Smartphone facts for kids
A smartphone is a special kind of mobile device that acts like a small computer you can carry in your pocket. It combines a regular mobile phone with many smart features. Smartphones usually have a touchscreen that lets you use many different apps and services. These include web browsing, email, and social media. You can also play music, watch videos, and stream content.
Smartphones come with built-in cameras, GPS navigation, and ways to communicate like voice calls, text messaging, and internet-based chat apps. What makes them different from older phones is their powerful parts and advanced mobile operating systems. They give you access to the internet, business tools, mobile payments, and lots of entertainment like music, videos, games, radio, and even TV.
Inside a smartphone, you'll find tiny electronic parts called integrated circuits. They also have many sensors, like ones that detect movement (accelerometers) or direction (magnetometers). These sensors help apps work better. Smartphones connect wirelessly using technologies like LTE, 5G NR, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. By the mid-2020s, some phones even started to include satellite messaging for emergencies in places without regular phone service.
Smartphones have taken the place of many older gadgets. These include personal digital assistants (PDAs), portable media players, simple point-and-shoot cameras, and GPS tracking units. They have also reduced the need for handheld game consoles and e-readers.
After the iPhone became popular in the late 2000s, most smartphones started to look similar. They became thin, with large touch screens that respond to multiple finger gestures instead of physical keyboards. Most modern smartphones let you download or buy extra apps from a special app store. They often support cloud storage to save your files online and have virtual assistants to help you. Since the early 2010s, better parts and faster wireless connections have helped the smartphone industry grow a lot. By 2014, over a billion smartphones were sold worldwide each year. In 2019, 1.54 billion smartphones were shipped. By 2020, about 75% of the world's population used a smartphone.
Contents
- How Smartphones Are Built: Hardware Basics
- The Smartphone's Brain: Central Processing Unit
- Buttons and Controls
- The Screen: Your Window to the Phone
- Smart Sensors in Your Phone
- Storage: Keeping Your Files Safe
- Sound: Hearing and Being Heard
- Battery: Powering Your Phone
- Cameras: Capturing Moments
- Back Cover Materials
- Accessories for Your Smartphone
- Software: The Brains Behind the Screen
- Popular Smartphone Brands Today
- Smartphone Sales Trends
- How We Use Smartphones
- Rules and Bans for Smartphones
- Smartphones Replacing Digital Cameras
- Smartphone Lifespan
- See also
How Smartphones Are Built: Hardware Basics
Smartphones contain many small electronic parts. These parts work together to make the phone smart. Some common parts include:
- The main brain, called the application processor.
- Flash memory to store your apps and files.
- Chips for connecting to cellular networks and Wi-Fi.
- The camera's image sensor.
- Chips that manage power and the screen.
- Sensors like gyroscopes that know how your phone is tilted.
- A special chip for the touchscreen.
Some phones also have an FM radio receiver, a small light for notifications, or an infrared transmitter to act as a remote control. A few special phones might even have extra sensors like a thermometer or a humidity sensor. Some unique phones have projectors or special camera lenses.
The Smartphone's Brain: Central Processing Unit
Smartphones have central processing units (CPUs), just like computers. These CPUs are designed to use less power. In a smartphone, the CPU is usually part of a larger chip called a system-on-a-chip (SoC). This chip handles many tasks at once.
The speed of a mobile CPU depends on more than just its clock rate. It also depends on how it handles memory. Because of this, smartphone CPU performance is often measured by special tests that show how well it runs common apps.
Buttons and Controls
Most smartphones have a power button and volume buttons. Some older phones had physical buttons for "home," "back," and "menu," but many newer phones use on-screen buttons or touch sensors instead.
Since 2013, some home buttons started to include fingerprint scanners, like on the iPhone 5s and Samsung Galaxy S5. You can also use button combinations for special actions. For example, you can usually take a screenshot by pressing the home and power buttons together (or volume-down and power on phones without a physical home button).
The Screen: Your Window to the Phone
The screen is a very important part of a smartphone. It usually covers most of the front of the device. Many smartphone screens have a 16:9 aspect ratio, but newer phones often have taller screens that go closer to the edges.
Screen Sizes and How We Use Them
Screen sizes are measured diagonally in inches. Phones with screens larger than 5.2 inches are sometimes called "phablets." It can be tricky to use very large phones with just one hand. You might need to shift the phone around or use both hands. However, new designs with "edge-to-edge" screens make large phones easier to hold.
Types of Screens
The most common screen types are Liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays. Some screens can sense pressure, like Apple's Force Touch system. A few phones even have a low-power electronic paper screen on the back, similar to what you find on e-book readers.
Other Ways to Interact with Your Screen
Some phones come with a stylus for more precise input, like drawing or writing notes. Some screens can even detect your finger hovering above them, which can show you previews or act like a mouse cursor on websites.
Certain styluses also support hovering and have a button for quick tools. Some phone series, like the Samsung Galaxy Note series, have a special slot to store the stylus.
A few phones, like some iPhone models and the Huawei Mate S, have pressure-sensitive touch screens. This means the screen can tell how hard you are pressing, which can be used for games or to access special menus.
Notification Lights
Many smartphones (but not iPhones) have small light-emitting diodes (LEDs) next to the screen. These lights can tell you about new messages, missed calls, or low battery. They use very little power. Different colors or blinking patterns can show you what kind of notification it is.
Smart Sensors in Your Phone
Smartphones have many sensors that help them work and allow apps to do cool things.
Common Sensors You Use Every Day
Accelerometers and gyroscopes help your screen rotate automatically when you turn your phone. They can also be used in games. An ambient light sensor adjusts screen brightness based on how bright your surroundings are.
Many phones also have a barometer to measure air pressure. This helps estimate your altitude. A magnetometer acts like a digital compass, helping you find your way.
Less Common, but Cool Sensors
Some phones, like certain Samsung Galaxy models, have a heart rate sensor for fitness tracking. A few rare phones have sensors for ambient temperature, humidity, or even UV radiation. Some LG phones use an infrared laser beam to help the camera focus faster.
Storage: Keeping Your Files Safe
Smartphones use flash storage to save your apps, photos, and videos. Newer phones use faster storage types like UFS.
Storage Capacity
The amount of storage in phones has grown a lot. For example, some Samsung phones went from 32 GB to 512 GB in just a few years.
Memory Cards for More Space
Some phones let you add more storage using MicroSD memory cards. These cards offer many benefits:
- You can access your files even without internet.
- They don't block your charging port.
- They don't rely on your data plan.
- You can easily move large amounts of data between devices.
- If your phone breaks, you might still be able to save data from the memory card.
Some phones that use two SIM cards have a "hybrid slot." This means you can choose to use either a second SIM card or a memory card in that slot. Other phones have three slots, allowing for two SIM cards and a memory card at the same time.
Memory cards and SIM cards are usually found in a small tray on the side of the phone. You often need a special tool to open it.
Transferring Files
Originally, you could connect your phone to a computer with a USB cable and access it like a regular hard drive. Now, phones often use a system called Media Transfer Protocol (MTP). MTP lets your computer access files without locking them from your phone. However, with MTP, you can only transfer one file at a time.
Sound: Hearing and Being Heard
Smartphones often have features like Voice over LTE (VoLTE) and HD Voice for clearer calls. Sound quality can depend on the phone's design and your network. Using a VoIP app over Wi-Fi can also improve call quality.
Phones have small speakers so you can use speakerphone or listen to music and videos without headphones. Some phones, like the HTC One M8, even have stereo speakers for a richer sound experience.
Headphone Jack
The 3.5mm headphone jack lets you plug in regular headphones or other audio devices. It's usually found at the bottom of the phone.
However, many new phones, starting with the Apple iPhone 7 in 2016, no longer have this jack. You might need an adapter that uses the charging port, or you can use wireless Bluetooth headphones. Bluetooth headphones are often more expensive because they have their own battery and wireless parts.
Battery: Powering Your Phone
Smartphones usually use lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries. These batteries store a lot of energy for their size.
Batteries naturally wear out over time with repeated charging and discharging. This means they hold less power and your phone might slow down. Some older phones had batteries you could easily swap out. However, most modern phones have batteries built-in that are not meant to be replaced by users. This design choice has been criticized for making phones less durable in the long run.
Charging Your Phone

To charge phones faster, special charging technologies like Qualcomm Quick Charge and MediaTek Pump Express were developed. These use higher voltages to send more power quickly. USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) is a newer standard that aims to make charging faster and more consistent across different devices.
Wireless charging has also become popular. This lets you charge your phone by placing it on a special pad, without plugging in a cable. The most common standard for this is Qi. Wireless charging is convenient, but it's usually slower than wired charging and can produce more heat.
By late 2017, smartphone battery life had generally improved. Earlier smartphones often had poor battery life because their batteries couldn't handle the power needed for their advanced features. Many users buy extra chargers or portable "battery packs" to keep their phones charged on the go.
Saving Battery Power
One way phones save power is called "panel self-refresh." This means the screen only updates the image from the processor when something changes. Otherwise, the screen remembers the last image and refreshes itself, saving battery.
Cameras: Capturing Moments

Cameras are a standard feature on smartphones. By 2019, phone cameras became a major selling point, with companies often highlighting their camera quality. Photos are usually saved as JPEG files, but some high-end phones can also save RAW images for more editing control.
Camera Design and Features
Most smartphones have at least one main camera on the back and a front-facing camera for "selfies" and video chat. Because phones are so thin, the rear cameras often stick out a little in a "bump." To improve photos, many phones now have multiple cameras, each designed for a different purpose, like zooming in or taking wide-angle shots.
Modern advanced smartphones have features like optical image stabilization (OIS) to reduce blur, larger sensors, and bright lenses. They also use computational photography to create amazing effects like HDR (for better light and shadow), "Bokeh mode" (for blurry backgrounds), and multi-shot night modes.
Dedicated Camera Button
Some phones, like certain Nokia Lumias and Sony Xperias, have a physical button just for the camera. These buttons often have two pressure levels, like a traditional camera: press halfway to focus, then fully to take the picture. This button can also be a quick way to open the camera app.
Back Cover Materials
Smartphone backs are usually made of polycarbonate (a type of plastic), aluminum, or glass. Plastic backs can be glossy or matte, and sometimes have textures.
While plastic backs might not feel as "fancy" to some, they are often more durable. They can absorb shocks better, are less likely to shatter than glass, and don't block radio signals or wireless charging like metal can.
Accessories for Your Smartphone
Many accessories are sold for smartphones. These include cases to protect your phone, memory cards for more storage, screen protectors, chargers, and wireless power stations. You can also get headphones, power banks (portable batteries), and Bluetooth speakers.
Cases come in many styles, from simple rubber ones to tough, heavy-duty cases. Some cases fold like a book and can even hold credit cards.
Some companies, like Apple, have stopped including chargers with new phones. They say this helps reduce their environmental impact, but it means customers often have to buy a charger separately.
Software: The Brains Behind the Screen
Mobile Operating Systems
A mobile operating system (or mobile OS) is the main software that runs your phone. It's like the conductor of an orchestra, making all the parts work together. Globally, Android and IOS are the two most popular mobile operating systems. Android has been the top-selling OS since 2013.
Mobile operating systems combine features from computer operating systems with special tools for mobile use. These include a touchscreen, cellular and Wi-Fi connections, Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation, cameras, speech recognition, a voice recorder, a music player, and near-field communication (NFC). By early 2018, Android ran on about 85.9% of smartphones sold, and iOS on 14.1%. Other well-known mobile operating systems include Flyme OS and Harmony OS.
Mobile Apps: Your Phone's Tools
A mobile app is a computer program made to run on a mobile device like a smartphone. "App" is short for "software application." Apps let your phone do many different things, from playing games to helping you with schoolwork.
App Stores: Where to Find Apps
The App Store for the iPhone, launched in 2008, made it popular for phone makers to offer online stores for apps. Before this, you had to find apps from many different places. Now, there are tons of apps for games, music, learning, and more. After Apple's success, other companies like Google (with Android Market, now Google Play Store) and RIM (with BlackBerry App World) launched their own app stores. By 2014, most app developers were creating apps for smartphones first.
Popular Smartphone Brands Today
Smartphone Sales Trends
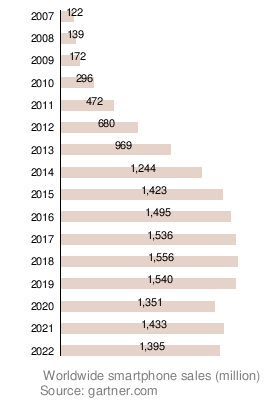
Since 1996, smartphone sales have generally increased. In 2011, 27% of all photos were taken with camera phones. By 2012, a study found that 4 out of 5 smartphone owners used their device to shop online. Global smartphone sales passed sales of simpler "feature phones" in early 2013. In 2013, over 1 billion smartphones were shipped worldwide, a 38% increase from 2012.
In early 2016, smartphone shipments dropped for the first time compared to the previous year. This was partly due to the market in China becoming more mature. A report showed that fewer than 10% of people in the US spent $1,000 or more on smartphones. This was because many phones were expensive without offering truly new features. Also, brands like Huawei, Oppo, and Xiaomi offered similar features at lower prices. In 2019, smartphone sales decreased by 3.2%, the biggest drop in smartphone history. China and India were still the main drivers of sales worldwide.
In the first quarter of 2024, global smartphone shipments increased by 7.8% to 289.4 million units. Samsung became the top smartphone maker, with a 20.8% market share, taking over from Apple. Apple's shipments dropped by 10%. Xiaomi secured the third spot with a 14.1% market share.
Top Smartphone Makers
In 2011, Samsung shipped the most smartphones globally, followed by Apple. By 2013, Samsung had 31.3% of the market, and Apple had 15.3%. Other companies like Huawei, LG, and Lenovo each had about 5%.
In early 2014, Samsung had a 31% share and Apple had 16%. By late 2014, Apple had 20.4% and Samsung had 19.9%. In mid-2016, Samsung had 22.3% and Apple had 12.9%. In early 2017, IDC reported Samsung was first with 80 million units, followed by Apple (50.8 million), Huawei (34.6 million), Oppo (25.5 million), and Vivo (22.7 million).
Realme, a brand owned by Oppo, was the fastest-growing phone brand worldwide since mid-2019. In China, Huawei and Honor (also owned by Huawei) had 46% of the market combined in 2019. In 2019, Samsung held a 74% market share of 5G smartphones in South Korea.
How We Use Smartphones
The popularity of touchscreen smartphones and apps led to them replacing many other devices. Now, most people carry just one smartphone instead of separate phones, organizers, and music players. Better cameras in phones also meant people used them instead of simple digital cameras. Built-in GPS and mapping apps replaced stand-alone navigation devices and paper maps.
Mobile gaming on smartphones grew hugely, making many people use them instead of handheld game consoles. Many people also choose smartphones over landline telephones. Music streaming apps and services have become very popular, replacing traditional radio. Streaming video services on phones can be used instead of watching TV. People often check the time on their smartphones instead of wearing wristwatches, and use phone alarms instead of alarm clocks. Smartphones are also great for taking digital notes and writing memos.
In many parts of the world, smartphones are the first and only way people get Internet access. This is because they are portable and personal computers are less common. Smartphone cameras can also be used to photograph documents and send them by email or messaging, replacing old fax machines. Payment apps and services on smartphones mean people use wallets, credit cards, and cash less often. Mobile banking apps let you deposit checks by just photographing them. Guide book apps can replace paper travel guides and museum audio guides.
Mobile Banking and Payments
In many countries, smartphones are used for mobile banking. This can include sending money through secure text messages. For example, Kenya's M-PESA service lets people store money on their SIM cards and transfer it electronically.
Branchless banking has been successful in places like South Africa and the Philippines. Another example is Zidisha, which uses mobile banking to help people in developing countries get small business loans from people around the world.
Mobile payments were first tested in Finland in 1998. The idea spread, and in 1999, the Philippines launched its first commercial mobile payment systems. Some phones can make contactless payments using near-field communication (NFC) if the phone and the store's payment system support it.
Sending Documents
Some apps let you send and receive digital documents, like faxes, using your smartphone.
Making Films with Smartphones
More and more films are being made using smartphones and tablets. This has led to special film festivals just for these types of movies, such as the SmartFone Flick Fest in Sydney and the Dublin Smartphone Film Festival.
Rules and Bans for Smartphones
Some countries are working to reduce how much students use digital devices, including smartphones.
- South Korea passed a nationwide classroom phone ban, which is scheduled to start in March 2026. Exceptions are allowed for students with disabilities, emergencies, and educational uses.
- France and Finland have partial bans, mostly for younger students.
- Italy, the Netherlands, and China have stronger rules. These policies improved the situation in Dutch schools.
- In Australia, there are state-level bans. Victoria and New South Wales are introducing rules that stop phone use during school hours.
Cho Jung-hun, who helped introduce the bill in South Korea, said that "smartphone addiction has extremely harmful effects on students’ brain development and emotional growth." However, not all students agree. Seo Min-joon, an 18-year-old high schooler, said, "Rather than simply taking phones away, I think the first step should be teaching students what they can do without them."
In 2024–2025, Australia and France began to create laws that would ban social media for children under 15–16. In Australia, this law is planned to start in 2026.
Smartphones Replacing Digital Cameras
As the 2010s began, sales of dedicated compact cameras dropped sharply. This was because smartphone cameras were becoming good enough for most people's needs.
Smartphones gained more computing power, allowing for fast image processing and high-resolution video. By 2011, phones could record 1080p Full HD video, and by 2013, they could record 2160p 4K video.
However, due to their thin design, smartphones still lack some features found in dedicated cameras. These include easily swappable memory cards and batteries, physical buttons for focusing and zooming, a tripod mount, and a brighter xenon flash. Dedicated cameras can also have larger image sensors and true optical zoom lenses.
Since the late 2010s, smartphone makers have added multiple rear cameras with different zoom levels to make up for the lack of optical zoom.
Smartphone Lifespan

For phones released since the mid-2010s, how long they last is often limited by their built-in batteries. These batteries are not designed to be easily replaced. Batteries wear out faster with heavy use and when they are fully charged or completely drained often.
Manufacturers have sometimes made it harder for smartphones to work after repairs. They might link a component's unique serial number to the device. If a part is replaced with one that doesn't match, the phone might not work or some features could be disabled. This was first seen in 2015 with the iPhone 6's home button. Later, some features were limited on Apple and Samsung phones if a battery was replaced by someone not authorized by the company.
See also
 In Spanish: Teléfono inteligente para niños
In Spanish: Teléfono inteligente para niños
- Comparison of smartphone brands
- Lists of mobile computers
- List of mobile app distribution platforms
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Mobile Internet device
- Portable media player
- Second screen
- Smartphone kill switch
- Smartphone zombie