Indo-Pakistani wars and conflicts facts for kids
Quick facts for kids India–Pakistan conflict |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Kashmir dispute and the Cold War | |||||||
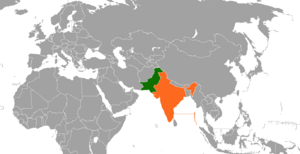 Location of India (orange) and Pakistan (green) |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
Since 1947, India and Pakistan have had several wars and conflicts. These two countries were created after the British India was divided. A big reason for their conflicts is a long-standing disagreement over a region called Kashmir. Another reason has been cross-border attacks. The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 was different. It happened because of problems in what was then East Pakistan (now Bangladesh).
Contents
How the Conflict Began
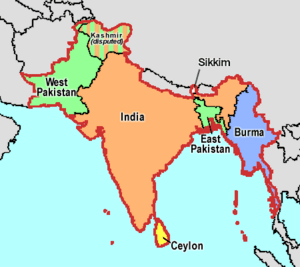
In 1947, British India gained independence. This led to the creation of two new countries: India and Pakistan. Many people wanted a clear division between these two new nations.
However, about one-third of the Muslim population stayed in the new India. This division caused a lot of violence between different religious groups. Between 200,000 and 2 million people died. About 14 million people had to leave their homes.
Before independence, India had many small princely states. These states were given a choice. They could join either India or Pakistan.
Major Wars Between India and Pakistan
The First Kashmir War (1947)
This war began in October 1947. Pakistan was worried that the ruler of Kashmir and Jammu would join India. Kashmir was a large princely state. It had many Muslim people but was ruled by a Hindu king named Hari Singh.
Tribal groups, supported by the Pakistani army, attacked parts of Kashmir. This made the king sign an agreement to join India. India then sent its army to help. The United Nations tried to help stop the fighting.
A ceasefire was declared on January 1, 1949. India gained control of about two-thirds of Kashmir. This included the Kashmir Valley, Jammu, and Ladakh. Pakistan took control of about one-third, known as Pakistan-administered Kashmir.
The Second Kashmir War (1965)
This war started after Pakistan launched a plan called "Operation Gibraltar". Their goal was to send soldiers into Jammu and Kashmir. They hoped to start a rebellion against India's rule.
India responded by attacking West Pakistan. The war lasted 17 days. Thousands of soldiers were hurt or killed on both sides. It included the largest tank battle since World War II. The fighting stopped after the Soviet Union and the USA stepped in. They helped create a ceasefire and the Tashkent Declaration. India was in a stronger position when the ceasefire was declared.
The Bangladesh Liberation War (1971)


This war was different because it was not about Kashmir. It started because of a big political problem in East Pakistan (now Bangladesh). The people of East Pakistan wanted more rights and eventually independence.
After a harsh crackdown by the Pakistani army, about 10 million people from East Pakistan fled to India. India then got involved in the fight for Bangladesh's freedom. Pakistan launched a surprise attack on India. This led to a full-scale war.
Pakistan attacked along India's western border. But the Indian Army held their ground. Indian forces quickly advanced in the west. They captured a lot of Pakistani land. Within two weeks, Pakistani forces in East Pakistan surrendered. This led to the creation of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. More than 90,000 Pakistani soldiers surrendered. Pakistan lost a large part of its navy, air force, and army.
The Kargil War (1999)
This conflict was mostly limited to one area. In early 1999, Pakistani troops crossed the Line of Control (LoC). They took over Indian territory in the Kargil district. India launched a major military and diplomatic effort to push them back.
After two months, Indian troops had retaken most of the areas. They regained control of nearly all the high ground. Other countries, especially the United States, put pressure on Pakistan. They urged Pakistan to withdraw its forces.
Pakistan's economy was already weak, and it faced international isolation. The morale of Pakistani soldiers dropped. Many units suffered heavy losses. Pakistan's Prime Minister, Nawaz Sharif, later said that over 4,000 Pakistani troops were killed. He admitted that Pakistan had lost the conflict. By the end of July 1999, the fighting in Kargil had stopped.
