Sulfur cycle facts for kids
Sulfur (S) is a natural element found all around us. It's super important for how our planet works, especially for living things and the climate. Most sulfur is hidden deep underground, like under the ocean or inside rocks. You can also find it naturally in places like swamps, where old plants and animals have broken down, and near volcanoes. But humans also add a lot of extra sulfur into the air, mostly from burning fossil fuels like coal and oil.
Contents
How Sulfur Moves Around: The Sulfur Cycle
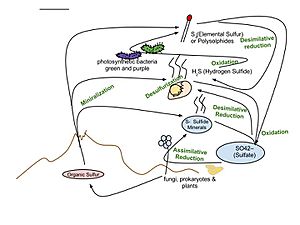
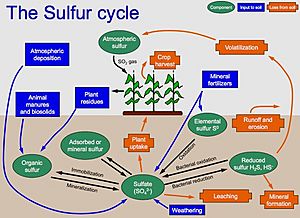
The sulfur cycle describes how sulfur travels through the Earth's land, water, and air. It's a bit like a big loop!
Sulfur from Rocks and Plants
- When rocks break down over time, a process called erosion, they release sulfur that was stored inside them.
- Once this sulfur touches the air, it changes into a form called sulfate (SO4).
- Plants then take up this sulfate from the soil or water during photosynthesis. This makes the sulfur part of the plant's body.
Sulfur in the Food Chain
- Animals like herbivores (plant-eaters) and omnivores (plant and meat-eaters) get sulfur when they eat these plants.
- Sulfur then moves up the food chain. For example, when other animals eat the plant-eaters, they also get sulfur.
Sulfur Returns to Nature
- When plants and animals die, their bodies break down. The sulfur from their bodies goes back into the air as sulfate.
- It also goes into the soil and water through tiny living things called decomposers.
- Sulfur in the air eventually comes back down to the ground and water when it rains. This is part of the water cycle.
- Volcanoes also naturally release a lot of sulfur into the air when they erupt.
How Humans Change the Sulfur Cycle
Humans have a big effect on the sulfur cycle. We are responsible for about one-third of the sulfur found in the atmosphere!
Air Pollution and Acid Rain
- Most of the sulfur we add comes from burning fossil fuels in power plants and cars. This releases sulfur mostly as sulfur dioxide.
- Sulfur dioxide is one of the main causes of acid rain, along with nitrogen and carbon.
- Acid rain forms when water in the air (H2O) mixes with sulfur trioxide, creating Sulfuric acid.
- Acid rain can harm forests, lakes, and even buildings. It makes water too acidic for many fish and other living things.
Sulfur in Fertilizers
- Sulfuric acid is also used to make many fertilizers for farms.
- When it rains, some of this fertilizer can wash off farms and into rivers and lakes. This is called runoff.
- Too much sulfur and other nutrients in the water can cause problems like eutrophication. This means there's too much plant growth, especially algae, which are called algal blooms.
- These algal blooms use up a lot of the oxygen in the water. This makes it hard for fish and other water creatures to breathe, reducing the number of different living things (biodiversity) in that water system.
Sulfur and Climate
- Even though sulfur dioxide causes acid rain, it can also absorb some of the sun's heat in the atmosphere.
- This can actually help keep the Earth's surface a little cooler. It can even reduce some of the effects of global warming. However, the negative impacts of sulfur pollution often outweigh this cooling effect.
See also
 In Spanish: Ciclo del azufre para niños
In Spanish: Ciclo del azufre para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Sulfur cycle Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.