Machine Age facts for kids

The Machine Age was a special time in history, mostly from the early to mid-1900s (around 1880 to 1945). It was a period when machines became super important in everyday life and work. This era was at its busiest between World War I and World War II.
The Machine Age started during the end of the Second Industrial Revolution (which finished around 1914). It then continued until 1945, when World War II ended. After 1945, the Atomic Age began, bringing new inventions like the atomic bomb, early computers, and the transistor. Today, we live in the Digital Revolution, sometimes called the Second Machine Age, where machines help us with thinking tasks, not just physical ones.
Contents
A Look at the Timeline
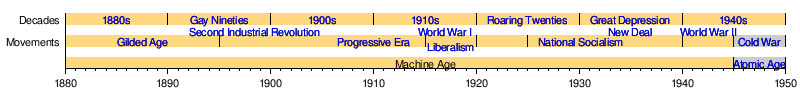
Amazing New Inventions


During the Machine Age, many incredible things were invented or improved. Here are some of them:
- New Engines: Older steam engines were replaced by gas turbines, internal combustion engines (like in cars), and electric motors.
- Widespread Electricity: Huge power plants were built to make electricity. This electricity was then sent to homes and factories everywhere.
- Mass Production: Factories started making lots of goods very quickly. They used moving assembly lines, especially for making automobiles.
- Giant Machines: New, very large machines were created. These machines could produce and shape metal, like steel for buildings or car parts.
- Powerful Construction Equipment: Strong earthmoving equipment made it easier to build roads and dig foundations.
- Tall Buildings: Skyscrapers, which are very tall buildings with steel frames, became common in cities.
- Communication and Entertainment: Radio and phonograph (record player) technology changed how people got news and listened to music.
- Faster Printing: High-speed printing presses made it cheap to print newspapers and magazines for everyone.
- Home Appliances: Affordable home appliances like vacuum cleaners and washing machines became popular. They used small electric motors.
- Faster Travel: People could travel long distances quickly and comfortably. This was thanks to better railways, cars, and aircraft.
- Modern War Machines: New war machines were developed. These included tanks, aircraft, submarines, and powerful battleships.
- Sleek Designs: Cars and trains started to have smooth, "streamlined" designs. These designs were inspired by how airplanes looked.
How Machines Changed Society
The Machine Age had a big impact on how people lived and worked:
- Advertising and Shopping: Mass advertising became a big deal. People were encouraged to buy more things, leading to consumerism.
- National Brands: Goods were sold all over the country. This meant that local handmade items became less common.
- Shared Culture: People across the country started watching the same movies and listening to the same radio shows. This helped create a more shared culture.
- Government Messages: Governments used mass production to spread propaganda through print, audio, and films.
- New Jobs: Many skilled jobs were replaced by simpler tasks that didn't need as much training.
- Big Companies: Large companies grew powerful. They could make things cheaper because they bought materials and equipment in huge amounts.
- Worker Rights: Sometimes, companies treated workers unfairly. This led to the creation of strong trade unions to protect workers' rights.
- More Democracy: Countries moved towards democracy where more people could vote. Before this, only certain groups (like men or rich people) could vote.
- Women's Rights: The first wave of feminism gained strength. Women fought for more rights, including the right to vote.
- Economic Planning: Governments started to plan the economy more. This included big public works projects and sometimes even rationing during wartime.
Impact on Our Planet
The Machine Age also changed how people treated the environment:
- Using Natural Resources: People used a lot of natural resources like wood, minerals, and oil. They often didn't think much about how this would affect nature.
- New Chemicals: Factories made new things like artificial colors and flavors. Sometimes, harmful chemicals were released without knowing if they were safe.
- Oil's Importance: Petroleum (oil) became a very important resource. Countries needed it for their machines and industries.
International Relationships
The need for resources like oil and metals led to problems between countries:
- Resource Conflicts: Nations often argued or fought over who could get these important resources. They wanted to make sure they had enough for themselves.
- World Wars: These conflicts over resources were one of the reasons for the two huge world wars.
- End of Empires: This period also saw the end of many old empires. Countries that had been ruled by others started to become independent.
Art and Design of the Machine Age
The Machine Age inspired many artists and designers:
- Movies: Films like Charlie Chaplin's Modern Times and Fritz Lang's Metropolis showed how machines affected people's lives.
- Streamline Moderne: This was a popular design style for appliances and buildings. It featured smooth, curved shapes, like a fast train or airplane.
- Bauhaus Style: The Bauhaus school of design focused on simple, useful, and modern designs.
- Modern Art: New art movements appeared, including:
See also
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |



