Kemi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kemi
Giepma
Kiemâ Ǩeeʹmm |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Town
|
||
| Kemin kaupunki Kemi stad |
||

Clockwise, from top left: Kemi Railway Station, Kemi City Hall, Karihaara School, Café at the inner harbour, and Kemi Church
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s):
Monaco of Finland
|
||
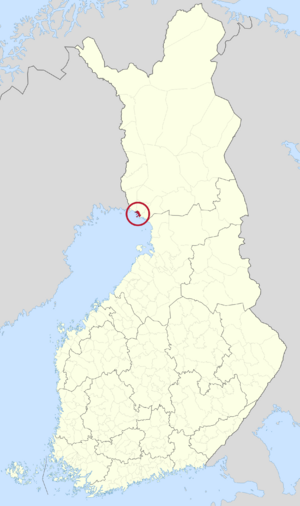
Location of Kemi in Finland
|
||
| Country | ||
| Region | Lapland | |
| Sub-region | Kemi–Tornio | |
| Charter | 1869 | |
| Area
(2018-01-01)
|
||
| • Total | 747.28 km2 (288.53 sq mi) | |
| • Land | 95.38 km2 (36.83 sq mi) | |
| • Water | 652.1 km2 (251.8 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 300th largest in Finland | |
| Elevation | 4 m (13 ft) | |
| Population
(2023-12-31)
|
||
| • Total | 19,371 | |
| • Rank | 61st largest in Finland | |
| • Density | 203.09/km2 (526.0/sq mi) | |
| Population by native language | ||
| • Finnish | 93.8% (official) | |
| • Swedish | 0.2% | |
| • Others | 6% | |
| Population by age | ||
| • 0 to 14 | 14.4% | |
| • 15 to 64 | 57.2% | |
| • 65 or older | 28.4% | |
| Time zone | UTC+02:00 (EET) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+03:00 (EEST) | |
| Postal code |
94100
|
|
Kemi is a town and municipality in Finland. It is located very close to the city of Tornio. Kemi is also near the border between Finland and Sweden. The town is about 105 kilometers (65 miles) south of Oulu. It is also 117 kilometers (73 miles) northeast of Rovaniemi.
Kemi was founded in 1869 by Alexander II of Russia, who was the Emperor of Russia. He chose this location because it had a good deepwater port. Today, Kemi has a population of about 19,371 people. The town covers an area of 747.28 km2 (288.53 sq mi). About 652.1 square kilometers (251.8 sq mi) of this area is water.
Contents
History of Kemi
Kemi During World War II
During World War II, Finland fought against Germany in the Lapland War. In October 1944, German forces took 132 Finnish civilians as hostages in Kemi. They also took 130 hostages in Rovaniemi. The Germans threatened to harm them if Finland did not release German prisoners of war.
However, Finland refused to give in to the demands. Finland warned that they would also harm German prisoners if the hostages were not freed. Luckily, all the hostages were released safely on October 11, 1944. This happened near Rovaniemi.
Geography and Climate
Kemi is located on the Bothnian Bay. This is a part of the Baltic Sea. The town is also at the mouth of the Kemijoki river. Kemi is part of the Lapland region in Finland.
Kemi's Climate
Kemi has a subarctic climate. This means it has long, cold winters. The summers are usually warm and short. Because Kemi is on the coast of the Gulf of Bothnia, its climate is not as extreme as places further inland.
| Climate data for Kemi (Kemi-Tornio Airport, 1991–2020 normals, records 1959–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
7.7 (45.9) |
9.6 (49.3) |
18.3 (64.9) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.4 (88.5) |
32.9 (91.2) |
29.2 (84.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.0 (50.0) |
6.8 (44.2) |
32.9 (91.2) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
3.1 (37.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
27.3 (81.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −5.7 (21.7) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
4.4 (39.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
17.2 (63.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
5.2 (41.4) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.6 (14.7) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
12.8 (55.0) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
2.3 (36.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −14.1 (6.6) |
−14.4 (6.1) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
1.5 (34.7) |
7.3 (45.1) |
11.0 (51.8) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.7 (40.5) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−2.2 (28.1) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | −28.1 (−18.6) |
−28.1 (−18.6) |
−23.2 (−9.8) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
0.8 (33.4) |
4.6 (40.3) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−23.6 (−10.5) |
−30.5 (−22.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −37.1 (−34.8) |
−43.2 (−45.8) |
−34.0 (−29.2) |
−25.4 (−13.7) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
−24.8 (−12.6) |
−31.3 (−24.3) |
−36.7 (−34.1) |
−43.2 (−45.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 32.3 (1.27) |
25.8 (1.02) |
28.7 (1.13) |
26.4 (1.04) |
30.3 (1.19) |
39.2 (1.54) |
52.2 (2.06) |
63.4 (2.50) |
58.1 (2.29) |
59.9 (2.36) |
44.8 (1.76) |
33.0 (1.30) |
494.1 (19.46) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 25 | 22 | 21 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 21 | 24 | 24 | 230 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 88 | 87 | 81 | 72 | 63 | 63 | 69 | 76 | 82 | 88 | 92 | 90 | 79 |
| Source: FMI | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kemi Ajos (1991–2020 normals, records 1993–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
5.4 (41.7) |
7.1 (44.8) |
16.5 (61.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.7 (83.7) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
24.0 (75.2) |
16.0 (60.8) |
8.5 (47.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
3.3 (37.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
15.9 (60.6) |
19.7 (67.5) |
17.6 (63.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
5.8 (42.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −8.6 (16.5) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
5.7 (42.3) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
14.9 (58.8) |
10.1 (50.2) |
3.8 (38.8) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
2.8 (37.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −12.5 (9.5) |
−13.2 (8.2) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.8 (56.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.9 (46.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −37.1 (−34.8) |
−33.8 (−28.8) |
−28.5 (−19.3) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.2 (43.2) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−12.9 (8.8) |
−23.3 (−9.9) |
−30.2 (−22.4) |
−37.1 (−34.8) |
| Source 1: https://www.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/ilmastollinen-vertailukaus | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: https://kilotavu.com/asema-taulukko.php?asema=101846 | |||||||||||||
Kemi's Economy
Kemi's economy mainly relies on two big factories. These factories make paper and wood pulp. The town also has the only chromium mine in Europe. This mine provides materials for a special steel plant in Tornio.
A Chinese company called Kaidi planned to build a special plant in Kemi. This plant would turn plant materials into energy. It was supposed to start working in 2019.
In 2007, the city of Kemi had money problems. Because of this, the city had to temporarily lay off all its workers for two weeks. This was due to high healthcare costs and businesses leaving the area. This was a very unusual event in Finland.
Fun Places to Visit in Kemi
Kemi is famous for having the world's largest snow castle. This amazing castle is rebuilt every year with a new design. You can usually find the SnowCastle of Kemi in the city's inner harbor.
The town also has a gemstone gallery. Here, you can see a model of The Crown of Finland. This crown was never actually made for a King of Finland. The gallery also has copies of other famous items. These include the British Imperial State Crown and the Russian Czar's scepter. You can also see the Orbs of Denmark and a diamond necklace like the one owned by Marie Antoinette.
Other cool places to visit in Kemi are:
- Kemi church
- Kemi Gemstone Gallery
- The Icebreaker Sampo
- The old sailing ship Jähti
Culture
Kemi is the home of the power metal band Sonata Arctica.
Getting Around Kemi
Train Travel
The Kemi railway station is an important stop on the train line. This line connects Lapland to Helsinki. The trains are run by a company called VR. North of Kemi station, the train lines to Kolari and Rovaniemi split off.
Roads and Highways
Major roads like Finnish national road 4 pass through Kemi. These roads are also part of European routes E8 and E75.
Air Travel
The Kemi-Tornio Airport is located about 4.5 kilometers (2.8 miles) north of Kemi's city center.
Sea Port
The Port of Kemi is a busy cargo port. It handles large shipping containers and other goods. It also deals with oil and chemical products.
Education
Kemi has a polytechnic university. This type of school offers practical, hands-on education.
Famous People from Kemi
- Juhani Paasivirta (1919–1993), a Finnish historian
- Ensio Seppänen (1924–2008), a Finnish sculptor and professor
- Anna-Liisa Tiekso (1929–2010), a Finnish politician
Kemi's Sister Cities
Kemi has special connections with other cities around the world. These are called twin towns or sister cities.
 Tromsø (Norway), since 1940
Tromsø (Norway), since 1940 Volgograd (Russia), since 1953
Volgograd (Russia), since 1953 Liptovský Mikuláš (Slovakia)
Liptovský Mikuláš (Slovakia) Newtownards (Northern Ireland)
Newtownards (Northern Ireland) Székesfehérvár (Hungary)
Székesfehérvár (Hungary) Luleå (Sweden)
Luleå (Sweden)
See also
 In Spanish: Kemi para niños
In Spanish: Kemi para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |





