Govia Thameslink Railway facts for kids
 |
|
|---|---|

A Thameslink Class 700 at Shepreth Branch Junction, south of Cambridge in 2019
|
|
| Franchise(s): |
|
| Main region(s): |
|
| Stations operated: | 238 |
| National Rail abbreviation: | GN, GX, SN, TL |
| Parent company: |
|
Govia Thameslink Railway (GTR) is a large British company that runs trains. It operates a big railway network called the TSGN rail franchise.
GTR runs trains under four main names:
- Thameslink
- Great Northern
- Southern
- Gatwick Express
GTR is part of a bigger company called Govia. Govia is a partnership between a British company, Go-Ahead Group (which owns 65%), and a French company, Keolis (which owns 35%).
GTR took over running these train services on 14 September 2014. By July 2015, it became the largest train company in the UK. It had the most passengers, staff, and trains. GTR's contract is a bit different. All the money from ticket sales goes straight to the government. In return, the government pays GTR a set amount of money to run the trains.
GTR has brought in many new trains, including the Class 387 , Class 700 , and Class 717 models. The company also planned to spend £50 million to improve the 239 stations it manages. These improvements included making stations easier to access, updating information screens, and having staff available for longer hours.
Over the years, GTR has faced some challenges. In May 2018, they introduced a new timetable. However, they had to switch to a temporary timetable with fewer trains because of frequent service problems. During the COVID-19 pandemic, GTR reduced its services a lot. More recently, GTR was one of several train companies affected by railway strikes in the UK from 2022 to 2024.
Contents
How GTR Started
Joining Train Services Together
In 2006, the Thameslink and Great Northern train services were combined. This was done because of a big project called the Thameslink Programme, which aimed to improve train lines.
Later, in 2012, the British government decided to combine even more services into one big franchise. This included trains from First Capital Connect, Southern (and Gatwick Express), and some routes from Southeastern. This new, larger franchise was named the Thameslink, Southern and Great Northern franchise (TSGN).
The government chose Govia Thameslink Railway to run this new, big train service on 23 May 2014.
GTR Takes Over
Govia Thameslink Railway (GTR) officially started running services on 14 September 2014. At first, GTR managed 122 stations and operated 226 trains. The separate names, Thameslink and Great Northern, were kept.
In July 2015, the Southern and Gatwick Express services also joined GTR. This made GTR the largest train company in the UK.
The way GTR's contract works is special. Unlike many other train companies, GTR does not keep the money from ticket sales. Instead, all the money goes to the government. The government then pays GTR a fixed amount to operate the trains. This setup was chosen because there were many big engineering projects planned around London. This type of contract helped manage the risks during these busy times.
Changes and Challenges
In December 2015, GTR announced that most of its ticket prices would not increase much. The average fare rise for the next year was only 0.8%.
However, GTR faced criticism for its performance in June 2016. Many people, including the Mayor of London Sadiq Khan, were unhappy with the train services. There were also disagreements with staff about how trains were operated. In July 2016, GTR had to cancel 15% of Southern services for a few weeks to try and make things more reliable.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, fewer people were traveling. So, GTR significantly reduced its services by mid-2020. For example, Gatwick Express services were stopped between March 2020 and April 2022.
In March 2022, the government extended GTR's contract until at least April 2025, with a possible extension to April 2028.
GTR was also affected by the 2022–2024 United Kingdom railway strikes. These were the first national rail strikes in the UK in 30 years. Many GTR workers voted to strike over pay and working conditions. Because of this, GTR could only run a very limited number of trains on strike days.
Thameslink and Great Northern Services
GTR has been running Thameslink and Great Northern services since September 2014.
- Thameslink is a long route that goes through London from north to south. It connects places like Bedford to Brighton. It also serves London Gatwick Airport and London Luton Airport.
- Great Northern services run on the southern part of Britain's East Coast Main Line. These trains go to and from London King's Cross and Moorgate. Destinations include Hertford North, Welwyn Garden City, Stevenage, Peterborough, Cambridge, and King's Lynn.
In May 2018, GTR introduced a new timetable. This included new direct services through the Canal Tunnels to places Thameslink hadn't served before. However, because of many delays and problems across the network, GTR had to create a temporary timetable with fewer trains. This temporary timetable started in July 2018.
Great Northern Train Routes
Since May 2018, many Great Northern services on the East Coast Main Line have been renamed Thameslink. Most of these trains now travel through central London and are part of the Thameslink network.
The only services that still use the Great Northern name are:
- Trains on the Northern City Line.
- Stopping trains to and from Cambridge and Letchworth Garden City.
- Express trains to and from Cambridge, Ely, King's Lynn, and Peterborough (during busy times).
Southern and Gatwick Express Services
The Southern and Gatwick Express train brands joined Govia Thameslink Railway on 26 July 2015.
- Southern trains run from London Victoria and London Bridge. They go through many South London areas like Croydon and Sutton. They also connect to towns further away, such as Brighton, Eastbourne, Horsham, and Portsmouth. Southern also runs services from Milton Keynes to South Croydon.
- Gatwick Express is a special service that runs directly from London Victoria to Gatwick Airport and Brighton. Southern has operated this service since 2008.
Improvements and Plans
GTR had many plans to improve its services and stations. They planned to invest £50 million into the 239 stations they manage.
Some of their plans included:
- Improving all 239 stations, making them easier to access.
- Replacing old electronic information screens with new ones.
- Working with local councils to redevelop stations like St Albans and Luton.
- Increasing the hours that staff are available at many stations. The 100 busiest stations would have staff from the first train to the last.
- Expanding the use of 'the key' smartcard, which Southern had already started using.
- Providing free Wi-Fi at 104 stations.
- Spending £1.5 million on improving station access, including more bike storage and electric vehicle charging points.
GTR also aimed to improve train services, such as:
- Having trains run every half-hour from King's Lynn to London.
- Introducing direct services from Peterborough, Cambridge, and other areas to places like Tattenham Corner and Horsham.
- Increasing Great Northern suburban services to four trains per hour on some routes.
- Having Great Northern suburban trains run to Moorgate on weekends and weekday evenings.
- Increasing train capacity from Uckfield to London during busy times by 50%.
- Doubling the number of Thameslink services that run overnight.
- Having Sevenoaks Thameslink services run on Saturdays.
- Working to extend the Oyster card network to more stations like Epsom, Gatwick Airport, and Luton Airport Parkway.
- Using new Class 387 Electrostars for King's Lynn express services.
Train Fleet
GTR has introduced many new trains to its network.
To replace older trains and expand the Thameslink network, 115 new Class 700 trains were ordered. These trains, which are either eight or twelve carriages long, started running between 2016 and 2019.
Because the Class 700 trains were delayed, 29 Class 387 trains were also ordered for the Thameslink route. These trains started service in 2014. It was originally planned that these Class 387s would move to another company, Great Western Railway, once the Class 700s arrived. However, Great Western Railway ordered their own new Class 387s. So, GTR's Class 387s were instead moved to the Great Northern route after the Class 700s were delivered.
GTR also ordered 25 new six-car trains to replace older Class 313 units. These older trains had been running on the Great Northern suburban services to Moorgate for 40 years. Siemens was chosen to build these new trains in December 2015. They were named the Class 717 in June 2016 and first started service in September 2018.
In September 2022, three Class 171 trains were moved to another company, East Midlands Railway. The remaining Class 171 trains were changed into shorter two- or three-car trains.
In April 2023, GTR looked for between 21 and 30 new trains to add more capacity for their Great Northern route. In March 2024, it was announced that Great Northern would lease all 30 Class 379 trains that were previously used by another company, Greater Anglia. These trains were ready for service by November 2024 and were expected to start running in 2025.
In May 2023, the Southern Class 313 trains were taken out of service.
In November 2024, Southeastern announced that 13 Class 377 trains would be moved from Southern. The first two trains were expected to move before December 2024, with the rest moving before December 2025.
