Acadia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Acadia
Acadie
|
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Division of New France | |||||||||||||||||
| 1604–1713 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Flag
|
|||||||||||||||||
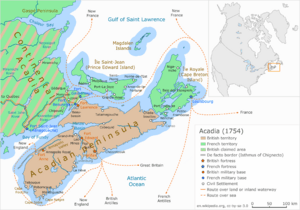 Acadia (1754) |
|||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Undetermined; Port-Royal (de facto) |
||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1604 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1713 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
Acadia (called Acadie in French) was a part of the French empire in North America. It covered areas that are now eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces in Canada, and parts of Maine in the United States. For a long time, its southern border reached the Kennebec River.
The French government described Acadia as the land along the Atlantic coast. This was roughly between the 40th and 46th parallels of latitude. Later, this territory was divided. It became British colonies. These colonies then turned into Canadian provinces and American states.
The first capital of Acadia was Port-Royal. It was founded in 1605. In 1613, British forces from Virginia attacked and burned the town. But it was rebuilt nearby. Port-Royal remained the capital of French Acadia. This lasted until the British took control in 1710. This event is known as the British conquest of Acadia.
Today, "Acadia" refers to places in North America that have a historical link to this French region. It especially means areas in The Maritimes that have French roots. These include parts of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, the Magdalen Islands, and Prince Edward Island. It also includes parts of Maine. The term can also refer to the Acadian people who moved to southern Louisiana. This area is sometimes called Acadiana. In a broader sense, Acadia means the presence of French culture in any of these places.
People who lived in Acadia were called Acadians. Their descendants are also called Acadians. After some moved to Louisiana, they became known as Cajuns.
Images for kids
-
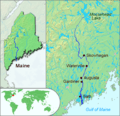
The French thought the Kennebec River was the border between Acadia and New England. This map shows Maine.
-
The Siege of Saint John in 1645. D'Aulnay defeated La Tour in Acadia.
-
The Duc d'Anville Expedition. This painting shows a battle between two ships.
-
Acadians in Annapolis Royal, painted by Samuel Scott in 1751. This is one of the earliest pictures of Acadians.
-
The St. John River Campaign. This painting shows the burning of Grimross (now Gagetown, New Brunswick) in 1758. It is the only picture from the time of the Expulsion of the Acadians.
-
Baron de Saint-Castin. He was involved in Castine's War.
-
Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville. He played a role in Queen Anne's War.
-
Daniel d'Auger de Subercase. He was the last governor of Acadia from 1706 to 1710.
-
Sébastien Rale. He was involved in Father Rale's War.
-
Chief Jean-Baptiste Cope. He was a leader during Father Le Loutre's War.
-
Jean-Louis Le Loutre. He was a key figure in Father Le Loutre's War.
See also
 In Spanish: Acadia para niños
In Spanish: Acadia para niños