Lake Wakatipu facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Wakatipu |
|
|---|---|

Lake Wakatipu and The Remarkables
|
|
| Location | Queenstown-Lakes District, Otago Region, South Island |
| Coordinates | 45°3′S 168°30′E / 45.050°S 168.500°E |
| Lake type | Glacial lake |
| Primary inflows | Dart River / Te Awa Whakatipu, Rees River |
| Primary outflows | Kawarau River |
| Catchment area | 2,674 km2 (1,032 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | New Zealand |
| Max. length | 75.2 km (46.7 mi) |
| Max. width | 5 km (3.1 mi) |
| Surface area | 289 km2 (112 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 230 metres (750 ft) |
| Max. depth | 380 metres (1,250 ft) |
| Residence time | c. 12 years |
| Surface elevation | 310 m (1,020 ft) |
| Islands | Pig Island, Pigeon Island, Tree Island & Hidden Island. |
| Settlements | Kingston, Queenstown, Glenorchy |
Lake Wakatipu is a long, narrow lake in the South Island of New Zealand. It is located in the southwest part of the Otago region. The name Lake Wakatipu comes from its original Māori name, Whakatipu wai-māori.
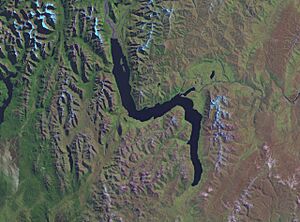
This lake is New Zealand's longest, stretching about 80 kilometres (50 mi). It is also the country's third largest lake by area, covering 291 km2 (112 sq mi). Lake Wakatipu is very deep, reaching a maximum depth of 380 metres (1,250 ft). Its lowest point is actually below sea level! The lake sits at an altitude of 310 metres (1,020 ft), surrounded by the Southern Alps.
The lake has a unique "N" shape. The Dart River / Te Awa Whakatipu flows into its northern end. The lake then flows south for about 30 kilometres (19 mi) before turning sharply east. After another 20 kilometres (12 mi), it turns south again, ending near Kingston.
The Kawarau River is the only river that flows out of Lake Wakatipu. It leaves the lake from the Frankton Arm, which is about 8 km (5.0 mi) east of Queenstown. Queenstown itself is on the northern shore of the lake.
Lake Wakatipu is famous for its amazing natural beauty. It is surrounded by tall mountains, including The Remarkables mountain range along its southeastern side.
Contents
Fun Facts About Lake Wakatipu
Lake Wakatipu has a special feature called a seiche. This is like a standing wave that makes the water level rise and fall regularly. In Queenstown Bay, the water level can go up and down by about 200 millimetres (7.9 in) every 26.7 minutes. It's like the lake is breathing!
The lake is a popular spot for adventure tourism. You can find skifields, paragliding, bungy jumping, and tramping tracks nearby. A historic steamboat, the TSS Earnslaw, still sails on the lake regularly. There are also several vineyards in the nearby Gibbston area.
What's in a Name?
The full original Māori name for the lake is Whakatipu-wai-Māori.
The name is thought to come from the Waitaha people. Later, the Kāti Māmoe people lived there. Today, elders from the Ngāi Tahu tribe say that the original meaning of Whakatipu is a mystery. However, whaka means "to cause" and tipu means "growth". So, Wakatipu might mean "growing bay".
There's a cool legend about how the lake was formed. It says that a giant ogre named Kopu-wai was burned while he was sleeping. Only his heart was left behind. According to the legend, this heart is what causes the lake's water level to rise and fall in a rhythm.
Flooding Events
Lake Wakatipu has had floods that have affected towns along its shores, like Kingston, Glenorchy, and Queenstown. Some big floods happened in 1878, 1995, and especially in 1999. The 1999 flood caused a lot of damage to Queenstown's main business area and roads.
Wildlife in the Lake
Lake Wakatipu is home to many different animals. You can find the New Zealand longfin eel here. One eel caught in 1886 was the biggest ever known of its kind! Other fish include brown trout, salmon, and rainbow trout.
These fish are food for birds like the pied shag. You can often see black-billed gulls around the lake. The mallard duck, which was brought to New Zealand, is also very common. A smaller bird that's sometimes hard to spot is the New Zealand scaup.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Wakatipu para niños
In Spanish: Wakatipu para niños