Host defence peptide facts for kids
A Host defence peptide (also called an antimicrobial peptide) is a tiny helper in your body's natural protection system, called the innate immune system. These special peptides are found in all kinds of living things, from plants to animals and even humans!
They act like tiny soldiers, fighting off invading microorganisms that can make us sick. These peptides can kill many types of bacteria, including those that are tough and resistant to regular antibiotics. They also work against mycobacteria (like the ones that cause tuberculosis), viruses with an outer layer, fungi, and even cancerous cells.
These peptides are very promising for medical use. They could work alongside regular antibiotics. They can fight many different types of germs and actually kill bacteria, rather than just stopping them from growing. Plus, they work very quickly!
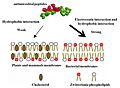
There are big differences between prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) and eukaryotic cells (like our own cells). Antimicrobial peptides are designed to target the germ cells without harming our own. These powerful peptides might also help improve our immune system by making it stronger.
Contents
What are Host Defence Peptides?
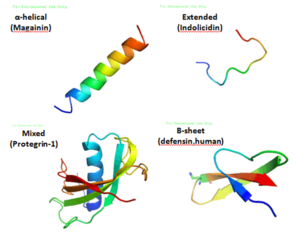
Host defence peptides, or HDPs, are small chains of peptides. Think of them as tiny protein fragments. They are a key part of the innate immune system, which is your body's first line of defense against invaders. This system is always ready to protect you from germs you encounter every day.
These peptides are found everywhere in nature. They are present in almost every living organism. This shows how important they are for survival. They help protect plants, insects, and animals, including humans, from harmful microbes.
How Do They Fight Germs?
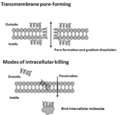
HDPs work in several ways to fight off germs. One main way is by attacking the outer layer of bacteria and fungi. They can poke holes in these layers, causing the germ to leak its contents and die. This is why they are called "bactericidal" – they kill bacteria directly.
They are effective against many different types of germs. This includes both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Some of these bacteria are very hard to treat with regular medicines. HDPs can even fight certain viruses and mycobacteria.
Why Are They Important for Medicine?
Because HDPs can kill many different types of germs, they are being studied as new antibiotics. They could be very useful, especially against germs that have become resistant to current medicines. This is a big problem in healthcare today.
Unlike many traditional antibiotics, HDPs don't just stop germs from growing; they destroy them. They also work very fast. This means they could be a powerful new tool in fighting infections. Scientists are also looking at how these peptides can boost the immune system, helping it fight off diseases even better.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Scanning electron microscopic images (50,000X magnification) showing how an experimental antimicrobial peptide (NN2_0050) affects the cell membrane of E. coli (K12 MG1655). ABOVE: Healthy cell membranes in the control group. BELOW: Damaged cell membranes and bacterial DNA leaking out (green) in the treated group.
See also
 In Spanish: Péptido antimicrobiano para niños
In Spanish: Péptido antimicrobiano para niños