Mount Veniaminof facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mount Veniaminof |
|
|---|---|

Steam rising from the intracaldera cinder cone at Veniaminof volcano in the waning stages of the 1983 to 1984 eruption.
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 8,225 ft (2,507 m) |
| Prominence | 8,199 ft (2,499 m) |
| Listing |
|
| Geography | |
| Parent range | Aleutian Range |
| Topo map | USGS Chignik A-5 |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano with a summit caldera |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Aleutian Arc |
| Last eruption | September 4, 2018-ongoing |
| Designated: | 1967 |
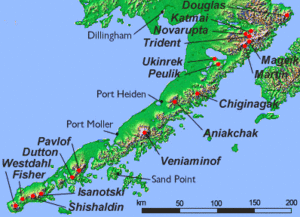
Mount Veniaminof (Russian: Вулкан Вениаминова) is an active stratovolcano located on the Alaska Peninsula. A stratovolcano is a tall, cone-shaped volcano built from many layers of hardened lava, ash, and rocks. Experts at the Alaska Volcano Observatory keep a close eye on it.
The mountain was named after Ioann (Ivan Popov) Veniaminov. He was a Russian Orthodox missionary priest who lived from 1797 to 1879. He wrote important books about the Aleut language and culture. Later in his life, he became a well-known bishop and is now a saint in the Orthodox Church.
Contents
Volcanic Activity
Mount Veniaminof has a long history of eruptions.
Past Eruptions
Around 1750 BCE, Mount Veniaminof had a truly massive eruption. Scientists measure the size of eruptions using something called the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI). This ancient eruption was a VEI 6, which is considered colossal. This huge event created a very large, bowl-shaped crater at the top of the volcano, known as a caldera.
In more recent times, the volcano has had many smaller eruptions. Since 1930, there have been over ten of these. All of these smaller eruptions have happened at a cinder cone inside the caldera. A cinder cone is a simple, cone-shaped hill built from volcanic ash and rock fragments.
Recent Activity
Mount Veniaminof began erupting again on September 3, 2018. Hot magma broke through the top of the volcano and flowed down its sides as a lava flow. At first, this was a gentle eruption, where lava flows out slowly.
However, by November 20, 2018, the eruption became much stronger. The volcano started sending ash up into the sky, reaching as high as 20,000 feet (about 6,100 meters). This ash can be dangerous for airplanes. Because of this, the Alaska Volcano Observatory issued a warning for aviation. They also issued an ashfall warning for the nearby town of Perryville.
As of November 22, 2018, experts rated Veniaminof as Aviation Color Code ORANGE and Volcano Alert Level WATCH. This means the volcano is showing increased activity and is being closely monitored.
Unique Features
Mount Veniaminof is one of the tallest volcanoes in Alaska. Because it is so high, much of it is covered by a large glacier. This glacier fills most of the caldera at the top of the volcano.
The combination of the glacier and the caldera walls creates a special situation. If there were a large eruption or a lot of melting, there could be a major flood. This type of flood, caused by water from a melting glacier, is sometimes called a glacier run.
National Natural Landmark
In 1967, Mount Veniaminof was recognized for its unique natural features. The National Park Service named it a National Natural Landmark. This means it is a special place that shows the best examples of natural history in the United States.
See also
 In Spanish: Monte Veniaminof para niños
In Spanish: Monte Veniaminof para niños