Kalyke facts for kids
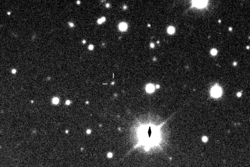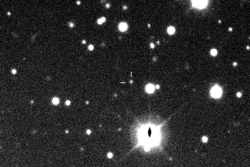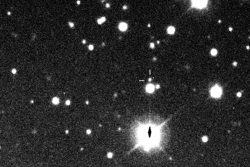
Kalyke imaged by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope in December 2001
|
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Scott S. Sheppard David C. Jewitt Yanga R. Fernandez Eugene A. Magnier |
| Discovery site | Mauna Kea Observatory |
| Discovery date | 23 November 2000 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | Jupiter XXIII |
| Pronunciation | /ˈkæləkiː/ |
|
Named after
|
Καλύκη Kalykē |
| S/2000 J 2 | |
| Adjectives | Kalykean /kæləˈkiːən/ |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 27 April 2019 (JD 2458600.5) | |
| Observation arc | 16.34 yr (5,967 days) |
| 0.1614179 AU (24,147,770 km) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3028225 |
| −766.61 d | |
| 63.16063° | |
|
Mean motion
|
0° 28m 10.57s / day |
| Inclination | 165.93730° (to ecliptic) |
| 132.43876° | |
| 323.78885° | |
| Satellite of | Jupiter |
| Physical characteristics | |
|
Mean diameter
|
6.9±1.3 km |
| Albedo | 0.029±0.014 |
| 21.8 | |
| 15.4 | |
Kalyke (pronounced KAL-uh-kee), also known as Jupiter XXIII, is one of the many moons that orbit the giant planet Jupiter. It is called an irregular satellite because it has an unusual orbit. Kalyke moves in a retrograde direction, meaning it orbits Jupiter opposite to the planet's rotation.
Kalyke was discovered in 2000 by a team of astronomers from the University of Hawaii. The team was led by Scott S. Sheppard. When it was first found, it was given the temporary name S/2000 J 2.
Contents
About Kalyke
Kalyke is a small moon. It is about 6.9 kilometers (4.3 miles) wide. Scientists figured out its size by measuring how much light it reflects. This is called its albedo, and Kalyke's albedo is very low, only about 2.9%. This means it is quite dark and doesn't reflect much sunlight.
Kalyke's Orbit Around Jupiter
Kalyke orbits Jupiter at an average distance of about 23,181,000 kilometers (14,404,000 miles). It takes Kalyke about 766 days to complete one full trip around Jupiter. Its orbit is also quite tilted, or has an inclination, of about 166 degrees compared to the ecliptic (the plane where most planets orbit the Sun). The moon's orbit is also not a perfect circle; it has an eccentricity of 0.2140, which means its path is more like an oval.
Naming Kalyke
Kalyke got its official name in October 2002. It was named after a figure from ancient Greek mythology. Kalyke (or Calyce) was a nymph, a nature spirit, in these old stories.
Kalyke's Family: The Carme Group
Kalyke belongs to a group of moons called the Carme group. This group is made up of several irregular moons that orbit Jupiter. They all move in a retrograde direction. These moons are found at similar distances from Jupiter, usually between 23 and 24 million kilometers. They also have similar orbital tilts, around 165 degrees.
However, Kalyke is a bit different from the other moons in the Carme group. It appears redder in color than its "siblings." This difference in color suggests that Kalyke might have a different origin. Scientists think it could be a captured centaur or a TNO. These are small icy bodies from the outer parts of our Solar System. Another idea is that Kalyke is a piece left over from a collision that happened long ago.
See also
 In Spanish: Cálice (satélite) para niños
In Spanish: Cálice (satélite) para niños


