Pseudopaludicola boliviana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Pseudopaludicola boliviana |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Leptodactylidae |
| Genus: | Pseudopaludicola |
| Species: |
P. boliviana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudopaludicola boliviana Parker, 1927
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Pseudopaludicola mirandae Mercadal de Barrio and Barrio, 1994 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Pseudopaludicola boliviana is a small type of frog that lives in South America. It belongs to a group of frogs called Leptodactylidae, which are often found in Central and South America. This frog was first described in 1927 by a scientist named Parker.
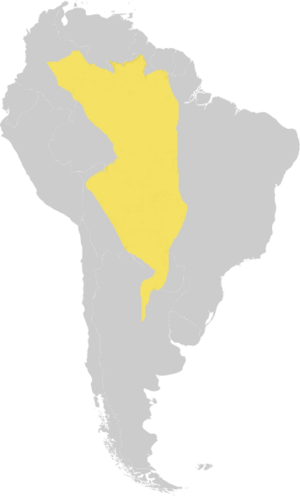
You can find this frog in many different countries. These include Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Suriname, and Venezuela. It likes to live in many kinds of places, from warm, wet forests to open grasslands.
Contents
Where the Bolivian Frog Lives
This frog is very good at living in many different environments. Its natural habitats are often warm and moist. It can be found in places like:
- Dry and wet tropical forests
- Moist savannas, which are like grassy plains
- Lowland grasslands that get wet or flooded during certain seasons
- Swamps and freshwater marshes, which are wet, muddy areas
- Even places that are sometimes wet and sometimes dry, like "intermittent" marshes
These frogs also live near people. They can be found in pastureland where animals graze. They also live near ponds, on land that is watered for farming, and in farm fields that flood at certain times of the year. This shows how adaptable this little frog is!
What the Bolivian Frog Looks Like
Like most frogs, the Pseudopaludicola boliviana has smooth, moist skin. It has strong back legs for jumping and webbed feet for swimming. Its colors usually help it blend in with its surroundings, like brown, green, or grey. This helps it hide from predators.
Frogs are amphibians, which means they can live both on land and in water. They breathe through their skin and lungs. The Pseudopaludicola boliviana is a small frog, but its exact size can vary.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Frogs have a fascinating life cycle. It usually starts with eggs laid in water. The Pseudopaludicola boliviana likely lays its eggs in the freshwater marshes, ponds, or flooded areas where it lives.
- The eggs hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles live in the water and breathe with gills, like fish.
- As they grow, tadpoles slowly change. They develop legs, their tails get shorter, and their gills turn into lungs.
- Eventually, they become young frogs, called froglets, and then adult frogs. They can then live on land and in water.
This process is called metamorphosis. It's a big change that helps frogs adapt to different parts of their habitat.
Conservation Status
The Pseudopaludicola boliviana is currently listed as a species of "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that its population is stable and it is not currently at risk of disappearing.
However, even common species can face threats. Changes to their habitats, like deforestation or pollution, can affect them. Protecting their natural homes, especially wetlands and forests, is important for these frogs and many other animals.
See also
 In Spanish: Pseudopaludicola boliviana para niños
In Spanish: Pseudopaludicola boliviana para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |


