Israeli–Palestinian conflict facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Israeli–Palestinian conflict |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab–Israeli conflict | |||||||||
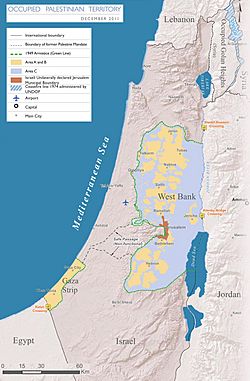 Map of Israel and Palestine, showing zones of control as outlined by the Oslo Accords |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
Governance (PNA): |
|||||||||
|
Supported by:
Former support:
|
Supported by:
Former support:
|
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
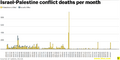
| 21,500+ casualties (1965–2013) | |||||||||
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is a long-lasting disagreement between Israel and the Palestinians. It started in the mid-1900s. Both groups claim the same area of land, which was once called Mandatory Palestine.
Some Palestinians are represented by groups like the Palestinian Authority, Fatah, or Hamas. This conflict is one of the world's most enduring disputes.
Contents
History of the Conflict
At the end of the 1800s, the idea of creating a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine began to spread. This idea caused tensions. After World War I, the British government controlled Palestine. They were supposed to help create this Jewish homeland, which many Palestinians did not agree with.
These tensions grew into open fighting between Jewish and Arab communities.
Dividing the Land
On November 29, 1947, the United Nations voted to divide Palestine. They suggested creating an Arab state, a Jewish state, and a special area for the City of Jerusalem. The very next day, violence erupted across Palestine.
This led to the 1947–1949 Palestine war, which caused about 15,000 deaths. In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Israel took control of some Palestinian territories.
Recent Peace Efforts
The most recent formal peace talks happened in July 2013 but stopped in 2014. Since 2006, Hamas and Israel have fought five wars. The most recent of these conflicts was in 2023.
Public Opinion on the Conflict
People on both sides have different ideas about how to solve the conflict.
Israeli Views
Only a small number of Jewish Israelis (about 32%) support a "two-state solution." This solution would mean having an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. Many Israeli Jews prefer to keep things as they are now.
More than two-thirds of Israeli Jews believe that if the West Bank became part of Israel, Palestinians living there should not be allowed to vote.
Palestinian Views
About 60% of Palestinians support armed attacks against Israelis inside Israel. This is seen as a way to end the occupation. This support is higher in the Gaza Strip (77%) than in the West Bank (46%).
About 70% of Palestinians believe that a two-state solution is no longer possible. They feel this way because Israeli settlements have expanded so much.
Casualties of the Conflict
The conflict has caused many deaths, not just among soldiers. A large number of civilians, meaning people who are not fighting, have also died on both sides.
According to one research group, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, about 13,000 Israelis and Palestinians were killed between 1948 and 1997. Other estimates suggest around 14,500 people died between 1948 and 2009.
Peace Process Efforts
Many attempts have been made to achieve a two-state solution. This idea involves creating an independent Palestinian state and an Israeli state, sharing the land between them.
However, support for this solution has decreased in recent years. Both Israeli Jews and Palestinians used to support it more. Some progress was made with the Oslo Accords agreements in 1993 and 1995.
International Involvement
The violence in the region has been discussed at many international meetings. These meetings deal with historical rights, safety issues, and human rights. The area is very important globally because it has many historic, cultural, and religious sites. The ongoing violence makes it difficult for tourists to visit.
The United Nations helps Palestinian refugees and keeps an eye on the situation in the region.
Images for kids
-
The Palestinian Arab Christian-owned Falastin newspaper featuring a caricature on its 18 June 1936 edition showing Zionism as a crocodile under the protection of a British officer telling Palestinian Arabs: "don't be afraid!!! I will swallow you peacefully...".
-
The Arab revolt of 1936–1939 in Palestine, motivated by opposition to mass Jewish immigration.
-
Yitzhak Rabin, Bill Clinton, and Yasser Arafat during the Oslo Accords on 13 September 1993.
-
Israeli settlers in Hebron, West Bank
-
Greater Jerusalem, May 2006. CIA remote sensing map showing what the CIA regards as settlements, plus refugee camps, fences, and walls
-
Home in Balata refugee camp demolished during the second Intifada, 2002
-
A neighbourhood in Ariel, home to the Ariel University
See also
 In Spanish: Conflicto israelí-palestino para niños
In Spanish: Conflicto israelí-palestino para niños