Intravenous therapy facts for kids
Intravenous injection or intravenous therapy means putting liquid medicine or fluids directly into a vein using a small needle. Many important medicines can be given this way.
Contents
Why are IVs helpful?
Medicines given through an IV work very quickly. This is because they go straight into your bloodstream. They can reach the brain and start working in about a minute or even faster.
Also, when a medicine is given by IV, your body gets 100% of the dose. This means none of the medicine is lost before it reaches your bloodstream.
When medicines are given in other ways, like by mouth, they might not work as fast. Also, not all of the medicine might reach your bloodstream.
However, medicines given by IV don't last as long as pills you swallow. As soon as the medicine enters your bloodstream, your body starts to break it down. This helps your body get rid of it when it's no longer needed.
How IV lines work
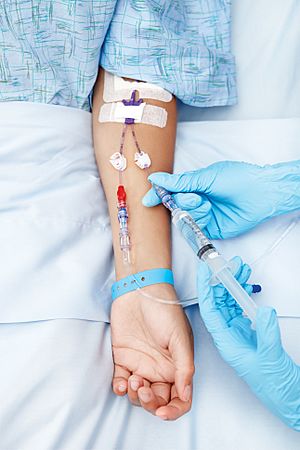
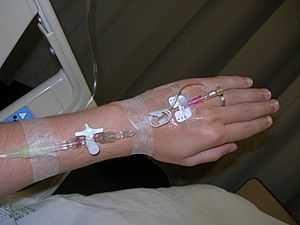
The most common type of IV injection is called an "intravenous (IV) line." This is what doctors and nurses usually mean when they say a patient is getting an IV.
To set up an IV line, a medical helper will:
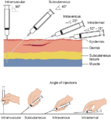
- Gently put a needle into one of your veins.
- Slide a hollow plastic tube, called a catheter, over the needle and into your vein.
- The needle is then removed, leaving only the soft plastic catheter inside your vein.
- They will attach the catheter to longer tubes that stay outside your body.
- When you need fluids or medicines, the liquid is put into a bag (called an IV bag). This bag is then connected to the longer tubes.
- The liquid slowly drips through the tubes, through the catheter, and into your vein.
Sometimes, if a medicine needs to be given very quickly, a medical helper can inject it directly into the IV line all at once. This is called an "IV push."
An IV line is very useful because it lets medical helpers give different liquids at different times. They don't have to put a new needle into a vein every time. They can also give many medicines at the same time if needed.
What are IVs used for?
IV lines are often used in emergency medicine and hospitals. Many different things can be given through an IV line.
Replacing lost body fluids
Special fluids called Volume expanders are used when a person has lost a lot of body fluids. This can happen if someone is very dehydrated or has lost blood. Volume expanders help replace these lost fluids. They are called "volume expanders" because they increase the amount of liquid in the bloodstream.
Losing too much fluid can be dangerous. Your body needs liquid in your bloodstream to carry blood cells, glucose (sugar), electrolytes (salts), and many other important things. The liquid part of your blood, called plasma, usually does this job.
Here are some reasons why people might lose plasma:
- If a person has heavy bleeding, they will lose a lot of their plasma and the important things it carries.
- If a person gets dehydrated, they lose some of the water in their plasma. Plasma is usually about 92% water.
Volume expanders add more liquid to the bloodstream. This helps your plasma do its job properly.
Common types of fluid replacement
There are a few common types of fluid replacements. They are mixtures of liquids and other things your body needs when it loses fluids:
- Saline: This is the most common fluid replacement. It's a simple mixture of water and sodium (a type of salt).
- Ringer's Lactate: This is a mixture of water and five important electrolytes: sodium, chloride, potassium, lactate, and calcium.
- D5W: This stands for "5% dextrose in water." Dextrose is another name for glucose (sugar). Your body needs glucose to make energy. D5W replaces lost fluids and also gives you more sugar for energy.
- D5W can also be mixed with saline or Ringer's Lactate to give a person extra electrolytes.
Giving medicines
Many medicines can be given by IV. They can be given alone or mixed into the fluid replacement bags.
Here are some examples of medicines given by IV:
- Some anti-nausea medicines: These are used when a person is vomiting and cannot swallow pills.
- Some anti-anxiety and antipsychotic medicines: These are used when people are very anxious or have psychotic symptoms.
- Medicines used to put a person to sleep before surgery: An example is propofol.
Blood transfusions
Blood transfusions are usually given through an IV line. A blood transfusion can give a person regular blood or only parts of the blood, such as:
- Plasma: The liquid part of blood.
- Red blood cells: These are often given alone when a person is very anemic (doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells).
- White blood cells: These may be given when treatments like chemotherapy kill white blood cells.
- Platelets and/or blood-clotting proteins: These are given when a person's blood is not clotting well.
Providing nutrition
If a person cannot eat for a short time, nutrition can be given through an IV line. IV nutrition mixtures include water, electrolytes, glucose, amino acids (building blocks of protein), lipids (fats), and vitamins. This ensures the body still gets the nutrients it needs to stay healthy.
Related pages
- Other ways to give medications
- Central venous catheter (a type of IV put into a large vein in the neck, chest, or groin)
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Terapia intravenosa para niños
In Spanish: Terapia intravenosa para niños