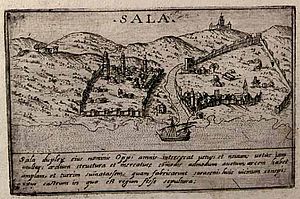
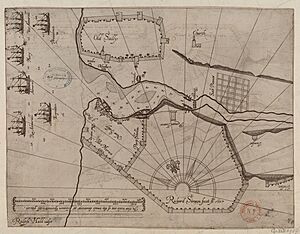
Republic of Salé facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Bou Regreg Republic
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1627–1668 | |||||||||
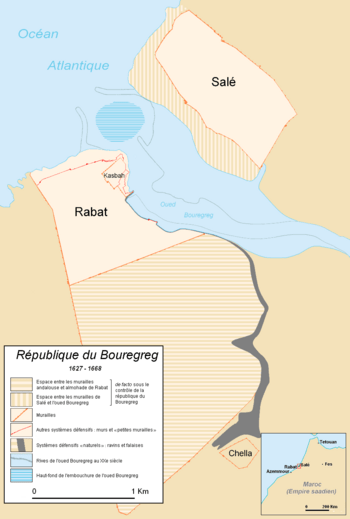
Rabat-Salé, where the republic was located.
|
|||||||||
| Status | Under the suzerainty of the Zawiya Dila'iya (1641–1661) | ||||||||
| Capital | Kasbah | ||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic Spanish Spanish-based lingua franca |
||||||||
| Government | Corsair republic | ||||||||
| Commander | |||||||||
|
• 1627–1641
|
Sidi al-Ayachi | ||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||
|
• 1651–1661
|
Abdullah ibn Mohammed al-Hajj | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
|
• Established
|
1627 | ||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1668 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1624–1668 | 0.91 km2 (0.35 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
|
• 1627–1640
|
13,000 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Today part of | Morocco | ||||||||
The Republic of Salé, also known as the Bou Regreg Republic, was a special kind of city-state in Morocco. It was located at the mouth of the Bou Regreg River, near the city of Salé. This republic was famous for its "corsairs," who were like privateers or pirates.
It was started in the 17th century by a group called the Moriscos. These were descendants of Muslims from Spain who had been forced to convert to Christianity. Many Moriscos were later expelled from Spain. The Republic of Salé became known for its trade and for its corsair activities during its short time in power.
Contents
History of the Republic
Who were the Moriscos?
The story of the Republic of Salé began in the early 1600s. About 3,000 wealthy Moriscos from a Spanish town called Hornachos arrived in the area. They had left Spain because they expected to be expelled by King Philip III.
After 1609, many more Moriscos, around 10,000, arrived from Spain. These new arrivals were not as wealthy. The local people of Salé and the Morisco newcomers had different cultures and languages. Because of this, the Moriscos settled on the opposite side of the Bou Regreg River, in the old city area of Rabat.
How did the Republic become powerful?
The corsairs who lived on the western bank of the river became very successful. They expanded their operations across the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. In 1614, a famous corsair named Brahim Vargas became the first governor. He made Rabat very rich through piracy and trade.
In 1624, a Dutch sailor named Jan Janszoon, also known as Murad Reis, became the "Grand Admiral" of the corsair republic. The local ruler, Sultan Zidan Abu Maali, even officially recognized him as governor.
When did Salé become independent?
In April 1627, the Hornacheros Moriscos, with help from Sidi al-Ayachi, removed the Sultan's governor. They then declared themselves an independent republic. Just a month later, an English diplomat named John Harrison even signed a treaty with Sidi al-Ayachi.
After Janszoon left Salé in 1627, the Moriscos stopped recognizing the Sultan's power. They refused to pay him taxes on their earnings. They set up a republic, similar to old Italian city-states like Venice. This republic was governed by a council called a Diwan.
The Diwan had 12 to 14 important members. Each year in May, they would elect a Governor and a "Captain General of the Fortalesa." In the early years, the Hornacheros controlled the Diwan. But other Moriscos, called Andalusians, grew in number and wanted more power. After some conflicts in 1630, they reached an agreement. A new Diwan was formed with 16 members, equally split between Andalusians and Hornacheros.
Why did the Republic decline?
In 1641, a religious group called the Zawiya Dila'iya gained control over much of Morocco. They also took control of Salé and its republic. By the early 1660s, the republic was fighting against the Zawiya.
Finally, in June 1668, Sultan Moulay al-Rashid of the Alaouite dynasty took over. This dynasty still rules Morocco today. He defeated the Dila'iya and ended the Republic of Salé's independence.
Piracy in Salé
Piracy in Salé started when the Moors from Spain arrived. They used their wealth to buy ships. They sailed the seas, mainly targeting Spanish ships. Before they rebelled against the Sultan, they would give 10% of their stolen goods and captives to the Saadians.
The Salé corsairs were very active. In 1625, they captured people from Plymouth in England. In 1626, they seized five ships off the coast of Wales. In 1627, they even reached Iceland. They raided the city of Reykjavik and the fishing village of Grindavík, an event known as the Turkish Abductions. They tried to raid the governor's home in Bessastaðir but could not land.
The corsairs also took control of Lundy island in the Bristol Channel. They held it for five years, using it as a base for their raids. They were very active in the waters between England and Ireland. In the Newfoundland area, the Salé fleet captured over 40 fishing boats in just two years. In 1624, about a dozen Salé ships appeared off the coasts of Acadia or Nova Scotia. In 1631, Murad Reis led a famous raid on Baltimore in Ireland.
European countries sent agents to Salé to deal with piracy and trade. From 1643, the Dutch had a consul in Salé. In 1648, the French government appointed a consul to live there.
Legacy of Salé
Even after the republic ended, piracy continued in Salé for some time, though it was declining. Later, Sultan Sidi Mohammed III (1757–1790) tried to bring piracy back. However, this only made the city decline faster.
The founding of Mogador in 1760, a new city better equipped for modern piracy, was a big blow to Salé's port. In 1818, Sultan Moulay Slimane officially ended the "holy war" and got rid of the Sherifian Navy. This finally ended Salé's role as a corsair city.
The descendants of Brahim Vargas are known as the Bargach family in Rabat. This family has remained important in the Moroccan capital for nearly 400 years.
See also
 In Spanish: República de Salé para niños
In Spanish: República de Salé para niños
- Thalassocracy
- Barbary Coast
- Barbary pirates
- Slave raid of Suðuroy
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |