Mount Cayley volcanic field facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mount Cayley volcanic field |
|
|
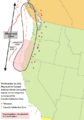
The Mount Cayley volcanic field
|
|
| Country | Canada |
|---|---|
| Province | British Columbia |
| District | New Westminster Land District |
| Part of | Garibaldi Volcanic Belt |
| Length | 31 km (19 mi) |
| Width | 6 km (4 mi) |
| Period | Pliocene-to-Holocene |
The Mount Cayley volcanic field is a special area in British Columbia, Canada, where many volcanoes are found. It stretches for about 31 kilometres (19 mi) along the south coast. This volcanic area is named after Mount Cayley, which is the largest of the active volcanoes here.
Many of these volcanoes formed when hot, melted rock, called magma, pushed up from deep inside the Earth. This magma then erupted onto the surface as lava. Some of these eruptions happened when thick layers of glacial ice from the last ice age covered the land. This created unique volcanoes called tuya, which are steep with flat tops, and also lava domes. The first eruptions in this field happened a very long time ago, between 1.6 and 5.3 million years ago. Scientists have found evidence of at least 23 eruptions in total.
The Mount Cayley volcanic field is divided into three main parts: south, central, and north. The southern part has the most volcanoes, with 11 known ones. The central area has at least five volcanoes, and the northern part has two.
Images for kids
-
This map shows the Cascadia subduction zone and the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, where Mount Cayley is, is at the very top of the red triangles.
-
The southwestern side of Mount Cayley. Its very steep face has caused several landslides in the past.
-
Mount Fee stands tall above the other mountains nearby. You can see it here from the south.
-
Little Ring Mountain is the northernmost volcano in this area. Like Ring Mountain to its south, it has a flat top and steep sides. This shape formed when hot magma pushed up and melted a hole through the thick Cordilleran Ice Sheet during the last ice age.
-
Mount Fee rising over Ember Ridge North, which has some small glaciers on it.
-
The northern side of Ring Mountain, which is a tuya volcano. Its flat top and steep sides were created when magma melted a vertical pipe in the Cordilleran Ice Sheet during the last ice age.
-
The pointy tops of the Vulcan's Thumb. Its rough shape is from being worn down by weather over a long time.
-
Mount Cayley seen from its southeastern side.
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |