American sycamore facts for kids
Quick facts for kids American sycamore |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Mature tree | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Platanaceae |
| Genus: | Platanus |
| Species: |
P. occidentalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Platanus occidentalis |
|
 |
|
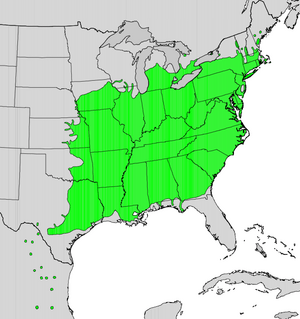
| Generalized natural range of Platanus occidentalis | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Platanus occidentalis, also known as the American sycamore, is a large tree found in North America. People also call it the American planetree, buttonwood, or water beech. It grows naturally in the eastern and central parts of the United States, the mountains of northeastern Mexico, and southern Ontario, Canada.
The word occidentalis means "western" in Latin. This name was given because the tree grows in the Western Hemisphere. At that time, the only other known tree in its group was P. orientalis, which means "eastern" and grows in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Contents
About the American Sycamore
An American sycamore tree is easy to spot because of its unique bark. The bark peels off in big, uneven pieces. This leaves the trunk looking patchy with gray, greenish-white, and brown colors.
All tree bark needs to stretch as the tree grows. Sycamore bark is not very stretchy. So, instead of stretching, it breaks off. This is why it looks so different from other trees.
How Big Can They Get?
Sycamores can grow very large. They usually reach about 30 to 40 meters (100 to 130 feet) tall. Their trunks can be 1.5 to 2 meters (5 to 7 feet) wide. The tallest sycamore ever measured was 53 meters (174 feet) high. Some trunks have been nearly 4 meters (13 feet) wide!
Long ago, even bigger sycamores were recorded. In 1744, a family in Virginia lived for most of a year inside a hollow sycamore tree. In 1770, George Washington wrote in his journal about a sycamore tree. Its trunk was 13.6 meters (44 feet 10 inches) around, about a meter (3 feet) from the ground.
Tree Shape and Parts
Sycamore trees often split into several large trunks near the ground. Their branches spread out at the top, making an open, uneven shape. The roots are thin and spread out. Very old trees often have hollow trunks.
A cool thing about sycamore leaves is how their buds grow. Most trees have tiny buds for next year's leaves in the leaf's armpit (where the leaf stem meets the branch). But the sycamore's leaf stem (called a petiole) swells up. This swelling completely covers and protects the new bud inside.
- Bark: The bark is dark reddish-brown and breaks into flat pieces. Higher up, it's smooth and light gray. It peels off easily, showing pale yellow, white, or greenish patches underneath.
- Wood: The wood is light brown with a red tint. It's heavy and not very strong, making it hard to split. It's often used for furniture, inside house finishes, and butcher's blocks.
- Winter Buds: These buds are large, sticky, green, and have three scales. They form in summer, hidden inside the base of the full-grown leaf stem. There is no bud at the very end of the branch.
- Leaves: Sycamore leaves grow one after another on the branch. They are large, about 10 to 23 centimeters (4 to 9 inches) long. They have three to five wide, shallow lobes. When they first appear, they are pale green and fuzzy. When fully grown, they are bright yellow-green on top and lighter underneath. In autumn, they turn brown and dry up before falling.
- Flowers: Sycamore flowers appear in May, at the same time as the leaves. They grow in dense, round clusters. Male and female flowers are on different stems on the same tree. Male flower clusters are dark red. Female flower clusters are light green with a red tint.
- Fruit: The fruit forms brown, round heads, about 2.5 centimeters (1 inch) across. They hang on thin stems that are 8 to 15 centimeters (3 to 6 inches) long. These fruit heads stay on the tree all winter. Each head is made of many tiny seeds called achenes. They ripen in October.
Where Sycamores Grow
American sycamores often grow near rivers and in wetland areas. Their natural home stretches from Iowa to Ontario and Maine in the north. It goes west to Nebraska and south to Texas and Florida.
Similar types of sycamore trees grow in Mexico and the southwestern United States. Sometimes, sycamores are grown for their wood. They have also started growing naturally in some places outside their original range, like parts of Argentina and Australia.
What Sycamores Are Used For
The American sycamore can handle city life well. It used to be planted a lot as a shade tree. However, a disease called anthracnose often makes it look bad. Because of this, the London plane tree, which is more resistant to the disease, is now often planted instead.
Sycamore wood is used a lot for butcher's blocks. It's also used for boxes and crates. Even though it has a coarse grain and can be hard to work with, it's also used to make furniture, house siding, and even musical instruments. Scientists have also looked into using sycamore as a crop to produce biomass (material for energy).
Problems and Diseases
The American sycamore is a favorite food for a bug called the sycamore leaf beetle.
Sycamores are also easily affected by a disease called plane anthracnose. This fungus came from the Oriental plane tree, which has learned to fight off the disease. The American sycamore usually doesn't die from anthracnose, but it often loses many of its leaves. This makes the tree look unhealthy.
The disease appears in early spring. It makes new leaves wilt and older leaves turn brown along their veins. Infected leaves usually shrivel up and fall off. So, by summer, the tree often grows new leaves. The fungus also creates sores (cankers) on twigs and branches. These cankers spread the disease and weaken the tree. Because cankers stop nutrients from flowing, the affected twigs and branches eventually die.
Because of the damage from this fungus, people often avoid planting American sycamores in their yards. Instead, they plant the London plane tree (a mix of American and Oriental sycamore), which is much stronger against the disease.
Sycamore History
The agreement that created the New York Stock Exchange is called the "Buttonwood Agreement." This is because it was signed under a buttonwood (sycamore) tree on Wall Street in New York City in 1792.
Sycamore trees were a big part of the forests in Greenland and Arctic America during the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods (very long ago). They once grew a lot in central Europe but are not found there anymore. The American sycamore was brought to Europe in the early 1600s.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Plátano occidental para niños
In Spanish: Plátano occidental para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |













