Neutrino facts for kids
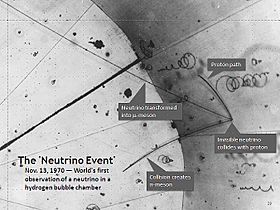
The first use of a hydrogen bubble chamber to detect neutrinos, on November 13, 1970. A neutrino hit a proton in a hydrogen atom. The collision occurred at the point where three tracks emanate on the right of the photograph.
|
|
| Composition | Elementary particle |
|---|---|
| Statistics | Fermion |
| Generation | First, second and third |
| Interactions | Weak interaction and gravitation |
| Symbol | Error no symbol defined, Error no symbol defined, Error no symbol defined |
| Antiparticle | Antineutrinos are possibly identical to the neutrino (see Majorana fermion). |
| Theorized | Error no symbol defined (Electron neutrino): Wolfgang Pauli (1930) Error no symbol defined (Muon neutrino): Late 1940s Error no symbol defined (Tau neutrino): Mid 1970s |
| Discovered | Error no symbol defined: Clyde Cowan, Frederick Reines (1956) Error no symbol defined: Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger (1962) Error no symbol defined: DONUT collaboration (2000) |
| Types | 3 – electron neutrino, muon neutrino and tau neutrino |
| Mass | Small, but non-zero. |
| Electric charge | 0 e |
| Spin | 1⁄2 |
| Weak hypercharge | −1 |
| B − L | −1 |
| X | −3 |
Neutrinos are tiny particles found all over the universe. Scientists, called physicists, study them. Neutrinos are very hard to find because they almost never interact with regular matter. For example, they can pass right through the entire Earth without hitting anything! These particles also travel incredibly fast, almost at the speed of light.
For a long time, scientists thought neutrinos had no mass at all. But a few years ago, they discovered that neutrinos do have a very small mass. They are much lighter than electrons. By studying neutrinos, we can learn important things about how the universe is built and how it has changed over time.
Contents
What Makes Neutrinos Special?
Neutrinos are very difficult to detect. They are very unlikely to collide with other particles as they move through space or through solid objects.
Unlike charged particles like electrons, neutrinos have no electric charge. The word "neutrino" even means "small neutral particle." This lack of charge means they are not affected by the electromagnetic force. This is why they can pass through so much without interacting. Special detectors built to find them might only see 10 to 15 neutrinos in a whole year!
Where Do Neutrinos Come From?
Neutrinos are made in many places. They are often created in particle accelerators, which are machines that speed up tiny particles. They also come from the Sun and other stars.
Neutrinos are also produced during nuclear reactions. One common way they are made is through a process called Beta decay. In this process, a neutron changes into a proton, an electron, and a neutrino.
Types of Neutrinos
There are three main types of neutrinos. Each type is named after a different kind of lepton, which is another group of tiny particles.
- The electron neutrino (written as ve)
- The muon neutrino (written as vµ)
- The tau neutrino (written as vτ)
Each type of neutrino also has an antiparticle, which is like its opposite twin. These are called antineutrinos. So, there is an electron antineutrino, a muon antineutrino, and a tau antineutrino.
Neutrino Oscillation
One amazing thing about neutrinos is that the three types can change into each other over time. This process is called neutrino oscillation. For example, an electron neutrino could turn into a tau neutrino and then change back again.
Scientists first thought of this idea because they noticed something strange. The number of electron neutrinos coming from the Sun was much lower than what their theories predicted. Neutrino oscillation helped explain this puzzle.
Most of the neutrinos passing through Earth come from the Sun. About 65 billion (6.5×1010) solar neutrinos pass through every square centimeter of your body each second!
Related pages
- Antares Telescope - uses neutrinos to make images
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Neutrino para niños
In Spanish: Neutrino para niños


