Lena (river) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lena |
|
|---|---|

The Lena Pillars along the river near Yakutsk
|
|
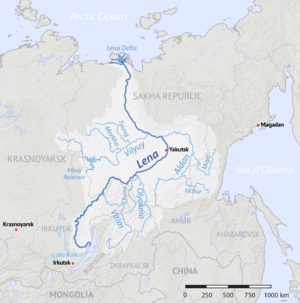
Lena watershed
|
|
| Country | Russia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Baikal Mountains, Irkutsk Oblast 1,640 m (5,380 ft) 53°58′3″N 107°52′56″E / 53.96750°N 107.88222°E (approximately) |
| River mouth | Lena Delta Arctic Ocean, Laptev Sea 72°24′31″N 126°41′05″E / 72.4087°N 126.6847°E |
| Length | 4,294 km (2,668 mi) |
| Width |
|
| Depth |
|
| Discharge (location 2) |
Tabaga, Yakutsk (Basin size: 987,000 km2 (381,000 sq mi) (Period of data: 1967-2017) 7,453.2 m3/s (263,210 cu ft/s)(max. 51,600 m3/s (1,820,000 cu ft/s)) |
| Discharge (location 3) |
|
| Discharge (location 4) |
|
| Discharge (location 5) |
|
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 2,460,742 km2 (950,098 sq mi) to 2,490,000 km2 (960,000 sq mi) |
| Tributaries |
|
The Lena River is a huge river in the Russian Far East. It's one of the three main rivers in Siberia that flow into the Arctic Ocean. The other two are the Ob and the Yenisey rivers.
The Lena River is super long! It's the eleventh-longest river on Earth. It's also the longest river that stays completely inside Russia. The Lena stretches for about 4,294 kilometres (2,668 mi). The area of land that drains into it, called its drainage basin, is about 2,490,000 square kilometres (960,000 sq mi).
Most of the land around the Lena River has permafrost. This means the ground is frozen all year round. About 77% of the river's basin has this continuous frozen ground.
Contents
Journey of the Lena River
The Lena River starts high up in the Baikal Mountains. This is south of the Central Siberian Plateau. Its source is about 1,640 meters (5,381 ft) high. It begins just 7 kilometres (4 mi) west of Lake Baikal.
The river first flows northeast across the Lena-Angara Plateau. Along the way, it meets other rivers like the Kirenga, Vitim, and Olyokma.
After passing Yakutsk, the Lena enters a flat area called the Central Yakutian Lowland. It flows north and is joined by the Aldan river from the right. It also meets the Vilyuy river, which is its most important tributary from the left.
Then, the Lena River turns west and then north. It flows between two mountain ranges: the Kharaulakh Range to the east and the Chekanovsky Ridge to the west. Finally, it spreads out into a huge Lena Delta and flows into the Laptev Sea. This sea is part of the Arctic Ocean. The delta is southwest of the New Siberian Islands.
The Lena Delta is enormous, covering about 30,000 square kilometres (12,000 sq mi). It has seven main channels. The Bykovsky channel is the most important one and is the farthest east.
Lena River Basin
The total area that drains into the Lena River is about 2,490,000 square kilometres (960,000 sq mi). Every year, the river carries about 489 cubic kilometers of water.
People have found gold in the sands of the Vitim and Olyokma rivers, which are part of the Lena basin. Also, mammoth tusks have been dug up from the delta area. There are many lakes in the flat areas near the river. The largest lakes in the Lena basin are Nedzheli and Ulakhan-Kyuel.
Rivers Joining the Lena
Many rivers flow into the Lena. These are called its tributaries.
- The Kirenga river flows north between the upper Lena and Lake Baikal.
- The Vitim river drains the area northeast of Lake Baikal.
- The Olyokma river flows north.
- The Amga river makes a long curve and flows into the Aldan.
- The Aldan river also flows somewhat parallel to the Lena. It then turns east and joins the Lena north of Yakutsk.
- The Maya river, which is a tributary of the Aldan, drains an area that almost reaches the Sea of Okhotsk.
- The T-shaped Chona-Vilyuy river system drains most of the land to the west of the Lena.
