Space Shuttle facts for kids

Discovery lifts off at the start of STS-120.
|
|||
| Manufacturer | United Space Alliance Thiokol/Alliant Techsystems (SRBs) Lockheed Martin/Martin Marietta (ET) Boeing/Rockwell (orbiter) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country of origin | United States | ||
| Specifications | |||
| Spacecraft type | Crewed orbital launch and reentry | ||
| Payload capacity | 27,500 kilograms (60,600 pounds) | ||
| Crew capacity | 8 | ||
| Production | |||
| Status | Retired | ||
| Built | 5 | ||
| Retired | 3 | ||
| Lost | 2 | ||
| Maiden launch | 12 April 1981, 12:00:03 UTC | ||
| Last launch | 8 July 2011 15:29:00 UTC | ||
 Space Shuttle program Space Shuttle program |
|||
|
|||
The Space Shuttle was a special spacecraft used by NASA, the American space agency. It carried astronauts and important cargo into space. This cargo included satellites, parts for the International Space Station, and science tools.
What made the Space Shuttle unique was that it could be used many times. Before the Shuttle, most spacecraft were used only once.
Contents
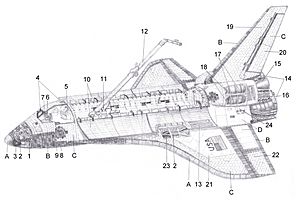
Parts of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was made of three main parts:
- The orbiter
- The external fuel tank
- Two solid rocket boosters
The orbiter looked like a big airplane with wings and a tail. This design allowed it to glide back to Earth and land on a runway, just like a plane. This meant the main part of the Shuttle could be very large and reusable. Earlier spacecraft, like Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo, landed in the ocean using parachutes.
To launch into space, the Shuttle used three rocket engines on the back of the orbiter. It also got a big push from two long, white Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs). Fuel for the orbiter's engines was stored in a large, orange External Fuel Tank (ET).
Before reaching orbit, the SRBs separated and fell into the Atlantic Ocean. They were then towed back to shore to be used again. The ET also separated but broke apart as it fell into the Indian Ocean and was not reused.
Cargo Bay Add-ons
The orbiter had a large cargo bay. It could carry different tools and modules for various missions. Here are some of them:
- Spacelab: This was a special laboratory used for doing science experiments in space.
- Spacehab: Similar to Spacelab, it came in different types to carry more cargo or provide extra space for astronauts.
- Inertial Upper Stage: This was a small rocket used to send payloads (like satellites) into higher orbits after the Shuttle reached space.
- Payload Assist Module: Like the IUS, this was another type of rocket used to boost payloads to higher orbits.
- Extended Duration Orbiter: This kit allowed the Shuttle to stay in space for longer missions.
- Multi-Purpose Logistics Module: This was a large container used to carry supplies and equipment to the International Space Station.
- Canadarm: This was a robotic arm used for many tasks, like moving satellites or helping with spacewalks.
The Space Shuttles
The United States had six Space Shuttles:
The '†' symbol next to a name means that the Shuttle was lost.
There was also a Russian Shuttle called Buran. It flew only one uncrewed flight before it was retired. The Buran was later destroyed in 2002 when its hangar collapsed.
History of the Shuttle
The Space Shuttle program began in 1973. It was designed to replace the Apollo capsules.
The first flight was a test of the Shuttle's landing and maneuvering. This flight used the Space Shuttle Enterprise. It did not go into space.
The first Space Shuttle flight into space happened on April 12, 1981. This mission used the Space Shuttle Columbia.
On January 28, 1986, the Space Shuttle Challenger was lost 73 seconds after launch during mission STS-51-L. This sad event caused space flights to stop for over a year.
In the 1990s, the Space Shuttle's main job became building the International Space Station (ISS). Shuttles carried many parts and supplies to the ISS.
Also in the 1990s, the Space Shuttle launched the amazing Hubble Space Telescope into space. Shuttles flew five times to repair and improve the telescope's cameras and science tools.
On February 1, 2003, the Space Shuttle Columbia broke apart while returning to Earth during mission STS-107. This accident happened because of damage to the heat shield. The heat shield protects the Shuttle from the extreme heat when it re-enters Earth's atmosphere. This event also caused a long delay in Shuttle flights.
In 2010, NASA decided to end the Space Shuttle program. Using the Shuttles was very expensive compared to other ways of launching things into space. The last Space Shuttle flight was by Atlantis on July 8, 2011.
Today, the United States relies on private companies like SpaceX (with their Crew Dragon) and Boeing (with their Starliner capsule) to send astronauts to the ISS. NASA is also developing the Orion capsule for missions beyond Earth's orbit.
The remaining Space Shuttles are now on display for everyone to see:
- Enterprise is at the Intrepid Sea-Air-Space Museum in New York City.
- Discovery is at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia.
- Endeavour is at the California Science Center in Los Angeles, California.
- Atlantis is on display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida.
Images for kids
-
Columbia undergoing installation of its ceramic tiles
-
Story Musgrave attached to the RMS servicing the Hubble Space Telescope during STS-61
-
The crawler-transporter with Atlantis on the ramp to LC-39A for STS-117.
-
Flight deck view of Discovery during STS-42 re-entry
-
Discovery deploying its brake parachute after landing on STS-124
See also
 In Spanish: Transbordador STS para niños
In Spanish: Transbordador STS para niños