Massawa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Massawa
Məṣṣəwaʿ (ምጽዋዕ)
Mitsiwa
|
|
|---|---|
|
City
|
|
| Motto(s):
Tigrinya: ሉል ቀይሕ ባሕሪ Pearl of the Red Sea
|
|
| Country | |
| Region | Semienawi Keyih Bahri Region |
| District | Massawa |
| Area | |
| • Total | 477 km2 (184 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 6 m (20 ft) |
| Population
(2012)
|
|
| • Total | 53,090 |
| • Density | 111.30/km2 (288.3/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
| Area code(s) | +291 4 |
| Climate | BWh |
Massawa (also called Mitsiwa) is a very old port city in Eritrea. It sits right on the Red Sea, near the Dahlak Archipelago. For many centuries, Massawa has been a super important port. Different groups have ruled it over time, like the Kingdom of Aksum, the Ethiopian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Italy.
Massawa was once the capital of the Italian Colony of Eritrea. This lasted until 1897, when the government moved to Asmara. Massawa is known for being one of the hottest coastal places in the world. Its average temperature is almost 30°C (86°F)!
Contents
History of Massawa
Massawa started as a small village by the sea. It was close to the powerful Kingdom of Aksum. Another port called Adulis, about 50 kilometers (31 miles) south, was more famous back then. Arab geographers knew about Massawa very early on. They called it Badi or Nase.
The city is home to what might be the oldest mosque in Africa. It's called the Mosque of the Companions. People say it was built by friends of the Prophet Muhammad who escaped unfair treatment.
After the Aksum kingdom fell in the 700s, the area around Massawa was taken over by the Umayyad Caliphate. Later, the Beja people ruled Massawa from 740 until the 1300s. During this time, the Sheikh Hanafi Mosque, one of Eritrea's oldest mosques, was built on Massawa Island.
In the early 1400s, Massawa came under the control of the Ethiopian Empire. Emperor Yeshaq I mentioned Massawa in his war songs. Later, Emperor Zara Yaqob made Massawa part of his Christian province of Mereb Melash. During this period, merchants from Armenia and Venice often visited the port.
Portuguese Influence
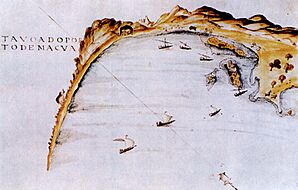
In the 1500s, Portugal wanted to control trade in the Red Sea. They managed to gain a foothold in Massawa and Arkiko in 1513. This port helped them connect with their ally, Ethiopia, to fight against the Ottomans. The Portuguese built wells and cisterns for their navy. A drawing of Massawa's port from 1541 by D. João de Castro still exists.
Ottoman Rule
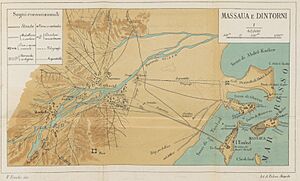
Massawa became very important when the Ottoman Empire captured it in 1557. The Ottomans tried to make it the capital of their Habesh province. They also tried to conquer more of Eritrea but faced strong resistance. The Ottomans then put a local leader, called a "Naib," in charge of Massawa. They built many parts of the old town on Massawa Island, making it a major port. These old buildings are still standing today, even after earthquakes and wars.
In 1855, Emperor Tewodros II of Ethiopia wanted to take Massawa. He believed the Turks were using it to kidnap Christian children and sell them as slaves. The British didn't support his plan because they were allies with the Ottomans.
In 1865, Massawa came under the rule of the Khedivate of Egypt. At first, the Egyptians found Massawa in poor condition. Many buildings were falling apart, and there were health problems like cholera. However, the Egyptian governor, Werner Munzinger, worked hard to improve the city. They built new government offices, a customs house, a school, and a hospital.
After a war between Egypt and Ethiopia, Emperor Yohannes IV demanded that Egypt give him Massawa. The Egyptians refused. Yohannes sent his army, but they eventually returned to the highlands, and Egypt kept control of the coast.
Italian Colonization
The British allowed Italy to take Massawa in February 1885. From 1885 to 1897, Massawa was the capital of the Italian colony. Then, the capital moved to Asmara. An attack by Ethiopian forces near Massawa led to the First Italo-Ethiopian War. Italy's big defeat at Adwa stopped their expansion into Ethiopia for a decade.
Massawa faced many earthquakes. A big one in 1921 destroyed most of the city. It took until 1928 to fully rebuild the port. Despite this, Massawa became the largest and safest port on the east coast of Africa. The Italians also built the Eritrean Railway, connecting Massawa to Asmara and then to Bishia. They also built the Asmara-Massawa Cableway, which was the longest ropeway conveyor in the world at 75 kilometers (47 miles) long.
By 1928, Massawa had 15,000 people, including 2,500 Italians. The city was improved with new buildings and areas for businesses. However, during this time, a system of segregation was put in place. Native people were separated from areas reserved for white people.
During the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, Massawa was a main base for Italy's invasion of Ethiopia. Many Italian soldiers came to the town. During World War II, Massawa was a homeport for the Italian Royal Navy. When the city was captured, many Italian and German ships were sunk to block the harbor.
After the war, in 1945, the British occupied Massawa. They damaged or removed many of the port's facilities.
Ethiopian Rule and Independence
From 1952 to 1990, Eritrea was part of a federation with Ethiopia. Massawa became the headquarters of the Ethiopian Navy. However, Ethiopia later ended the federation and took full control of Eritrea. This led to the Eritrean War of Independence (1961–1991). Massawa was a key battleground.
In February 1990, the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF) captured Massawa in a surprise attack. This battle, called Operation Fenkil, cut off supplies to the Ethiopian army in Asmara. In response, Ethiopia's leader ordered Massawa to be bombed from the air, causing a lot of damage.
When Eritrea gained its independence in 1991, Ethiopia became a landlocked country again. Its navy was disbanded. During the Eritrean-Ethiopian War, the port of Massawa was not very active. This was because the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia was closed. In 2001, a large ship carrying relief food from the United States was the first major shipment to arrive at the port since the war began.
Transportation
Massawa has a naval base and large docks for traditional boats called dhows. It also has a station on the railway line that goes to Asmara. Ferries travel from Massawa to the Dahlak Islands and Sheikh Saeed Island.
The city also has an airport, the Massawa International Airport, for air travel.
Main Sights
Some important buildings in Massawa include the shrine of Sahaba and the 15th-century Sheikh Hanafi Mosque. Many houses are built from coral. You can still see old Ottoman buildings. The local bazaar is also a popular spot.
Newer buildings include the Imperial Palace, built in the 1870s, St. Mary's Cathedral, and the 1920s Banca d'Italia. To remember the Eritrean War of Independence, there is a memorial with three tanks in the middle of Massawa.
Climate
Massawa has a hot desert climate. It gets very little rain each year, only about 185 millimeters (7.3 inches). The temperatures are always very high, day and night. The average yearly temperature is almost 30°C (86°F), making it one of the hottest places in the world. Even though it's a desert city, Massawa has very high humidity in the summer. This mix of heat and humidity makes it feel even hotter. The sky is usually clear and sunny all year.
| Climate data for Massawa (1961 to 1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.1 (84.4) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.8 (89.2) |
33.9 (93.0) |
36.8 (98.2) |
40.2 (104.4) |
40.8 (105.4) |
40.3 (104.5) |
38.7 (101.7) |
35.6 (96.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
30.5 (86.9) |
35.0 (95.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
27.9 (82.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
33.9 (93.0) |
32.1 (89.8) |
29.5 (85.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.0 (84.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 19.1 (66.4) |
19.1 (66.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
25.7 (78.3) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.5 (77.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 34.7 (1.37) |
22.2 (0.87) |
10.2 (0.40) |
3.9 (0.15) |
7.6 (0.30) |
0.4 (0.02) |
7.8 (0.31) |
7.8 (0.31) |
2.7 (0.11) |
22.4 (0.88) |
24.1 (0.95) |
39.5 (1.56) |
183.3 (7.23) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 3.1 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 15.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76.3 | 75.3 | 73.3 | 70.5 | 65.0 | 53.8 | 53.0 | 55.6 | 60.8 | 66.6 | 69.1 | 74.5 | 66.1 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
See also
- Massawa International Airport