Leaning Tower of Pisa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Leaning Tower of Pisa |
|
|---|---|
|
Torre Pendente di Pisa
|
|

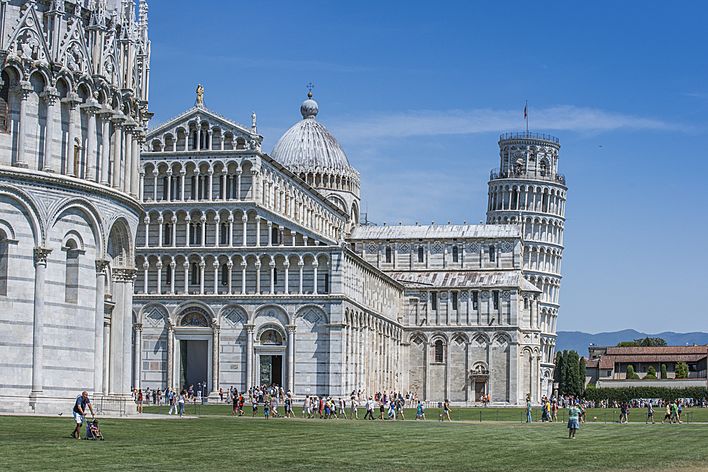
Leaning Tower of Pisa in 2022
|
|
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Catholic Church |
| Ecclesiastical or organizational status | Active |
| Location | |
| Location | Pisa, Italy |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Bonanno Pisano |
| Architectural style | Romanesque |
| Groundbreaking | 1173 |
| Completed | 1372 |
| Specifications | |
| Height (max) | 55.86 m (183 ft 3 in) |
| Materials | |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Part of | Piazza del Duomo, Pisa |
| Criteria | Cultural: i, ii, iv, vi |
| Inscription | 1987 (11th Session) |
The Leaning Tower of Pisa (which in Italian is Torre Pendente di Pisa) is a famous bell tower in Pisa, Italy. It's also known simply as the Tower of Pisa. This tower is special because it leans a lot, almost four degrees! This tilt happened because its base was built on soft, unstable ground.
The tower is part of a group of three important buildings in Pisa's Cathedral Square, also called Piazza del Duomo. The other buildings are the main cathedral and the Pisa Baptistry.
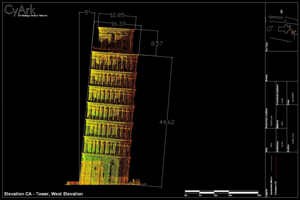
The tower stands about 55.86 meters (183 feet) tall on its lower side. On its higher side, it reaches about 56.67 meters (185 feet). The walls at the bottom are about 2.44 meters (8 feet) thick. Experts believe the tower weighs around 14,500 metric tons. Inside, there are about 296 steps to climb to the top.
The tower started to lean during its construction in the 1100s. The soft ground couldn't hold its weight properly. The lean got worse as more parts of the tower were built over the next centuries. By 1990, the tower was leaning by 5.5 degrees. But between 1993 and 2001, engineers worked to fix it. They made the tower more stable and reduced its lean to 3.97 degrees.
Contents
Who Designed the Leaning Tower?
It's a bit of a mystery who designed the Leaning Tower of Pisa. For a long time, people thought it was designed by a man named Guglielmo or by Bonanno Pisano. Bonanno Pisano was a well-known artist from Pisa in the 1100s. He was famous for making things out of bronze, especially for the Pisa Duomo.
In 1820, a piece of bronze with Bonanno Pisano's name on it was found near the tower. However, this might have been from a bronze door on the cathedral that was destroyed later. Some studies in 2001 suggested that another architect, Diotisalvi, might have been the original designer. This is because the tower's style is similar to other buildings Diotisalvi designed in Pisa, like the bell tower of San Nicola and the Baptistery.
How Was the Tower Built?
Building the Leaning Tower of Pisa took a very long time, almost 200 years! It was built in three main stages.
Starting the Construction
On August 9, 1173, the foundations of the tower were laid. Work on the first floor began on August 14 of the same year. This first floor has columns with classic Corinthian capitals. A writer named Giorgio Vasari later wrote that Guglielmo and the sculptor Bonanno started the tower's foundations in 1174.
Why the Tower Started to Lean
The tower began to sink after the second floor was built in 1178. This happened because the foundation was only three meters deep. It was built on weak, unstable soil, which was a big problem from the start.
Building stopped for nearly a century. This break was actually helpful! The Republic of Pisa was often fighting with other cities like Genoa, Lucca, and Florence. This long pause allowed the soil under the tower to settle. If construction had continued, the tower would likely have fallen over.
On December 27, 1233, work on the tower started again.
Continuing the Building Process
In 1272, construction continued under a master builder named Giovanni di Simone. To try and fix the lean, engineers built the upper floors with one side taller than the other. This is why the tower looks a bit curved.
Building stopped again in 1284. This was because the people of Pisa were defeated by Genoa in a big battle called the Battle of Meloria.
Finishing the Tower
The seventh floor was finished in 1319. The bell-chamber, where the bells are kept, was finally added in 1372. It was built by Tommaso di Andrea Pisano. He managed to blend the Gothic style of the bell-chamber with the older Romanesque style of the tower.
There are seven bells in the tower, one for each note of a musical scale. The biggest bell was put in place in 1655.

The Tower's History After It Was Built
The Leaning Tower has a lot of interesting stories from its long history.
Galileo's Famous Experiment
Between 1589 and 1592, a famous scientist named Galileo Galilei lived in Pisa. People say he dropped two different-sized cannonballs from the tower. He wanted to show that heavy and light objects fall at the same speed, if you ignore air resistance. This idea was part of his work on the law of free fall. The story comes from a book written by Galileo's student, Vincenzo Viviani, in 1654.
Saving the Tower in World War II
During World War II, the Allies thought German soldiers might be using the tower as a lookout spot. An American sergeant named Leon Weckstein was sent to check. He was so amazed by the beauty of the tower and the cathedral that he decided not to order an artillery attack. This saved the tower from being destroyed.
Efforts to Stop the Lean
Over the years, many people tried to make the tower stand straight or at least stop it from falling. Most of these attempts didn't work, and some even made the lean worse!
In 1964, the Italian government asked for help to save the tower. But they also wanted to keep some of the lean, because it was famous and brought many tourists to Pisa.
In 1990, the tower was closed to visitors. This happened after another tower, the Civic Tower of Pavia, suddenly collapsed in 1989. To help stabilize the Leaning Tower, the bells were removed to make it lighter. Cables were also wrapped around the third level and anchored far away.
Engineers decided to remove about 38 cubic meters (1,342 cubic feet) of soil from underneath the higher side of the tower. This helped to reduce the lean by about 45 centimeters (18 inches). This brought the tower back to how it was leaning in 1838.
After ten years of hard work to fix and stabilize it, the tower reopened to the public on December 15, 2001. Experts said it would be stable for at least another 300 years. In total, about 70 metric tons of soil were removed.
Since then, the tower has also been cleaned and restored to fix damage from weather and age. In May 2008, engineers announced that the tower had finally stopped moving. They believe it will be stable for at least 200 years now.
The Leaning Tower, along with the nearby cathedral, baptistery, and cemetery, is part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site called the Piazza del Duomo. This site was recognized in 1987.
-
Plaque in memory of Galileo Galilei's experiments
How the Tower Survived Earthquakes
The Leaning Tower of Pisa has survived at least four strong earthquakes since 1280. This is quite amazing, considering how much it leans!
In 2018, engineers studied how the tower managed to stay standing. They found that the tower's height and stiffness, combined with the soft soil of its foundation, actually helped it. The soft soil makes the tower vibrate in a way that doesn't match the vibrations of an earthquake. This means it doesn't shake too much during a tremor. So, the very same soft soil that caused the tower to lean also helped it survive!
Interesting Facts About the Tower
- The ground level of the square is about 2 meters (6 feet) above sea level.
- The tower has 8 stories.
- The outer base of the tower is about 15.48 meters (50 feet) wide.
- The inner base of the tower is about 7.36 meters (24 feet) wide.
- The tower leans at an angle of 3.97 degrees. This means the top of the tower is about 3.9 meters (12.8 feet) off from where it would be if it were perfectly straight.
- The tower weighs around 14,700 metric tons.
- The walls at the base are about 2.44 meters (8 feet) thick.
- There are 7 bells in the tower, each tuned to a musical note. They are:
- L'Assunta: The largest bell, weighing about 3,620 kg (7,981 lbs). It was made in 1654.
- Il Crocifisso: Weighs about 2,462 kg (5,428 lbs). Made in 1572.
- San Ranieri: Weighs about 1,448 kg (3,192 lbs). Made between 1719 and 1721.
- La Terza: The first small bell, weighing about 300 kg (661 lbs). Made in 1473.
- La Pasquereccia or La Giustizia: Weighs about 1,014 kg (2,235 lbs). Made in 1262. This bell was used to announce the executions of criminals.
- Il Vespruccio: The second small bell, weighing about 1,000 kg (2,205 lbs). Made in the 14th century.
- Dal Pozzo: Weighs about 652 kg (1,437 lbs). Made in 1606 and again in 2004.
- There are 296 steps to reach the top of the tower.
The tower's round shape and great height were very unusual for its time. The bell-chamber at the top looks a bit different in style from the rest of the tower. It was built with a slight correction to make up for the lean below. The tower is also not perfectly lined up with the cathedral and baptistery in the square.
Other Leaning Towers Around the World
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is famous, but it's not the only leaning tower!
- Two churches in Germany have bell towers that also lean: the Leaning Tower of Suurhusen (built in the 1400s) and a bell tower in Bad Frankenhausen (built in the 1300s).
- Guinness World Records measured the Pisa tower's lean at 3.97 degrees.
- In 2010, Guinness World Records named the Capital Gate building in Abu Dhabi, UAE, as the "World's Furthest Leaning Man-made Tower." It leans at an amazing 18 degrees! But this building was designed to lean on purpose.
- The Leaning Tower of Wanaka in Wānaka, New Zealand, also built on purpose, leans at 53 degrees to the ground.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Torre de Pisa para niños
In Spanish: Torre de Pisa para niños
- Leaning Tower of Niles, a replica of the Tower of Pisa
- Leaning Tower of Zaragoza, was a famous European leaning tower