Summer Olympic Games facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Summer Olympic Games |
|
|---|---|

The Olympic flame in Paris during the 2024 Summer Olympics
|
The Summer Olympic Games are a huge international sports event. Athletes from all over the world come together to compete. These games usually happen every four years. The very first modern Summer Olympics were held in Athens, Greece, in 1896. The most recent games took place in Paris, France, in 2024. Pierre de Coubertin helped start the modern Olympics, creating the International Olympic Committee (IOC). Medals for first, second, and third place (gold, silver, and bronze) began in 1904. The Summer Olympics are known as the biggest and most exciting sports event globally. Their success even led to the creation of the Winter Olympic Games.
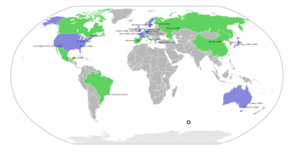
The Games have grown a lot since 1896. Back then, fewer than 250 male athletes from 14 countries competed in 42 events. By the 2020 Summer Olympics in 2021, there were over 11,000 athletes from 206 nations. Almost half of these athletes were women! Many countries across five continents have hosted the Games. The United States has hosted four times, and Great Britain and France have each hosted three times.
London and Paris have hosted the Games three times each. Los Angeles, Athens, and Tokyo have hosted twice. The United States has won the most medals in total for the Summer Olympics. They have also finished first in the medal count 19 times.
Contents
Hosting the Olympic Games
The United States has hosted the Summer Olympics four times. These were in St. Louis (1904), Los Angeles (1932 and 1984), and Atlanta (1996). Los Angeles will host again in 2028, making it five times for the U.S.
Paris first hosted twice in 1924. London became the first city to host three times in 2012. Paris hosted for its third time in 2024. Tokyo (1964 and 2021) and Athens (1896 and 2004) have each hosted twice.
Australia, Germany, Greece, and Japan have all hosted the Games twice. Australia will host for a third time in 2032. Tokyo was the first city outside Europe and English-speaking countries to host twice. It is also the largest city to ever host the Games. Many other countries have hosted the Summer Olympics once.
Asia has hosted the Games four times: Tokyo (1964 and 2021), Seoul (1988), and Beijing (2008). The 2016 Games in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, were the first in South America. They were also the first held during the local winter season. Australia and Brazil are the only countries in the Southern Hemisphere to have hosted. No country in Africa has hosted the Summer Olympics yet.
Stockholm, Sweden, hosted the entire Games in 1912. It also hosted the horse riding events for the 1956 Games. This was because of animal health rules in Australia. Amsterdam, Netherlands, hosted the Games in 1928. It also hosted some sailing races in 1920. For the 2008 Summer Olympics, Hong Kong hosted the horse riding events.
Hosting the Olympics helps cities build new roads, buildings, and sports venues. It also helps cities become more well-known and attract visitors from around the world.
History of the Summer Olympics
The Early Years of the Games

The International Olympic Committee (IOC) was started in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin. He was a French teacher and historian. He wanted to bring countries together through sports. The first modern Olympic Games were held in Athens in 1896. Only 245 athletes competed, mostly from Greece. Only 14 countries were represented. This was still a huge international event for its time.
At first, women were not allowed to compete. One woman, Stamata Revithi, ran the marathon course on her own to show her determination. Women officially joined the Games in Paris in 1900. There were 22 women competing in five sports. Since then, many more women have participated. In recent Games, almost half of the athletes are women.
The 1896 Athens Games were a big success. About 100,000 people watched the opening ceremony. The Panathinaiko Stadium was packed with the largest crowd ever for a sports event. A Greek runner named Spiridon Louis won the marathon, causing huge celebrations. A German athlete, Carl Schuhmann, was the most successful, winning four gold medals in wrestling and gymnastics.
Many people wanted Athens to be the permanent host city. However, the IOC decided to move the Games to different cities around the world. The next Olympics were held in Paris.
The 1900 Summer Olympics in Paris had many more athletes, including 20 women. They competed in sports like croquet, golf, sailing, and tennis. These Games were part of the Paris World's Fair.

The 1904 Summer Olympics were held in St. Louis, USA. Fewer international athletes attended due to travel difficulties and a major global conflict. This was the first time gold, silver, and bronze medals were given for first, second, and third place.
In 1906, Athens hosted another event called the "Second International Olympic Games." While not officially recognized by the IOC today, many historians believe these games helped keep the Olympics going strong. They were more successful than the 1900 and 1904 Games.