Current Trains Used by GTR
| Family | Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Number | Carriages | Routes operated | Built | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||||
| Southern | |||||||||
| Bombardier Turbostar | 171/2 |   |
DMU | 100 | 160 | 1 | 3 | Brighton Main Line (London Bridge to South Croydon) Oxted line (to Uckfield only) East Coastway line Marshlink line |
2003–04 |
| 171/7 | 12 | ||||||||
| 171/8 | 4 | 2 | |||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar | 377/1 |    |
EMU | 64 | 4 | Entire Southern network apart from sections between Hurst Green and Uckfield & between Ore and Ashford International | 2001–05 | ||
| 377/2 | 15 | ||||||||
| 377/3 | 28 | 3 | |||||||
| 377/4 | 75 | 4 | |||||||
| 377/6 | 26 | 5 | |||||||
| 377/7 | 8 | ||||||||
| 387/2 |  |
110 | 177 | 5 (Varies) | 4 | Units borrowed from Gatwick Express on a rotational basis according to demand. Brighton Main Line East Coastway line West Coastway line (Brighton to Southampton Central) |
2016–17 | ||
| Gatwick Express | |||||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar |
387 |
 |
EMU | 110 | 177 | 22 | 4 | Gatwick Express services between London Victoria & Brighton | 2015–2016 |
| Great Northern | |||||||||
| Bombardier Electrostar |  |
EMU | 100 | 160 | 30 | 4 | Great Northern express services between London King's Cross & Ely / King's Lynn / Peterborough and Great Northern semi-fast services between London King's Cross & Letchworth Garden City / Cambridge | 2010–2011 | |
 |
|||||||||
|
387 |
  |
110 | 177 | 38 | 4 | Great Northern express services between London King's Cross & Ely / King's Lynn / Peterborough and Great Northern semi-fast services between London King's Cross & Letchworth Garden City / Cambridge | 2014–2017 | ||
| Siemens Desiro |
717 Desiro City |
 |
85 | 137 | 25 | 6 | Northern City Line services between Moorgate & Welwyn Garden City / Stevenage via Hertford North | 2018 | |
| Thameslink | |||||||||
| Siemens Desiro | 700 Desiro City |   |
EMU | 100 | 161 | 60 | 8 | All Thameslink services | 2015–2018 |
| 55 | 12 | ||||||||
Past Trains Used by GTR
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Carriages | Number | Built | Routes | Withdrawn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||||
| 171 |  |
DMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 3 | 2003-2004 | Oxted line Marshlink line |
2022 |
| 365 Networker Express |  |
EMU | 100 | 161 | 4 | 40 | 1994-95 | Express services between London King's Cross and / Ely / King's Lynn / Peterborough | 2018–2021 |
| 313 | 
|
75 | 121 | 3 | 63 | 1976–1977 | Northern City Line West Coastway line East Coastway line Seaford branch line |
2019 (Great Northern) 2023 (Southern) |
|
| 319 |  |
100 | 161 | 4 | 86 |
|
All Thameslink services | 2015–2017 | |
| 321 |  |
100 | 161 | 4 | 13 | 1989–1990 | Express services between London King's Cross to Peterborough and Cambridge | 2016 | |
| 377 Electrostar |  |
26 | 2008–2009 | Some Thameslink services | 2017 | ||||
| 455 |  |
75 | 120 | 4 | 46 | 1982–1984 | Metro and commuter services from London Victoria & London Bridge | 2022 | |
How GTR Performs
In February 2015, a survey by Which? magazine asked customers about train companies. Thameslink and Great Northern were at the bottom of the list, with only 43% of customers saying they were satisfied. They scored poorly in areas like reliability, punctuality (being on time), and cleanliness of toilets.
In the 2017 Which? survey, Thameslink and Great Northern improved slightly to 46% satisfaction. However, they were still near the bottom. Southern was in last place that year, but it had faced many problems due to staff disagreements.
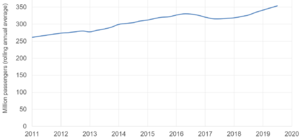
Despite these issues, the number of passengers on Govia Thameslink Railway (including Southern and Gatwick Express) grew. It went from 262 million passengers per year in 2010-11 to 327 million passengers per year in 2015-16.
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |