Antoine Lavoisier facts for kids
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier (born August 26, 1743 – died May 8, 1794) was a French nobleman, chemist, and biologist. Many people call him the "Father of Modern Chemistry". His work is a very important part of the history of chemistry and biology. He also helped start the idea of atomic theory. He was the first scientist to find and name the elements hydrogen and oxygen. He was sadly executed during the French Revolution, like many other nobles.
Contents
- Biography of Antoine Lavoisier
- Lavoisier's Contributions to Chemistry
- Awards and Honors
- Images for kids
- See also
Biography of Antoine Lavoisier
Early Life and Education
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier was born in Paris on August 26, 1743. His family was very wealthy. When he was five, his mother passed away, and he inherited a large fortune.
Lavoisier started school at the Collège des Quatre-Nations in Paris in 1754, when he was 11. In his last two years there, he became very interested in science. He studied chemistry, botany, astronomy, and mathematics. He also studied law and became a lawyer, but he never worked as one. Instead, he kept studying science in his free time.
Beginning His Scientific Work
Lavoisier was inspired by the ideas of the French Age of Enlightenment. He loved chemistry and published his first paper in 1764. From 1763 to 1767, he studied geology. He even worked on a geological map of France in 1769.
In 1764, he shared his first scientific paper with the French Academy of Sciences. This was France's top scientific group. In 1766, the King gave him a gold medal for his ideas on how to light city streets better. In 1768, he became a member of the Academy of Sciences.
Lavoisier's Work for the Public
Improving Public Life with Science
Lavoisier is famous for his science, but he also used his money and time to help people. He cared deeply about his country's citizens. He wanted to improve their lives through farming, industry, and science.
In 1765, he wrote about how to make city street lighting better. Three years later, in 1768, he worked on a plan to bring clean drinking water to Paris from the Yvette river. When that plan didn't happen, he focused on cleaning water from the Seine river. This made him interested in water chemistry and public health.
He also studied air quality. He looked into the health risks of gunpowder affecting the air. In 1772, he studied how to rebuild the Hôtel-Dieu hospital after a fire. He wanted to make sure it had good ventilation and clean air.
Lavoisier also looked into the terrible conditions in Paris prisons in 1780 and 1791. He suggested ways to make them more livable, but his ideas were mostly ignored.
Supporting Science for Everyone
Lavoisier believed that public education should include science. He used his wealth to open a very advanced laboratory in France. This allowed young scientists to study without worrying about money.
He also pushed for public science education. He started two organizations, Lycée [fr] and Musée des Arts et Métiers. These places were created to teach the public. Wealthy people funded the Lycée, and it started teaching courses to the public in 1793.
His Marriage and Role in Tax Collection
At 26, Lavoisier bought a share in the Ferme générale. This was a company that collected taxes for the French government. He helped build a wall around Paris to collect customs duties on goods entering and leaving the city. This role in tax collection later hurt his reputation during the French Revolution.
In 1771, at age 28, Lavoisier married Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze. Her father was a senior member of the Ferme générale. Marie-Anne was very important to Lavoisier's scientific work. She translated English science papers for him. She also helped him in the lab and drew pictures of his equipment. Madame Lavoisier edited and published her husband's scientific writings. She also hosted parties where scientists talked about new ideas.
A famous artist, Jacques-Louis David, painted a portrait of Antoine and Marie-Anne Lavoisier in 1788. This painting was not shown publicly because people feared it would upset those who disliked the rich.
For a few years after joining the Ferme générale, Lavoisier did less science. He was busy with tax work. However, he did prove that water does not turn into earth when it evaporates. He showed that the "earthy" stuff left behind was actually tiny bits of glass from the container. He also tried to improve France's money and tax system to help farmers.
Improving Tobacco Quality
The tax collection company, the Farmers General, controlled tobacco in France. They made a lot of money from it. But people started smuggling tobacco or mixing it with things like ash and water.
Lavoisier found a way to check if ash was added to tobacco. He also found that adding a tiny bit of ash or water could make tobacco taste better. He suggested that the factories add a small, consistent amount of water to their tobacco. He also set up strict checks to stop illegal tobacco and ensure quality. These rules made him very unpopular with tobacco sellers. This unpopularity would later cause problems for him during the French Revolution.