Nuclear Weapons and Their Impact
Both India and Pakistan have nuclear weapons. This means they have a very serious way to defend themselves. Pakistan has a "first strike" policy. This means they might use nuclear weapons first if they are being invaded or if a nuclear attack happens against them. India has a "no first use" policy. This means they will only use nuclear weapons if they are attacked with them first.
Scientists have studied what would happen if a nuclear war broke out between India and Pakistan. A study in 2022 suggested it could kill over 2 billion people indirectly. This would happen due to starvation during a "nuclear winter".
- India's First Test (1974): On May 18, 1974, India exploded a nuclear device. This test was called Smiling Buddha. India became the first country outside the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council to have nuclear weapons. This made Pakistan want its own nuclear bomb. Pakistan's Prime Minister, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, had said they would get one even if they had to "eat grass."
- Pakistan's Early Tests (1980s): In the 1980s, Pakistan conducted many secret "cold tests" of nuclear devices. These tests helped them develop their own nuclear weapons program.
- India's Further Tests (1998): On May 11, 1998, India exploded five more nuclear devices. This was called Operation Shakti. India celebrated, but other countries placed sanctions on them. Pakistan was very angry. They said India was starting a nuclear arms race. Pakistan promised to match India's nuclear power.
- Pakistan's Response (1998): Just half a month after India's tests, Pakistan exploded five nuclear devices on May 28, 1998. This day is now called Youm-e-Takbir (The Day of Greatness). Pakistanis celebrated becoming the only Muslim country with nuclear weapons. Two days later, on May 30, 1998, Pakistan detonated a sixth nuclear device. These were the last nuclear tests by either nation to date.
Annual Celebrations
Both India and Pakistan have special days to remember these conflicts:
- May 28: Youm-e-Takbir (The Day of Greatness) in Pakistan. This day celebrates Pakistan's nuclear tests in 1998.
- July 26: Kargil Vijay Diwas (Kargil Victory Day) in India. This day marks India's victory in the Kargil War of 1999.
- September 6: Defence Day (Youm-e-Difa) in Pakistan. This day remembers the 1965 war.
- September 7: Air Force Day (Youm-e-Fizaya) in Pakistan. This day honors the Pakistani Air Force.
- September 8: Victory Day/Navy Day (Youm-e-Bahr'ya) in Pakistan. This day celebrates the Pakistani Navy.
- December 4: Navy Day in India. This day honors the Indian Navy.
- December 16: Vijay Diwas (Victory Day) in India. This day celebrates India's victory in the 1971 war.
- December 16: Bijoy Dibosh (Victory Day) in Bangladesh. This day celebrates Bangladesh's independence in 1971.
Other Countries Involved
 Soviet Union: The Soviet Union stayed neutral in the 1965 war. They helped negotiate the peace agreement. During the 1971 war, they supported India. They sent warships to the Indian Ocean when the US and UK sent their own ships.
Soviet Union: The Soviet Union stayed neutral in the 1965 war. They helped negotiate the peace agreement. During the 1971 war, they supported India. They sent warships to the Indian Ocean when the US and UK sent their own ships. United States: The US did not give military aid to Pakistan in the 1965 war. They supported Pakistan in the 1971 war by sending a warship to the Indian Ocean. However, the US did not support Pakistan during the Kargil War. They pressured Pakistan to stop the fighting.
United States: The US did not give military aid to Pakistan in the 1965 war. They supported Pakistan in the 1971 war by sending a warship to the Indian Ocean. However, the US did not support Pakistan during the Kargil War. They pressured Pakistan to stop the fighting. China: China has helped Pakistan in different wars with diplomatic support.
China: China has helped Pakistan in different wars with diplomatic support. Russia: Russia has tried to stay neutral. They helped negotiate peace in 2001–02 and helped calm down a crisis in 2008.
Russia: Russia has tried to stay neutral. They helped negotiate peace in 2001–02 and helped calm down a crisis in 2008.
See Also
- United Nations Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan
- India–Pakistan relations
- Two-nation theory
- Patriotic hacking
- List of wars involving India
- List of wars involving Pakistan



