato, and Andouille sausage
-
Chicken-fried steak (or Country Fried Steak)
-
A submarine sandwich, which includes a variety of Italian luncheon meats
-
American style breakfast with pancakes, maple syrup, sausage links, bacon strips, and fried eggs
-
A hot dog sausage topped with beef chili, white onions and mustard
-
A barbecue pulled-pork sandwich with a side of coleslaw
-
An apple cobbler dessert
Sports in the U.S.
In the 1800s, colleges started focusing on sports like track and field and American football. Physical education became part of school lessons in the 20th century.

Baseball is the oldest major American team sport. Professional baseball started in 1869 and was the most popular sport until the 1960s. It's still called "the national pastime." Major League Baseball teams play many games from late March to early October, ending with the World Series.
American football, simply called "football" in the U.S., is now the most popular sport. The 32-team National Football League (NFL) is the top professional league. Each NFL team plays 17 games from September to December, leading to the Super Bowl in January or February. The Super Bowl is one of the most-watched TV events each year.
College football is also very popular. Many communities, especially in rural areas, strongly support their local high school football teams. Football games often include cheerleaders and marching bands to entertain the crowd.
Basketball is another major sport, with the National Basketball Association (NBA) as its professional league. It was invented in 1891 in Massachusetts. College basketball is also popular, especially the "March Madness" tournament.
Ice hockey is the fourth most popular professional team sport. It's very popular in the Great Lakes and New England areas.
Lacrosse is a team sport that originated with Native American and Canadian First Nations people. It's most popular on the East Coast.
Soccer is very popular for people to play, especially among young people. American national soccer teams compete well internationally. The professional league, Major League Soccer, is growing but is not as popular on TV as other American sports.
Other popular sports include tennis, softball, rodeo, swimming, volleyball, skiing, and snowboarding.
The U.S. is very successful in women's sports, partly due to a law called Title IX that requires equal funding for men's and women's sports in colleges. The United States consistently wins many medals in both the Summer Olympics and Winter Olympics.
Sports and Community
Homecoming is an annual tradition where communities, high schools, and colleges welcome back former residents and students. It usually happens in late September or early October and often centers around a football game, a parade, and the crowning of a "Homecoming Queen."
American high schools commonly have teams for football, basketball, baseball, softball, volleyball, soccer, golf, swimming, track and field, and cross-country.
Public Holidays

The United States celebrates holidays based on its history, Christian traditions, and national figures.
Thanksgiving is a main American holiday, coming from the English Pilgrims' tradition of giving thanks. It's usually a family gathering with a big meal. Independence Day (July 4th) celebrates the country's freedom from Great Britain, with parades and fireworks.
Christmas Day, celebrating the birth of Jesus Christ, is a widely celebrated federal holiday, important for both religious and non-religious reasons. Other Christian holidays like Easter and St. Patrick's Day are also observed.
Halloween comes from an ancient Celtic festival and is now a holiday where children and teens dress up in costumes and go trick-or-treating for candy. It's also a time for spooky stories and movies. Mardi Gras, a Catholic tradition, is celebrated in Louisiana.
| Date | Official name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | Celebrates the start of the new year. |
| Third Monday of January | Birthday of Martin Luther King Jr., or Martin Luther King Jr. Day | Honors Martin Luther King Jr., a leader in the Civil Rights movement. |
| Third Monday of February | Washington's Birthday | Honors George Washington, the first U.S. President. Often called "Presidents' Day" to honor all presidents. |
| Last Monday of May | Memorial Day | Honors soldiers who died in wars; marks the unofficial start of summer. |
| June 19 | Juneteenth | Juneteenth celebrates the end of slavery for African Americans in the United States. |
| July 4 | Independence Day | Celebrates the Declaration of Independence. |
| First Monday of September | Labor Day | Celebrates the achievements of workers; marks the unofficial end of summer. |
| Second Monday of October | Columbus Day | Honors Christopher Columbus. In some areas, it's also a celebration of Italian heritage or Native American Day. |
| November 11 | Veterans Day | Honors all veterans of the United States armed forces. |
| Fourth Thursday of November | Thanksgiving Day | Celebrates giving thanks for the autumn harvest. Traditionally includes a turkey dinner. |
| December 25 | Christmas | Celebrates the birth of Jesus. |
Names
The U.S. has few rules about what you can name a child. People have the freedom to choose names, which has led to a wide variety of names and trends. Creativity is common, and names can show personality, cultural identity, and values. For example, African Americans have developed unique naming traditions.
Fashion and Dress
Fashion in the United States is varied and mostly informal. While clothing reflects the many cultures in America, cowboy hats, boots, and leather motorcycle jackets are distinct American styles.
Blue jeans became popular as work clothes in the 1850s and were later adopted by teenagers. They are now worn by people of all ages and social classes across the country. Jeans are considered one of America's main contributions to global fashion.
Even though informal dress is common, some professionals, like bankers and lawyers, dress formally for work. Special events like weddings and parties often require formal wear. The annual Met Gala in Manhattan is a famous fashion event.
Some cities are known for specific fashion styles. Miami is known for swimwear, Los Angeles for casual wear, and Chicago for sportswear. Cities in the South like Dallas and Nashville are big markets for fast fashion and often feature cowboy boots and lighter fabrics.
Family Life
Family arrangements in the U.S. reflect modern American society. A traditional nuclear family is a married man and woman with children. Today, a person might grow up in a single-parent family, marry without having children, or divorce and remarry.
It's common for young adults to leave home when they turn 18. However, in some cultures, like Italian and Hispanic American families, and in cities with very high rents, young adults might stay home longer.
Marriage laws are set by individual states. Weddings usually involve a couple making promises to each other in front of family and friends, often led by a religious leader or a judge. Same-sex marriage became legal in all states in 2015.
Divorce laws also vary by state. If children are involved, state law provides for child support.
Housing
Historically, most Americans lived in rural areas. The Industrial Revolution led to more people moving to cities. After World War II, many soldiers bought homes in the suburbs, which are areas outside of cities.
In some American cities, middle-income neighborhoods have seen changes. More well-off middle-class families have moved to larger homes in more exclusive suburbs. In expensive areas like California, more affluent families have moved in, changing some middle-class neighborhoods into wealthier ones.
Volunteerism
Americans have a long history of helping others. A 2011 study found that Americans were among the most willing to help strangers and donate time and money. Many minor crimes are punished with "community service," where offenders do volunteer work. Some high schools also require community service for graduation. U.S. citizens can also be called for jury duty to serve as jurors in legal cases.
Arts in the U.S.
Architecture

Architecture in the United States is diverse and has been shaped by many outside influences. It has influences from English and Greco-Roman architecture. A main feature of American city architecture is modernity, seen in the many skyscrapers built in the 20th century. Homes in rural and suburban areas tend to be more traditional.
Visual Arts
In the late 1700s and early 1800s, American artists mostly painted landscapes and portraits in a realistic style, often looking to Europe for techniques. Later in the 19th century, America developed its own art movements, like the Hudson River School, which focused on American landscapes, and unique portrait artists like Winslow Homer.
The American craft movement also began in rural America as a response to the Industrial Revolution. As the country became wealthier, people could buy European art, and foreign artists came to teach. Photography became very popular for both journalism and art. Museums in New York, Boston, Philadelphia, and Washington, D.C., started collecting many artworks, influencing fashion and architecture. After World War II, New York became a major center for the art world. Today, American painting includes many styles and famous artists like Jackson Pollock, John Singer Sargent, Georgia O'Keeffe, and Norman Rockwell.
Theater and Performing Arts
American theater is based on Western traditions. The U.S. created stand-up comedy and modern improvisational theater, where performers use ideas from the audience.
Early American Theater
The minstrel show was an early American theatrical art form developed in the 19th century. These shows often featured white actors in blackface makeup, imitating and making fun of African Americans. While now seen as racist, minstrel shows influenced American entertainment. Many songs by Stephen Foster, like "Camptown Races" and "Oh Susanna," became popular American folk songs. Tap dancing and stand-up comedy have roots in minstrel shows.
Drama and Musicals
American drama became unique with playwrights like Eugene O'Neill in the early 20th century. He is considered the father of American drama and won many awards. Later, other famous American playwrights included Arthur Miller and Tennessee Williams. American theater often explores social issues not widely discussed.
The United States is also the home of modern musical theater, producing famous composers like Rodgers and Hammerstein and Stephen Sondheim. Broadway in New York City is one of the largest theater communities in the world and a center for commercial theater.
Music
American music styles, such as country, jazz, blues, rock, pop, techno, soul, and hip hop, are heard all over the world. The U.S. has the world's largest music market.
The rhythmic and lyrical styles of African-American music have greatly influenced American music, making it different from European and African traditions. Country music developed in the 1920s, and rhythm and blues in the 1940s. These styles, along with blues and old-time music, became popular genres worldwide. Jazz was created by artists like Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington in the early 20th century.
Elvis Presley and Chuck Berry were pioneers of rock and roll in the 1950s. Rock bands like Metallica and the Eagles are among the highest-selling artists globally. In the 1960s, Bob Dylan became a celebrated songwriter. American pop stars like Bing Crosby, Frank Sinatra, Elvis Presley, Michael Jackson, Madonna, and Whitney Houston became global celebrities.
American popular music has a worldwide influence. Artists like Taylor Swift, Miley Cyrus, Ariana Grande, Eminem, Lady Gaga, and Katy Perry are very popular globally today. The annual Coachella music festival in California is one of the largest and most famous music festivals in the world.
Cinema

The United States movie industry has a worldwide influence. Hollywood, a part of Los Angeles, California, is the leading center for making movies and is the most recognized movie industry in the world. Major U.S. film studios produce many of the most commercially successful movies globally.
The main style of American cinema is classical Hollywood cinema, which developed from 1913 to 1969 and is still common today. While French inventors are credited with the start of modern cinema, American cinema quickly became a major force. The world's first movie with synchronized sound, The Jazz Singer, was released in 1927. Orson Welles's Citizen Kane (1941) is often called one of the greatest films of all time.
Broadcasting
Television is a big part of traditional media of the United States. Most American homes (96.7%) have at least one TV, and many have more. U.S. television networks are the largest and most widely shared in the world.
In recent years, many critics say American television is in a "golden age" because of the high quality and popularity of its TV series.
Society in the U.S.
Science and Technology

American culture values scientific progress and new technology, leading to many modern inventions. Famous American inventors include Robert Fulton (the steamboat), Samuel Morse (the telegraph), Eli Whitney (the cotton gin), and Thomas Edison (who invented many things, including the lightbulb). Many new technologies in the 20th and 21st centuries were either invented in the U.S. or first widely used by Americans. Examples include the lightbulb, the airplane, the personal computer, and the Internet. The U.S. also developed the Global Positioning System (GPS).
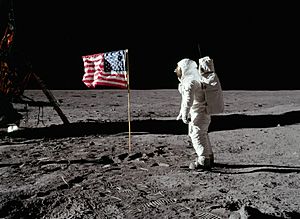
The United States has been a leader in technology since the late 1800s and in science since the mid-1900s. New ways of making things, like interchangeable parts and the assembly line, led to mass production. This focus on applying scientific ideas continued with achievements like the Apollo Moon landings, the creation of the personal computer, and the Human Genome Project. The U.S. has the most active satellites in space.

