José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
The Most Excellent
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero
|
|
|---|---|

Rodríguez Zapatero in 2023
|
|
| Prime Minister of Spain | |
| In office 17 April 2004 – 21 December 2011 |
|
| Monarch | Juan Carlos I |
| Deputy | First deputy María Teresa Fernández de la Vega Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba Elena Salgado Second deputy Pedro Solbes Elena Salgado Manuel Chaves |
| Preceded by | José María Aznar |
| Succeeded by | Mariano Rajoy |
| Secretary-General of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party | |
| In office 22 July 2000 – 4 February 2012 |
|
| President | Manuel Chaves |
| Deputy | José Blanco |
| Preceded by | Joaquín Almunia |
| Succeeded by | Alfredo Pérez Rubalcaba |
| Leader of the Opposition | |
| In office 22 July 2000 – 16 April 2004 |
|
| Monarch | Juan Carlos I |
| Prime Minister | José María Aznar |
| Preceded by | Luis Martínez Noval |
| Succeeded by | Mariano Rajoy |
| Member of the Congress of Deputies | |
| In office 24 March 2004 – 27 September 2011 |
|
| Constituency | Madrid |
| In office 9 July 1986 – 2 August 2004 |
|
| Constituency | León |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 4 August 1960 Valladolid, Castile and León, Spain |
| Political party | PSOE (since 1979) |
| Spouses |
Sonsoles Espinosa
(m. 1990) |
| Children | 2 |
| Alma mater | University of León |
| Signature | 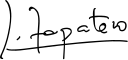 |
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero (born 4 August 1960) is a Spanish politician who was the Prime Minister of Spain from 2004 to 2011. He is a member of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE). He was elected prime minister twice, in the 2004 and 2008 general elections.
During his time as prime minister, Zapatero's government made several major changes. He withdrew Spanish soldiers from the war in Iraq and increased the number of troops in Afghanistan. He also passed a law to allow same-sex marriage. His government also tried to make peace with the armed group ETA.
Contents
Early Life and Family
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero was born in Valladolid, Spain. He grew up in the city of León. His father, Juan, was a lawyer. His mother was named María.
Zapatero's family history was deeply affected by the Spanish Civil War. His grandfather, Juan Rodríguez y Lozano, was a captain in the Spanish Republican Army. He was killed in 1936 by the Nationalist forces of Francisco Franco because he refused to fight for them. This family history had a big influence on Zapatero's political beliefs.
He studied law at the University of León and graduated in 1982. After graduating, he worked as a teaching assistant in constitutional law at the same university. He met his wife, Sonsoles Espinosa, in 1981, and they married in 1990. They have two daughters.
Start in Politics
Zapatero became interested in politics as a teenager. In 1976, he went to a political rally for the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE). He was inspired by a speech from Felipe González, who would later become Prime Minister of Spain.
He joined the PSOE in 1979. At first, he kept it a secret from his parents because he thought they would feel he was too young. In 1982, he became the leader of the socialist youth group in the province of León.
Member of Parliament
In 1986, at the age of 26, Zapatero was elected to the Spanish parliament, the Cortes. He was the youngest member of parliament at the time. He represented the province of León.
During the 1980s and 1990s, the PSOE was divided into two main groups. Zapatero did not formally join either group. He became known for his hard work and was given an award in 1999 as the "Most promising MP of the year."
Leader of the PSOE
In March 2000, the PSOE lost its second election in a row to the People's Party. The leader of the PSOE, Joaquín Almunia, resigned. Zapatero decided to run for the leadership of the party.
He created a new group within the party called Nueva Vía (New Way) to support his campaign. He was seen as a fresh face who could bring new ideas to the party. On 22 July 2000, he was elected Secretary-General of the PSOE, winning by a small number of votes.
As the leader of the opposition, Zapatero was known for his calm and dialogue-based style. This was very different from the more confrontational style of the Prime Minister at the time, José María Aznar. He criticized the government on several issues, including the war in Iraq, which was very unpopular in Spain.
The 2004 General Election
The general election was held on 14 March 2004. Just three days before the election, on 11 March, a series of bombs exploded on commuter trains in Madrid. The attacks killed 191 people and injured many more.
The government at first blamed the Basque separatist group ETA. However, evidence soon pointed to an Islamist extremist group. The government was accused of hiding information to avoid blame, as the attack was likely linked to Spain's role in the Iraq War.
The attacks and the government's handling of them had a huge impact on the election. The PSOE, led by Zapatero, won the election with 164 seats in parliament. He became Prime Minister on 17 April 2004.
Time as Prime Minister (2004–2011)
| Styles of José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Reference style | Excelentísimo Señor (Don) |
| Spoken style | Señor Presidente |
| Alternative style | Señor Zapatero, Don José Luis |
Zapatero's style as prime minister was often described with the Spanish word talante, which means having a good and pleasant attitude. He focused on social issues and tried to be less confrontational than the previous prime minister.
Key Policies and Events
Withdrawal of Troops from Iraq
One of Zapatero's first actions as prime minister was to withdraw all Spanish troops from Iraq. He had promised to do this during his campaign, calling the invasion of Iraq "an error based on lies." The decision was popular in Spain but was criticized by the United States government.
Social Reforms
Zapatero's government passed several important social laws. In 2005, Spain became one of the first countries in the world to legalize same-sex marriage, including the right for same-sex couples to adopt children.
His government also passed the Historical Memory Law in 2007. This law officially recognized the victims of the Spanish Civil War and the dictatorship of Francisco Franco. As part of this, the last remaining statue of Franco in Madrid was removed.
The ETA Ceasefire
The armed Basque separatist group ETA had been a major problem in Spain for decades. In March 2006, ETA declared a "permanent ceasefire." Zapatero's government began talks with the group to try to end the violence for good.
However, on 30 December 2006, ETA broke the ceasefire with a car bomb at Madrid's airport. Zapatero stopped all talks with the group. ETA later declared an end to its armed activity in 2011.
Foreign Policy

Zapatero focused on strengthening Spain's relationship with the European Union, especially with France and Germany. He also tried to improve relations with countries in Latin America.
His relationship with the United States under President George W. Bush was difficult, mainly because of his opposition to the Iraq War. Relations improved after Barack Obama became president in 2009.
After the Premiership
Zapatero did not run for a third term in the 2011 election. He left office in December 2011. In 2012, he stepped down as leader of the PSOE.
Since leaving office, he has taken on roles in international organizations. He has worked as a mediator to help solve political conflicts in other countries, such as Venezuela. He is also a member of the Puebla Group, a conference of left-leaning political leaders from Latin America and Spain.
Decorations
- Grand Cross of the Order of the Sun of Peru (2004)
- Grand Cross of the Order of Christ (2006)
- Grand Cross of the Order of the Liberator San Martín (2009)
- Collar of the Order of Isabella the Catholic (2011)
Images for kids
-
Zapatero with U.S. President George W. Bush, 14 November 2008
-
Zapatero with German Chancellor Angela Merkel, 3 February 2011
See also
 In Spanish: José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero para niños
In Spanish: José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero para niños
- Viva Zapatero!
- Governments of Rodríguez Zapatero
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |






