Longitude of the ascending node facts for kids
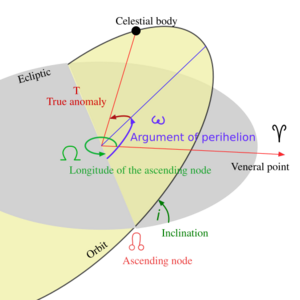
The longitude of the ascending node (pronounced "long-ih-tood of the ah-SEN-ding node") is a special measurement. It helps scientists and engineers describe exactly where an object is moving in space. Think of it as one of the key pieces of information, like an address, that tells us about a space object's path.
This measurement is an angle. It tells us how far around an imaginary circle an object's path crosses a special flat surface. This crossing point is called the "ascending node."
Contents
What is an Orbit?
An orbit is the curved path an object takes around another, much larger object. For example, the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Moon orbits the Earth. Satellites also orbit the Earth. These paths are usually shaped like an ellipse, which is like a stretched circle.
Why Do We Need to Describe Orbits?
Knowing an object's orbit is super important! It helps us:
- Track satellites.
- Plan space missions.
- Predict where planets or comets will be.
- Understand how gravity affects objects in space.
What are Orbital Elements?
To fully describe an orbit, scientists use a set of six numbers called orbital elements. These elements are like coordinates that give us all the details about an object's path. The longitude of the ascending node is one of these six important numbers.
The Six Key Orbital Elements
The six main orbital elements are:
- Semi-major axis: This tells us the size of the orbit.
- Eccentricity: This describes how "stretched out" the orbit is (how much it's not a perfect circle).
- Inclination: This is the tilt of the orbit compared to a main reference plane.
- Longitude of the ascending node: This is what we are talking about! It tells us where the orbit crosses the reference plane going "up."
- Argument of periapsis: This tells us where the closest point in the orbit is.
- Mean anomaly: This helps us know where the object is along its orbit at a specific time.
Understanding the Ascending Node
Imagine a flat, imaginary surface in space. For objects orbiting the Sun, this surface is often the plane of Earth's orbit (called the ecliptic plane). For satellites orbiting Earth, it's often Earth's equator.
When an object orbits, its path might be tilted compared to this flat surface. The ascending node is the exact point where the object's orbit crosses this flat surface while moving from "below" to "above" it. Think of it like a plane taking off from a runway – the point where it lifts off is similar to an ascending node.
How is the Longitude Measured?
The longitude of the ascending node is an angle measured on that flat reference surface. It starts from a special "zero" direction, like the Prime Meridian on Earth. From this zero point, you measure the angle around the circle to reach the ascending node. This angle tells us the direction in space where the object's orbit crosses "up" through the reference plane.
Why is This Measurement Important?
This specific angle is crucial for several reasons:
- Spacecraft Navigation: When launching a satellite, engineers need to know this angle precisely. It helps them put the satellite into the correct orbit.
- Predicting Collisions: By knowing the longitude of the ascending node for many objects, scientists can better predict if two objects might come too close to each other.
- Observing Planets: For astronomers, this measurement helps them understand the orientation of planets' and other celestial bodies' orbits.
Knowing the longitude of the ascending node helps us map out the universe. It's a key piece of the puzzle for understanding how everything moves in space.
See also
 In Spanish: Longitud del nodo ascendente para niños
In Spanish: Longitud del nodo ascendente para niños

