Octave Mirbeau facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Octave Mirbeau
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | 16 February 1848 Trévières, France |
| Died | 16 February 1917 (aged 69) Paris, France |
| Occupation | Novelist, playwright, journalist, pamphleteer |
| Genre | Novel, comedy, chronicles, art critic |
| Literary movement | Impressionism, expressionism, decadent, avant-garde |
| Notable works | The Torture Garden (1899) The Diary of a Chambermaid (1900) |
| Spouse |
Alice Regnault
(m. 1887) |
Octave Mirbeau (born February 16, 1848 – died February 16, 1917) was a famous French writer. He wrote many different things, including novels, plays, and articles. He was also an art critic and a journalist.
Mirbeau became very well-known in Europe. His stories often made people think deeply about society. His books have been translated into 30 different languages.
Contents
About Octave Mirbeau
Octave Mirbeau's Early Life and Ideas
Octave Mirbeau grew up in a village in Normandy, France. His father was a doctor. He went to a Jesuit school in Vannes, but he was asked to leave when he was fifteen.
After a difficult war in 1870, Mirbeau started working as a journalist. At first, he wrote for others. But soon, he began to write his own ideas. He wanted to share his thoughts about right and wrong, and about art.
Mirbeau believed strongly in freedom and fairness for everyone. He supported the idea that people should have more control over their own lives. He also stood up for Alfred Dreyfus, a soldier who was wrongly accused. Mirbeau thought it was important for thinkers to get involved in big public issues. He always tried to see things clearly and honestly.
As an art critic, he praised many famous artists. He admired Auguste Rodin, Claude Monet, Camille Pissarro, and Paul Cézanne. He was also one of the first to support Vincent van Gogh and Camille Claudel. His writings on art are collected in a book called Combats esthétiques.
He also wrote about other writers. He helped discover new talents like Maurice Maeterlinck. He also admired writers such as Remy de Gourmont and Alfred Jarry.
Octave Mirbeau's Novels
Stories from His Life
Mirbeau wrote many novels. Some of his early books were like his own story. For example, Le Calvaire (1886) was his first novel published under his own name.
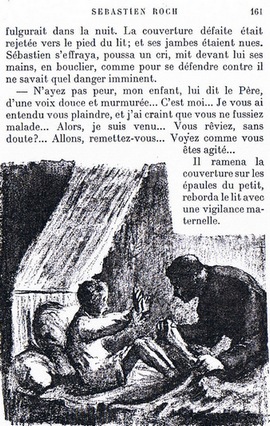
In 1888, he wrote Abbé Jules. This book explored the deep thoughts and feelings of its characters. In Sébastien Roch (1890), Mirbeau wrote about his own difficult time at the Jesuit school. Writing this book helped him deal with those memories.
Challenging Traditional Stories
Later, Mirbeau went through a tough time in his life and writing. During this period, he wrote Dans le ciel (In the Sky). This novel was about an artist's struggles, inspired by Vincent van Gogh.
After a big event called the Dreyfus Affair, Mirbeau felt more sad about the world. He then wrote two novels that caused a stir: Le Jardin des supplices (1899) and Le Journal d'une femme de chambre (1900). These books challenged what people thought was proper. He used new ways of writing, mixing different styles.
New Kinds of Novels
In his last two novels, La 628-E8 (1907) and Dingo (1913), Mirbeau moved even further from traditional storytelling. He added fantasy elements. In Dingo, his own dog became a main character! These stories showed a complete break from how novels were usually written.
Octave Mirbeau's Plays
Mirbeau also wrote for the theatre. His first play was Les Mauvais bergers (The Bad Shepherds, 1897). It was a serious play about working people.
He became famous around the world for his play Les affaires sont les affaires (Business is Business, 1903). This play was a classic comedy about manners and characters, much like the plays of Molière. It featured a character named Isidore Lechat, who was a master of business. He made money from everything and had influence everywhere.
In 1908, after a long fight, his play Le Foyer (Home) was performed. In this play, he talked about a difficult topic: how young people were sometimes used for money in homes that were supposed to be for charity.
He also wrote six short plays called Farces et moralités (1904). In these plays, Mirbeau questioned language itself. He made fun of politicians and even the language of love.
His Lasting Influence
Octave Mirbeau's works have continued to be published over the years. For a long time, he was mainly known for just a few of his books. People sometimes thought his ideas were too strong or "politically incorrect."
However, more recently, people have started to look at Mirbeau's work in a new way. They now appreciate the important role he played in the world of politics, literature, and art during his time.
Octave Mirbeau is buried in the Passy Cemetery in Paris.
Works
Novels
- Le Calvaire (1886)
- L'Abbé Jules (1888)
- Sébastien Roch (1890)
- Dans le ciel (1892–1893)
- Le Jardin des supplices (1899)
- Le Journal d'une femme de chambre (1900)
- Les Vingt et un Jours d'un neurasthénique (1901)
- Dingo (novel) (1913)
- Un gentilhomme (1919)
- Les Mémoires de mon ami (1920)
Plays
- Les Mauvais bergers (The Bad Shepherds) (1897)
- Les affaires sont les affaires (1903) (Business Is Business)
- Farces et moralités, six short plays (1904)
- Le Foyer (1908)
Short Stories
- Dans l'antichambre (Histoire d'une Minute) (1905)
- La Mort de Balzac (1889)
- Contes cruels, 2 volumes (1890 and 1900)
- Contes drôles (1895)
Art and Literary Writings
- Combats esthétiques, 2 volumes (1893)
- Combats littéraires (1906)
Travel Writings
- La 628-E8 (1907)
Political and Social Writings
- Voters strike (1888)
- L'Affaire Dreyfus (1891)
See also
 In Spanish: Octave Mirbeau para niños
In Spanish: Octave Mirbeau para niños