The 1908 Summer Olympics in London saw even more athletes. The marathon distance was set to its current length of 42.195 km (26 miles 385 yards). This was chosen so the race would finish in front of the British royal family. Great Britain won the most medals at these Games. A famous moment involved Italian runner Dorando Pietri. He collapsed near the finish line of the marathon and was helped by officials. He was later disqualified for this, but Queen Alexandra gave him a special silver cup.
The Games continued to grow. The 1912 Summer Olympics in Stockholm had 2,504 competitors. Jim Thorpe, a great all-around athlete, won both the decathlon and pentathlon. His medals were taken away for a time because he had played baseball for money, which was against the rules for amateur athletes back then. His medals were given back to his family in 1983. The 1912 Games were the first where athletes from all five inhabited continents competed in the same stadium.
The 1916 Summer Olympics were planned for Berlin but were cancelled because of World War I.
The Interwar Period
The 1920 Summer Olympics in Antwerp, Belgium, were a quiet event after the war. Still, a record number of athletes competed. This record was broken at the 1924 Summer Olympics in Paris. Over 3,000 athletes competed, including the famous Finnish runner Paavo Nurmi. He won three team gold medals and two individual races on the same day.
The 1924 Paris Games were the last under the leadership of Pierre de Coubertin. The Olympic motto Citius, Altius, Fortius (Faster, Higher, Stronger) was introduced. The first Olympic Village for athletes was also created. These Games also saw the start of the Winter Olympic Games.
The 1928 Summer Olympics in Amsterdam allowed women to compete in track and field for the first time. These Games also saw the first commercial sponsorship from the Coca-Cola Company. A standard medal design was introduced, showing the Greek goddess Nike. This design was used until 1972.
The 1932 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles were the first to feature an Olympic Village and a victory podium for medal winners.
The 1936 Berlin Games were used by the German government to promote their ideas. A filmmaker created a movie about the Games, which was considered a masterpiece. Despite this, African-American sprinter Jesse Owens won four gold medals, showing amazing athletic skill. The host country won the most medals overall. The 1936 Games also introduced the Olympic Torch Relay.
Due to World War II, the 1940 Summer Olympics (planned for Tokyo, then Helsinki) and the 1944 Summer Olympics (planned for London) were cancelled. London hosted the first Games after the war in 1948.
After World War II
The first post-war Games were held in 1948 in London. Germany and Japan were not invited to participate. Dutch sprinter Fanny Blankers-Koen won four gold medals in track events.
At the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki, the USSR team competed for the first time. They quickly became a strong team, finishing second in medals. A Czechoslovak army lieutenant, Emil Zátopek, became a legend. He won the 10,000-meter and 5,000-meter races. Then, he entered the marathon, even though he had never run one before. He won that too, completing an amazing triple victory.
The 1956 Summer Olympics in Melbourne, Australia, were the first in the Southern Hemisphere. They were mostly successful. However, a water polo match between Hungary and the Soviet Union became heated due to political tensions between their countries. The horse riding events were held in Stockholm, Sweden. This was because of strict animal health rules in Australia at the time.
At the 1960 Summer Olympics in Rome, a young boxer named Cassius Clay, later known as Muhammad Ali, became famous. He won a gold medal. Other great athletes included Wilma Rudolph, who won three gold medals in sprinting.
The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo were the first in Asia. They were also the first to be broadcast worldwide on television, thanks to new communication satellites. This greatly increased the popularity of the Olympics. Judo became an official sport.

The 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City were held at a high altitude, which affected some performances. American high jumper Dick Fosbury won gold using his new "Fosbury flop" technique. During the men's 200-meter race medal ceremony, American athletes Tommie Smith and John Carlos raised their black-gloved fists. This was a protest for civil rights and equality. They were later asked to leave the Games.
Politics sadly affected the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich. A tragic event occurred when a group took Israeli athletes hostage. This led to a terrible loss of life. After much discussion, the Games continued, but everyone was deeply saddened. Despite this, there were amazing athletic moments. American swimmer Mark Spitz won a record seven gold medals. Finland's Lasse Virén won gold in both the 5,000 and 10,000 meters. Soviet gymnast Olga Korbut won three gold medals, including a historic backflip off the high bar. In the men's basketball final, the United States lost to the Soviet Union in a very controversial game. The U.S. team refused to accept their silver medals.
The 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal faced financial challenges. The costs were much higher than planned. Many African nations boycotted the Games. This was a protest against unfair treatment of people in South Africa. Romanian gymnast Nadia Comăneci made history by earning the first perfect scores in Olympic gymnastics. Lasse Virén repeated his double gold in distance running.