Throughout history, American culture has benefited from talented scientists moving to the U.S. These include Alexander Graham Bell (telephone), Charles Steinmetz (electrical systems), and Nikola Tesla (induction motor). The rise of difficult political situations in Europe in the 1920s and 30s led many European scientists, like Albert Einstein, to move to the United States.
Thomas Edison's lab developed the phonograph, the first long-lasting light bulb, and an early movie camera. The Wright brothers made the first successful powered flight in 1903. Car companies like Henry Ford's popularized the assembly line in the early 20th century.
Education
Education in the United States is mainly provided by the government, with funding and control from federal, state, and local levels. School attendance is required for almost all children at the elementary and high school levels.
Students can go to public schools, private schools, or be homeschooled. In most schools, education is divided into elementary school, junior high school (or middle school), and high school. Children are grouped by age into grades. Education after high school, known as "college," is usually managed separately.
Most adults in the U.S. have finished high school, and many have a bachelor's degree or higher. The U.S. has many of the world's top universities, including Harvard University, and has won the most Nobel Prizes in history.
Religion
Self-identified religious affiliation in the United States (2023 The Wall Street Journal-NORC poll) Protestantism (26%) Catholicism (21%) "Just Christian" (20%) Mormonism (1%) Unitarianism (1%) Judaism (2%) Buddhism (2%) Something else (2%) Islam (1%) Nothing in particular (12%) Agnostic (8%) Atheist (4%)
Compared to other developed countries, the U.S. is one of the most religious. Most Americans say religion is "very important" in their lives. Governments at all levels in the U.S. are secular, meaning they are separate from religious institutions. This is often called the "separation of church and state." The most popular religion in the U.S. is Christianity, followed by most of the population.
Even though fewer people are joining organized religions, public life and popular culture in the U.S. still include many Christian ideas about doing good and forgiveness.
Self-identified religiosity (2023 The Wall Street Journal-NORC poll) Very religious (17%) Moderately religious (31%) Slightly religious (23%) Not religious at all (29%)
Early British colonies in America were not always tolerant of different religions. For example, the Puritans in the Massachusetts Bay Colony were very strict and punished those who didn't follow their beliefs. They even outlawed Christmas for a time.
However, the colony of Maryland was founded by a Catholic leader and was more open to religious freedom. The Maryland Toleration Act in 1649 allowed freedom of worship for most Christians.
The founders of the United States Constitution wanted to avoid a state religion. The First Amendment says the government cannot create an official religion or stop people from practicing their own. This was influenced by Enlightenment ideas and the desire to protect minority religious groups.
Polls show that most Americans believe in some idea of a God, and many pray daily. About 30% of Americans say they have no religion. Younger Americans are becoming less religious.
Transportation
Cars and Driving

Most personal travel in the U.S. is by car, using a huge network of public roads, the longest in the world. In 2001, 90% of Americans drove to work. The U.S. is a major maker of cars and has the highest number of vehicles per person in the world.
Since the 1990s, Americans have tended to buy larger cars because fuel and land are cheaper. In the 1950s and 1960s, American culture often focused on cars, with places like motels and drive-in restaurants. Outside of big cities, most Americans need to own and drive cars. New York City is one of the few places where most homes don't own a car.
The U.S. was a pioneer in the automotive industry in the early 20th century. General Motors was founded in 1908 and became the world's largest carmaker for many years. The U.S. was also the first country to have a mass market for cars and mass production methods. In the 1950s and 1960s, car enthusiasts started modifying cars into hot rods. Later, in the late 1960s and early 1970s, carmakers started making muscle cars and pony cars for people who wanted powerful, stylish cars. This car culture is now a worldwide hobby.
Cultural Institutions
Government Cultural Institutions
The U.S. government doesn't have a single "ministry of culture," but several government groups have cultural responsibilities. These include the Smithsonian Institution, the Library of Congress, and the National Endowment for the Arts, which support arts, humanities, and knowledge. Many state and city governments also have departments for cultural affairs.
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the U.S. government's official list of places, buildings, and objects that are important enough to be saved for their historical or artistic value. The National Park Service manages this list.
Private Cultural Institutions
Important private cultural groups in the U.S. include the Poetry Foundation, the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation, and the J. Paul Getty Trust.
Museums
The United States has many museums, both public and private. Major museums include the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the Museum of Modern Art, the museums of the Smithsonian Institution, and the American Museum of Natural History.
Archives
The National Archives and Records Administration and other archives in the U.S. work to save and preserve historical documents and cultural items.
See also
 In Spanish: Cultura de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Cultura de Estados Unidos para niños
- African-American culture
- American Dream
- Americanization
- Americana
- Society of the United States
- Etiquette in North America
- Folklore of the United States

















































