Mount Holmes (Utah) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mount Holmes |
|
|---|---|

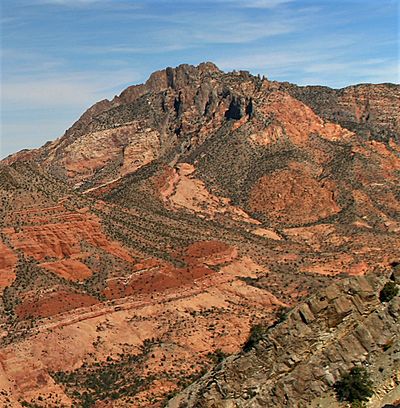
North aspect, from Highway 276
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 7,998 ft (2,438 m) |
| Prominence | 2,278 ft (694 m) |
| Isolation | 4.09 mi (6.58 km) |
| Parent peak | Mount Ellsworth (8,235 ft) |
| Naming | |
| Etymology | William Henry Holmes |
| Geography | |
| Location | Garfield County, Utah, U.S. |
| Parent range | Henry Mountains |
| Topo map | USGS Mount Holmes |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Oligocene |
| Mountain type | Laccolith |
| Type of rock | Igneous |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | class 2+ scrambling |
Mount Holmes is a tall mountain in Garfield County, Utah, in the United States. It stands 7,998 feet (2,438 meters) high. Mount Holmes is part of the Henry Mountains range.
This area is very dry and rugged. It is located west of Glen Canyon National Recreation Area. The land is managed by the Bureau of Land Management. Water from Mount Holmes flows into streams that lead to the nearby Colorado River. This part of the river forms Lake Powell, which is about six miles east of the mountain.
How Mount Holmes Got Its Name
A geologist named Grove Karl Gilbert explored this area in 1875 and 1876. He wrote a book about his discoveries in 1879 called The Geology of the Henry Mountains.
Gilbert was the first to use the word "laccolith" (pronounced LACK-oh-lith). This word describes a type of rock formation. It's like a mushroom-shaped blob of igneous rock that pushes up the layers of rock above it. He saw these formations in the Henry Mountains.
Mount Holmes was named around 1878 by Grove Karl Gilbert. He later became the chief geologist for the United States Geological Survey in 1889. The mountain was named after William Henry Holmes (1846–1933). William Henry Holmes was an artist and explorer. He drew a famous picture of the Grand Canyon. This drawing appeared in a report by John Wesley Powell in 1879. There is also another Mount Holmes in Yellowstone National Park named after the same person.
Weather and Climate
The best times to visit Mount Holmes are during spring and fall. The area has a Cold semi-arid climate. This means the coldest month has an average temperature below 32 °F (0 °C). Also, at least half of the yearly rain falls during spring and summer.
This desert climate gets less than 10 inches (250 mm) of rain each year. Snowfall in winter is usually light.