End of the 20th Century
Following a major international conflict in 1979, 66 nations, including the United States, boycotted the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow. This meant fewer countries participated, and the host country dominated the events. There were also concerns about athletes using banned substances to gain an unfair advantage.
In 1984, the Soviet Union and 13 allied countries boycotted the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. However, a record 140 National Olympic Committees still took part. These Games were successful financially. China participated for the first time.
The 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul were well-organized. However, some athletes, including 100-meter winner Ben Johnson, failed drug tests. This raised concerns about fair play in sports.
The 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona allowed professional basketball players from the NBA to compete. The U.S. "Dream Team" was very popular. Several smaller European countries, which had been part of the Soviet Union, rejoined the Games. Gymnast Vitaly Scherbo won five individual gold medals, a new record for a Summer Olympics.
By this time, choosing host cities became a big business. There were concerns about fairness in the selection process.
At the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, American runner Michael Johnson broke the world record in the 200 meters. Muhammad Ali, affected by Parkinson's disease, lit the Olympic torch. He also received a replacement medal for the one he had discarded in 1960. A sad event occurred when a bomb exploded in Centennial Olympic Park.

The 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia, were called the "Games of the New Millennium." Australian swimmer Ian Thorpe and runner Cathy Freeman were local heroes. Briton Steve Redgrave won a rowing gold medal in his fifth straight Olympics. Eric "the Eel" Moussambani, a swimmer from Equatorial Guinea, became famous for his very slow but determined 100-meter freestyle swim. North and South Korea marched together in the opening ceremony for the first time.
Start of the 21st Century
In 2004, the Olympic Games returned to their birthplace in Athens, Greece. American swimmer Michael Phelps won his first Olympic medals, with six golds and two bronzes. Pyrros Dimas became the most decorated weightlifter ever with four Olympic medals. Despite some initial concerns, the Games were well-attended and considered a success. All 202 National Olympic Committees participated.
The 2008 Summer Olympics were held in Beijing, China. New sports like BMX cycling and women's steeplechase were added. Michael Phelps set a new record for gold medals at a single Games with eight. Jamaican sprinter Usain Bolt became the first male athlete to set world records in both the 100 and 200 meters in the same Games.
London hosted the 2012 Summer Olympics, becoming the first city to host three times. The host nation, Great Britain, won 29 gold medals. The United States returned to the top of the medal table. These Games were very popular, with all tickets selling out.
Recent Games

Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, hosted the 2016 Summer Olympics. This was the first time a South American city hosted the Games. There were some challenges before the Games, including concerns about health and the environment. There was also a major scandal involving some Russian athletes using banned substances, which affected their participation.
The 2020 Summer Olympics were planned for Tokyo, Japan, in 2020. However, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, they were postponed until 2021. This was the first time the Olympic Games had ever been delayed. The Games took place without spectators because of health concerns. Despite this, there were many memorable moments. American gymnast Simone Biles bravely stepped back to focus on her mental health. She later returned to win a bronze medal. Norway's Karsten Warholm broke his own world record in the 400m hurdles.
The 2024 Summer Olympics were held in Paris, France. This marked Paris's third time hosting, exactly 100 years after its last time. These were the first Games after the pandemic to allow spectators. For the first time, the opening ceremonies were held outside the main stadium. Athletes paraded on boats along the River Seine.
Future Games
The 2028 Summer Olympics will be held in Los Angeles, USA. This will be Los Angeles's third time hosting.
The 2032 Summer Olympics will be held in Brisbane, Australia. This will be the third Australian city to host the Games.
Olympic Sports and Events
Over time, 42 different sports have been part of the Olympic program. The recent 2020 Summer Olympics featured 33 sports. The upcoming 2024 Summer Olympics had 32 sports.
The different groups that manage each Olympic sport are part of a larger organization. It is called the Association of Summer Olympic International Federations (ASOIF).
Current sport No longer included
|
How Athletes Qualify for the Games
Each sport has its own rules for how athletes can qualify for the Olympics. These rules are set by the international group that manages that sport.
For individual sports, athletes usually qualify by doing well in big international competitions. Or they might be high on a sport's ranking list. Generally, only up to three athletes from each country can compete in an individual event.
For team sports, teams usually qualify through special tournaments. Each continent gets a certain number of spots in the Olympic tournament. Each country can only send one team per competition.
Sometimes, countries that don't have many qualified athletes can get special "Universality Places." These are like wild cards that allow more nations to participate.
Popularity of Olympic Sports
The IOC groups Summer Olympic sports into categories (A to E). This is based on how popular they are. They look at things like how many people watch on TV, how popular they are online, and how many tickets are sold. A sport's category helps decide how much Olympic funding it receives. New sports like rugby and golf were placed in Category E when they joined.
The current categories are:
| Cat. | No. | Sport |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3 | athletics, aquatics, gymnastics |
| B | 5 | basketball, cycling, football, tennis, volleyball |
| C | 8 | archery, badminton, boxing, judo, rowing, shooting, table tennis, weightlifting |
| D | 9 | canoe/kayaking, equestrian, fencing, handball, field hockey, sailing, taekwondo, triathlon, wrestling |
| E | 3 | modern pentathlon, golf, rugby |
| F | 6 | baseball/softball, karate, skateboarding, sport climbing, surfing |
Aquatics includes artistic swimming, diving, swimming, and water polo.
All-Time Olympic Medal Table
This table shows the total medals won by countries in the Summer Olympics. It uses official data from the IOC.
Defunct nationstatus after the 2024 Summer Olympics
| No. | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total | Games |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1105 | 879 | 780 | 2764 | 29 | |
| 2 | 395 | 319 | 296 | 1010 | 9 | |
| 3 | 303 | 226 | 198 | 727 | 12 | |
| 4 | 298 | 340 | 343 | 981 | 30 | |
| 5 | 239 | 277 | 299 | 815 | 29 | |
| 6 | 229 | 201 | 228 | 658 | 29 | |
| 7 | 213 | 220 | 255 | 688 | 18 | |
| 8 | 189 | 162 | 191 | 542 | 24 | |
| 9 | 187 | 161 | 182 | 530 | 28 | |
| 10 | 182 | 192 | 226 | 600 | 28 | |
| 11 | 153 | 129 | 127 | 409 | 5 | |
| 12 | 151 | 181 | 182 | 514 | 28 | |
| 13 | 147 | 126 | 150 | 423 | 6 | |
| 14 | 110 | 112 | 134 | 356 | 28 | |
| 15 | 109 | 100 | 111 | 320 | 19 | |
| 16 | 101 | 85 | 119 | 305 | 27 | |
| 17 | 93 | 101 | 123 | 317 | 23 | |
| 18 | 86 | 70 | 88 | 244 | 22 | |
| 19 | 80 | 117 | 156 | 353 | 28 | |
| 20 | 73 | 93 | 142 | 308 | 23 |
Countries Leading the Medal Count Each Year
|
Number of times a country led the medal count:
| Rank | Country | Number of games |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 times | |
| 2 | 6 times | |
| 3 | 1 time | |
List of Summer Olympic Games Host Cities
The IOC has never officially decided which events in the early Games were "Olympic" and which were not. The founder of the modern Olympics, Pierre de Coubertin, let the organizers of those Games make that decision.
| Olympiad | No. | Host | Games dates / Opened by |
Sports (Disciplines) |
Competitors | Events | Nations | Top nation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | |||||||||
| 1896 | I | 6–15 April 1896 King George I of Greece |
9 (10) | 241 | 241 | 0 | 43 | 14 | |||
| 1900 | II | 14 May – 28 October 1900 Baron Pierre de Coubertin |
19 (21) | 1,226 | 1,202 | 24 | 95 | 26 | |||
| 1904 | III | 1 July – 23 November 1904 Governor David R. Francis |
16 (18) | 651 | 645 | 6 | 95 | 12 | |||
| 1908 | IV | 27 April – 31 October 1908 King Edward VII |
22 (25) | 2,008 | 1,971 | 37 | 110 | 22 | |||
| 1912 | V | 6–22 July 1912 King Gustaf V |
14 (18) | 2,407 | 2,359 | 48 | 102 | 28 | |||
| 1916 | VI | Awarded to Germany (Berlin). Cancelled due to World War I | |||||||||
| 1920 | VII | 14 August – 12 September 1920 King Albert I of Belgium |
22 (29) | 2,626 | 2,561 | 65 | 156 | 39 | |||
| 1924 | VIII | 5–27 July 1924 President Gaston Doumergue |
17 (23) | 3,089 | 2,954 | 135 | 126 | 44 | |||
