Aleutian Range facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aleutian Range |
|
|---|---|

Alaska Peninsula, Peulik Volcano and Ukinrek Maars
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Redoubt |
| Elevation | 10,197 ft (3,108 m) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 600 mi (970 km) |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Range coordinates | 57°4′N 156°59.3′W / 57.067°N 156.9883°W |
| Borders on | Tordrillo Mountains |
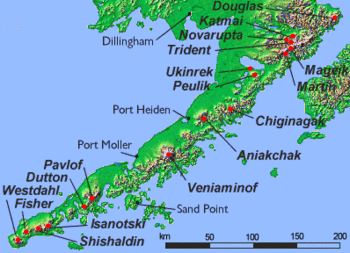
The Aleutian Range is a big mountain range located in southwest Alaska. It stretches from Chakachamna Lake (about 80 miles or 130 km southwest of Anchorage) all the way to Unimak Island, which is at the very tip of the Alaska Peninsula. This range includes all the mountains found on the Peninsula.
The Aleutian Range is special because it has many active volcanoes. These volcanoes are also part of a larger chain of volcanoes called the Aleutian Arc. The main part of the range on the mainland is about 600 miles (1000 km) long. The Aleutian Islands are like a long, partly underwater extension of this range, stretching even further west. However, the official "Aleutian Range" name only includes the peaks on the mainland and Unimak Island.
This mountain range is mostly wild and has almost no roads. Katmai National Park and Preserve, a large national park within the range, can only be reached by boat or plane.
Contents
Parts of the Aleutian Range
The main Aleutian Range can be divided into three groups of mountains. From southwest to northeast, they are:
- Mountains of the Alaska Peninsula and Unimak Island
- Chigmit Mountains
- Neacola Mountains
The Aleutian Islands continue the range to the west of Unimak Island. Just north of the Aleutian Range, you'll find the Tordrillo Mountains, which are part of the Alaska Range.
Famous Mountains in the Range
Here are some of the well-known mountains in the Aleutian Range:
- Mount Redoubt (3,108 m), in the Chigmit Mountains
- Iliamna Volcano (3,054 m), in the Chigmit Mountains
- Mount Neacola (2,873 m), in the Neacola Mountains
- Mount Shishaldin (2,857 m), on Unimak Island
- Mount Pavlof (2,715 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Mount Veniaminof (2,508 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Isanotski Peaks (2,446 m), on Unimak Island
- Mount Denison (2,318 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Mount Griggs (2,317+ m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Mount Douglas (2,153 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Mount Chiginagak (2,134 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Double Peak (2,078 m), in the Chigmit Mountains
- Mount Katmai (2,047 m), on the Alaska Peninsula
- Pogromni Volcano (2,002 m), on Unimak Island
- Mount Okmok (1,073 m), on the Fox Islands
Volcano Eruptions
Two volcanoes in the eastern Aleutian Islands erupted during the summer of 2008.
On July 12, 2008, Mount Okmok erupted. It continued to erupt for a whole month! This eruption sent a huge, fast-moving cloud of ash and gas up to 15,240 meters (about 50,000 feet) into the sky.
The other eruption happened at Mount Kasatochi on August 7 and 8. This volcano also shot a gas cloud up to about 15,000 meters (about 49,000 feet) high. These powerful eruptions released gases and tiny particles into the air. This caused some flight disruptions in the area for a short time after the eruptions.
Earthquakes in the Aleutian Range
A strong earthquake, measuring 7.9 on the Mw scale, happened in the Aleutian Islands in June 2014. This earthquake occurred deep underground, about 107 km (66 miles) below the surface.
The earthquake was caused by the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. In this area, the Pacific plate is slowly sliding underneath the North American plate. This boundary where plates meet and one slides under another is called a convergent boundary. The plates here move at about 59 mm (about 2.3 inches) per year.
See also
 In Spanish: Cordillera Aleutiana para niños
In Spanish: Cordillera Aleutiana para niños