Plumbeous forest falcon facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Plumbeous forest falcon |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Falconiformes |
| Family: | Falconidae |
| Genus: | Micrastur |
| Species: |
M. plumbeus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Micrastur plumbeus Sclater, WL, 1918
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The plumbeous forest-falcon (Micrastur plumbeus) is a bird of prey that lives only in the Chocó region. This area is found in Colombia and Ecuador. This rare bird is not seen very often, which makes it hard to study.
For a long time, people thought it was part of the lined forest-falcon family. But now we know it is its own unique species. This bird is currently considered a vulnerable species. This means it is at risk because its home is being destroyed by deforestation.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
Adult plumbeous forest-falcons have a grey back and a grey head. Their legs and face are a very bright orange. Their chest has stripes and is lighter than their back. Their belly is more whitish near the tail.
This raptor has a black tail with a white tip. It also has a white band in the middle that goes all the way across. Their eyes are dark brown. These birds are about 30-34 cm (13 inches) long. Female falcons are bigger than males. Females weigh 180-213 grams, while males weigh 172-188 grams.
Younger birds look similar to adults. However, their chest is whiter. Their eyes are also a bit beige, which is lighter than adult eyes.
Forest-falcons usually have long tails and round wings. But the plumbeous forest-falcon has a shorter tail and longer wings.
How It's Related to Other Birds
For some time, scientists wondered if the plumbeous forest-falcon was a type of lined forest-falcon. They also thought it might be a subspecies because they look alike. But it turned out these birds are two different species. They live in completely separate areas.
M. plumbeus and M. ruficollis interestes live in the same environment. However, they do not breed with each other. They also do not bother each other. This means they live in the same place without mixing.
The plumbeous forest-falcon became a separate species about 3 million years ago. This happened after populations in South America split apart. A drier and cooler climate helped to separate them. This was linked to the formation of ice sheets in colder places.
Forest-falcons are part of a bird group called Herpetotherinae. Birds in this group are usually found in forests and wetlands.
Where It Lives
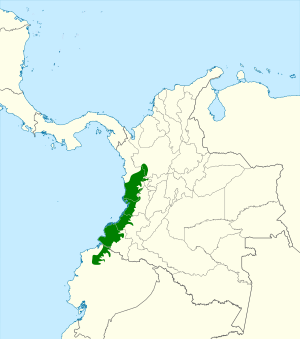
The plumbeous forest-falcon lives only in the southern part of the Chocó region. This region is in the southwest of Colombia and the northwest of Ecuador. This bird stays all year long in lowland forests and foothill forests. It is not a migratory bird.
Its home can be from sea level up to about 1500 meters high. One study found that a few pairs of these birds had a territory of about 35-40 hectares.
Conservation Status
This species is listed as vulnerable by the IUCN. This is because it is losing its home. Deforestation is destroying more and more land. This means the plumbeous forest-falcon's habitat is shrinking.
It is not a protected species. More studies are needed to help save it. Efforts should focus on the Chocó area. This is the only place where this bird lives.
Behavior
Vocalizations
This bird makes two main types of sounds. They make yapping kew notes every 1.5 to 2.5 seconds. They also sing a series of cah cah cah-cah-cah notes. Sometimes, a pair of birds will sing these together.
Forest falcons have three types of calls and songs. The most common one is the "territorial advising song." The plumbeous forest-falcon repeats a series of five notes to claim its area.
The "excited cackling call" and the "quacking song" are also heard from Micrastur species. However, these are heard less often than the first call. Two birds of the same species sometimes sing as a pair.
Diet
We don't know everything about what this forest-falcon eats. This is because it has not been studied much. But it probably eats whatever small animals it can find. This includes small vertebrates (animals with backbones) and large invertebrates (animals without backbones).
Scientists found land crabs, small birds, and lizards in some of these falcons. Lizards are thought to be their main food source. This family of birds also hunts forest birds and rodents.
They have two main ways to hunt for food. First, they stay on the ground. They run after their prey and catch it with their feet. They keep their tail high when they chase. The second way is to sit on a branch about 2 meters (6.5 feet) above the ground. They listen for sounds and look for movement in the leaf litter. Then, they jump on the prey they find.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Not much is known about the plumbeous forest-falcon's reproduction. But it likely builds its nests in holes in trees. Other birds in the Micrastur family have been studied more. For example, the collared forest-falcon and the barred forest-falcon both nest in trees.
See also
 In Spanish: Halcón montés plomizo para niños
In Spanish: Halcón montés plomizo para niños


