Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Plevna Monument near the walls of Kitai-gorod |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
Montenegro |
|||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78 was a big conflict between the Ottoman Empire and a group of countries led by the Russian Empire. This group included Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro. The war was fought in two main areas: the Balkans (in Southeast Europe) and the Caucasus (a region between Europe and Asia).
This war started because of a few important reasons. One main reason was the rise of nationalism in the Balkans during the 19th century. People in these areas wanted to be free from the Ottoman Empire's rule. Russia also wanted to get back land it had lost in an earlier war, the Crimean War (1853–56). Russia also wanted to become a strong power again in the Black Sea region. Plus, Russia supported the idea of Balkan nations becoming independent.
The group led by Russia won the war. Because of this victory, Russia gained some new areas in the Caucasus, like Kars and Batum. Russia also took control of the Budjak region. Countries like Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro had already been mostly independent for some time. After the war, they officially declared their full independence from the Ottoman Empire.
After nearly 500 years of Ottoman rule (from 1396 to 1878), a new Bulgarian state was created. This new state, called the Principality of Bulgaria, covered the land between the Danube River and the Balkan Mountains. The city of Sofia became its capital. In 1878, a meeting called the Congress of Berlin also allowed Austria-Hungary to take over Bosnia and Herzegovina. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland gained control of Cyprus.
The first peace agreement, called the Treaty of San Stefano, was signed on March 3, 1878. Today, this date is celebrated as Liberation Day in Bulgaria.
Contents
Why the War Started: Main Reasons
The war had several key causes that led to the fighting. People in the Balkan region wanted to be free.
Balkan Nationalism and Independence
Many groups in the Balkans, like Bulgarians, Serbs, and Romanians, wanted their own independent countries. They had been under the rule of the Ottoman Empire for a very long time. They wanted to govern themselves and have their own cultures and traditions.
Russia's Goals and Interests
Russia had its own reasons for getting involved. It wanted to regain land lost in the Crimean War. This war had weakened Russia's power in the Black Sea. Russia also saw itself as a protector of the Orthodox Christian people in the Balkans. Many people in the Ottoman Empire were Orthodox Christians, like the Russians.
Who Fought in the War?
The war involved two main sides. On one side was the Ottoman Empire. On the other side was a group of countries led by Russia.
The Russian-led Coalition
The Russian Empire was the main power on this side. They were joined by several Balkan states. These included the Serbian, Romanian, and Montenegrin armies. There were also Bulgarian volunteers who fought alongside the Russians.
The Ottoman Empire's Forces
The Ottoman Empire fought to keep control of its lands. They had a large army and several skilled commanders.
What Happened During the War?
The war involved many battles and important events in different regions.
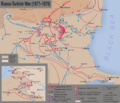
Fighting in the Balkans
Much of the fighting happened in the Balkan Peninsula. Key battles took place as Russian and allied forces moved through the region. The goal was to push back the Ottoman army and free the Balkan people.
Battles in the Caucasus
Another important area of conflict was the Caucasus region. Here, Russian forces fought against the Ottoman army to gain control of strategic areas and cities.
What Happened After the War?
The war ended with a victory for Russia and its allies. This led to big changes in the region.
New Independent States
As a direct result of the war, Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro became fully independent countries. They no longer had to answer to the Ottoman Empire. This was a huge step for these nations.
The Rebirth of Bulgaria
One of the most important outcomes was the creation of a new Bulgarian state. After centuries of Ottoman rule, Bulgaria became a self-governing principality. This was a dream come true for many Bulgarians.
Territorial Changes and Agreements
Russia gained some new territories in the Caucasus. The Congress of Berlin in 1878 finalized many of these changes. It also decided that Austria-Hungary would occupy Bosnia and Herzegovina. The United Kingdom took control of Cyprus. These changes reshaped the map of Europe.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Russia preparing to release the Balkan dogs of war, while Britain warns him to take care. Punch cartoon from June 17, 1876
-
Dragoons of Nizhny Novgorod pursuing the Turks near Kars, 1877.Painting by Aleksey Kivshenko.
-
The Ottoman surrender at Niğbolu (Nicopolis, modern Nikopol) in 1877 was important. It was the site of an important Ottoman victory in 1396. That victory marked the Ottoman Empire's expansion into the Balkans.
-
The Red Cross and the Red Crescent emblems
-
Bashi-Bazouks, returning with the spoils from the Romanian shore of the Danube.
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra ruso-turca (1877-1878) para niños
In Spanish: Guerra ruso-turca (1877-1878) para niños