Here are some of the main rivers that join the Lena, listed from where the Lena starts to where it ends:
- Tutura (right side)
- Ilga (left side)
- Kuta (left side)
- Tayura (right side)
- Kirenga (right side)
- Pilyuda (left side)
- Chechuy (right side)
- Ichera (left side)
- Chaya (right side)
- Chuya (right side)
- Vitim (right side)
- Peleduy (left side)
- Nyuya (left side)
- Derba (left side)
- Ura (left side)
- Bolshoy Patom (right side)
- Cherendey (left side)
- Biryuk (left side)
- Olyokma (right side)
- Chara
- Markha (left side)
- Markhachan (left side)
- Tuolba (right side)
- Sinyaya (left side)
- Buotama (right side)
- Menda (right side)
- Myla (right side)
- Tamma (right side)
- Lyutenge (right side)
- Suola (right side)
- Aldan (right side)
- Batamay (right side)
- Belyanka (right side)
- Munni
- Lyapiske (right side)
- Tympylykan (left side)
- Dyanyshka (right side)
- Tyugyuene (left side)
- Sitte (left side)
- Khanchaly (left side)
- Kenkeme (left side)
- Lungkha (left side)
- Namana (left side)
- Vilyuy (left side)
- Chona
- Linde (left side)
- Undyulyung (right side)
- Nuora (left side)
- Begidyan (right side)
- Khoruongka (left side)
- Sobolokh-Mayan (right side)
- Kyuelenke (left side)
- Muna (left side)
- Menkere (right side)
- Motorchuna (left side)
- Molodo (left side)
- Syungyude
- Natara (right side)
- Uel-Siktyakh (right side)
- Kuranakh-Siktyakh (right side)
- Byosyuke (right side)
- Tikyan (right side)
- Eyekit (left side)
- Bulkur (left side)
History of the Lena River
The name "Lena" probably comes from the Even-Evenk word Elyu-Ene. This means "the Large River."
Early Explorations
Stories say that between 1620 and 1623, a group of Russian fur hunters found the Lena River. They were led by Demid Pyanda. Pyanda explored about 2,400 kilometres (1,500 mi) of the river. He traveled from its start down to central Yakutia.
In 1628, Vasily Bugor and ten men reached the Lena. They collected a tribute, called 'yasak', from the local people. In 1632, they founded a settlement called Kirinsk. A year later, in 1631, another group led by Pyotr Beketov built a fort at Yakutsk. This fort was founded in 1632. From Yakutsk, more explorers traveled south and east. The Lena delta was reached in 1633.
Later Expeditions
In September 1881, two groups of survivors from the Jeannette expedition reached the Lena Delta. One group, led by George W. Melville, was saved by local Tungus hunters. The other group, led by Captain George W. De Long, faced a harder time. Only two men survived, while the others died from starvation.
In 1885, Baron Eduard Von Toll and Alexander von Bunge led an expedition. They explored the Lena delta and the New Siberian Islands. They did this for the Russian Imperial Academy of Sciences. In 1886, they also explored the New Siberian Islands and the Yana River. Over a year, their expedition traveled about 25,000 kilometres (16,000 mi). They surveyed the land as they went.
Important Events
The Lena massacre happened in 1912. This was when striking gold miners and local citizens were shot. They were protesting bad working conditions at a mine near Bodaybo. This event was reported in the Russian parliament, called the Duma. Many believe it helped to start revolutionary feelings in Russia.
Interestingly, Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov might have chosen his famous name, Lenin, from the Lena River. He was exiled to the Central Siberian Plateau at one point.
Lena River Delta
At the end of the Lena River, there is a very large delta. It stretches about 100 kilometres (62 mi) into the Laptev Sea. It is also about 400 km (250 mi) wide.
The delta is frozen tundra for about seven months each year. But in May, the area changes into a green, wet land for a few months. Part of this area is protected as the Lena Delta Wildlife Reserve.
The Lena delta is made up of many flat islands. Some of the important ones are Chychas Aryta, Petrushka, Sagastyr, and Ullakhan Ary. One island, Ostrov Amerika-Kuba-Aryta, was even named after the island of Cuba during Soviet times. It is on the northern edge of the delta.
More to Explore
 In Spanish: Río Lena para niños
In Spanish: Río Lena para niños
- Lena Cheeks
- Lena Pillars
- Lena Plateau
- List of rivers of Russia
- List of longest undammed rivers
- Tukulan
- William Barr, who wrote about the first Soviet convoy to the Lena River.
Images for kids