| 1928 | IX | 28 July – 12 August 1928 Duke Henry of Mecklenburg-Schwerin |
14 (20) | 2,883 | 2,606 | 277 | 109 | 46 | |||
| 1932 | X | 30 July – 14 August 1932 Vice President Charles Curtis |
1,332 | 1,206 | 126 | 117 | 37 | ||||
| 1936 | XI | 1–16 August 1936 Chancellor Adolf Hitler |
19 (25) | 3,963 | 3,632 | 331 | 129 | 49 | |||
| 1940 | XII | Originally awarded to Japan (Tokyo), then awarded to Finland (Helsinki). Cancelled due to World War II | |||||||||
| 1944 | XIII | Awarded to United Kingdom (London). Cancelled due to World War II | |||||||||
| 1948 | XIV | 29 July – 14 August 1948 King George VI |
17 (23) | 4,104 | 3,714 | 390 | 136 | 59 | |||
| 1952 | XV | 19 July – 3 August 1952 President Juho Kusti Paasikivi |
4,955 | 4,436 | 519 | 149 | 69 | ||||
| 1956 | XVI | 22 November – 8 December 1956 Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh |
3,314 | 2,938 | 376 | 151 | 72 | ||||
| 1960 | XVII | 25 August – 11 September 1960 President Giovanni Gronchi |
5,338 | 4,727 | 611 | 150 | 83 | ||||
| 1964 | XVIII | 10–24 October 1964 Emperor Hirohito |
19 (25) | 5,151 | 4,473 | 678 | 163 | 93 | |||
| 1968 | XIX | 12–27 October 1968 President Gustavo Díaz Ordaz |
18 (24) | 5,516 | 4,735 | 781 | 172 | 112 | |||
| 1972 | XX | 26 August – 11 September 1972 President Gustav Heinemann |
21 (28) | 7,134 | 6,075 | 1,059 | 195 | 121 | |||
| 1976 | XXI | 17 July – 1 August 1976 Queen Elizabeth II |
21 (27) | 6,084 | 4,824 | 1,260 | 198 | 92 | |||
| 1980 | XXII | 19 July – 3 August 1980 Chairman of the Presidium Leonid Brezhnev |
5,179 | 4,064 | 1,115 | 203 | 80 | ||||
| 1984 | XXIII | 28 July – 12 August 1984 President Ronald Reagan |
21 (29) | 6,829 | 5,263 | 1,566 | 221 | 140 | |||
| 1988 | XXIV | 17 September – 2 October 1988 President Roh Tae-woo |
23 (31) | 8,391 | 6,197 | 2,194 | 237 | 159 | |||
| 1992 | XXV | 25 July – 9 August 1992 King Juan Carlos I |
25 (34) | 9,356 | 6,652 | 2,704 | 257 | 169 | |||
| 1996 | XXVI | 19 July - 4 August 1996 President Bill Clinton |
26 (37) | 10,318 | 6,806 | 3,512 | 271 | 197 | |||
| 2000 | XXVII | 15 September – 1 October 2000 Governor-General Sir William Deane |
28 (40) | 10,651 | 6,582 | 4,069 | 300 | 199 | |||
| 2004 | XXVIII | 13–29 August 2004 President Konstantinos Stephanopoulos |
10,625 | 6,296 | 4,329 | 301 | 201 | ||||
| 2008 | XXIX | 8–24 August 2008 President Hu Jintao |
28 (41) | 10,942 | 6,305 | 4,637 | 302 | 204 | |||
| 2012 | XXX | 27 July – 12 August 2012 Queen Elizabeth II |
26 (39) | 10,768 | 5,992 | 4,776 | 302 | 204 | |||
| 2016 | XXXI | 5–21 August 2016 Acting President Michel Temer |
28 (42) | 11,238 | 6,179 | 5,059 | 306 | 207 | |||
| 2020 | XXXII | 23 July – 8 August 2021 Emperor Naruhito |
33 (50) | 11,476 | 5,982 | 5,494 | 339 | 206 | |||
| 2024 | XXXIII | 26 July – 11 August 2024 President Emmanuel Macron |
32 (48) | 10,714 | 5,357 | 5,357 | 329 | 206 | |||
| 2028 | XXXIV | 14–30 July 2028 TBA |
36 (51) | 11,198 | 5,167 | 5,333 | 353 | TBA | TBA | ||
| 2032 | XXXV | 23 July – 8 August 2032 TBA |
TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | ||
| 2036 | XXXVI | TBA | TBA 2036 TBA |
TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | |
See also
 In Spanish: Juegos Olímpicos de Verano para niños
In Spanish: Juegos Olímpicos de Verano para niños
- List of participating nations at the Summer Olympic Games
- List of Olympic Games scandals and controversies
- Lists of Olympic medalists
- Olympic Games ceremony
- Olympic Stadium
- Summer Paralympic Games
- Paralympic Games
- Winter Olympic Games