Helping Agriculture and Gunpowder Production
Lavoisier pushed for a Royal Commission on Agriculture. He became its secretary and spent his own money to improve farming in the Sologne region. This area had poor soil and often had rye blight, which caused illness. In 1788, he reported on his ten years of trying new crops and animals. He found that the tax system made it hard for farmers to change their old ways.

In 1775, Lavoisier became one of four people in charge of gunpowder production for France. Thanks to his efforts, French gunpowder became much better and more plentiful. This also brought him a house and laboratory at the Royal Arsenal, where he lived and worked until 1792.
Lavoisier also taught Éleuthère Irénée du Pont how to make gunpowder. Du Pont later started the famous DuPont company in America.
During the French Revolution
In 1791, Lavoisier helped fund a newspaper that would report on the government and science. He also led a group that created the metric system for weights and measures. This new system was adopted in 1793.
However, the French Revolution grew more intense. The tax collection company, Ferme générale, was shut down in 1791. In 1792, Lavoisier had to leave his job and home at the Royal Arsenal. In 1793, all scientific societies, including the Academy of Sciences, were closed.
His Final Days and Execution

On November 24, 1793, all former tax collectors were ordered to be arrested. Lavoisier and 27 others faced charges of cheating the state and adding water to tobacco. Lavoisier wrote their defense, explaining they had not defrauded the state and had maintained tobacco quality. However, the court wanted to take their money and goods.
Lavoisier was found guilty and executed by guillotine on May 8, 1794, in Paris. He was 50 years old.
A popular story says that the judge, Coffinhal, refused to spare Lavoisier's life to continue his experiments. The judge supposedly said, "The Republic needs neither scholars nor chemists; the course of justice cannot be delayed." The judge himself was executed less than three months later.
Another scientist, Joseph Louis Lagrange, sadly said after Lavoisier's death, "It took them only an instant to cut off this head, and one hundred years might not suffice to reproduce its like." This showed how important Lavoisier was to science.
Lavoisier Is Cleared
About a year and a half after his execution, the French government officially cleared Lavoisier's name. His belongings were returned to his wife with a note that said, "To the widow of Lavoisier, who was falsely convicted."
Lavoisier's Contributions to Chemistry
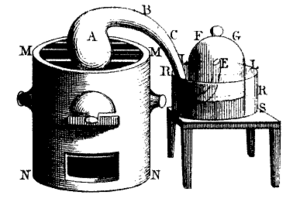
Lavoisier made huge changes to how chemistry was studied. Much of his work focused on combustion, which is how things burn. He was the first to explain that burning happens because of oxidation. To prove this, he studied air. In 1776, he burned mercury in a closed container. He concluded that air is a mix of oxygen and other gases, not a single element.
He also discovered the law of conservation of mass. This law states that nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed. It means that in a chemical reaction, the total mass of the starting materials is the same as the total mass of the products. Today, this idea is a basic rule of modern chemistry.
Lavoisier, along with other scientists, created the first system for naming chemicals in the 1780s. This system helped chemists around the world understand each other better.
Overall, his work is seen as the most important in making chemistry as advanced as physics and mathematics were in the 1700s.
Awards and Honors
During his life, Lavoisier received a gold medal from the King of France for his work on city street lighting in 1766. He also became a member of the French Academy of Sciences in 1768. In 1775, he was chosen as a member of the American Philosophical Society.
In 1999, Lavoisier's work was recognized as an International Historic Chemical Landmark. This honor came from the American Chemical Society, the Académie des sciences de L'institut de France, and the Société Chimique de France.
Several Lavoisier Medals have been created in his honor. These are given by groups like the Société chimique de France and the DuPont company. There is also the Franklin-Lavoisier Prize, which celebrates the friendship between Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier and Benjamin Franklin. This prize includes a medal and is given by organizations in Paris and Philadelphia.
Images for kids
-
Joseph Priestley, an English chemist who found oxygen.
-
A statue of Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier by Jules Dalou from 1866.
See also
 In Spanish: Antoine Lavoisier para niños
In Spanish: Antoine Lavoisier para niños










