Transpiration facts for kids
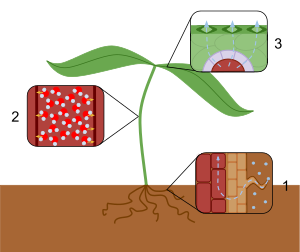
- Water goes into the roots and then into the xylem (plant tubes).
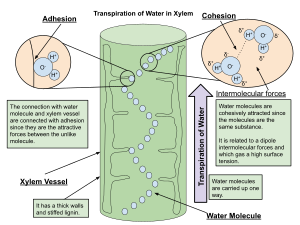
- Water molecules stick together, forming a column in the xylem.
- Water moves from the xylem into leaf cells, turns into vapor, and leaves the plant through tiny holes called stomata.
Transpiration is when water evaporates from plants, especially from their leaves. It's like plants sweating! This process is a key part of the water cycle on Earth. The amount of water a plant loses depends on many things. These include the plant's size, how much sunlight it gets, the temperature, how humid the air is, how fast the wind blows, and how much water is in the soil. Transpiration also helps plants control their temperature, keeping them cool.
A long time ago, an English clergyman named Stephen Hales (born 1677, died 1761) was the first to understand transpiration. He showed that water evaporating from leaves is the main reason water is pulled up from the roots. This idea is still true today.
Contents
How Plants Release Water
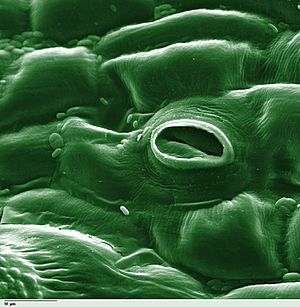
Leaf surfaces have many tiny openings called stomata. Think of them like tiny pores on your skin. Most plants have more stomata on the underside of their leaves. Each stoma has two special cells around it called guard cells. These guard cells open and close the stoma.
Transpiration happens when the guard cells open the stomata. This allows oxygen and water vapor to leave the plant. At the same time, carbon dioxide from the air enters the plant. Plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, which is how they make their food. Oxygen is a product of photosynthesis.
Water Movement in Plants
Transpiration also helps pull water all the way through the plant. This movement brings important mineral nutrients from the roots up to the shoots (stems and leaves). As water leaves the leaves and goes into the atmosphere, it creates a pulling force. This force helps pull the water column up the plant, even against gravity.
Water first enters the plant's roots through a process called osmosis. Then, it travels up through special tubes called xylem. These xylem tubes carry the water and dissolved minerals to all parts of the plant. A large, fully grown tree can lose hundreds of gallons (thousands of liters) of water through its leaves on a hot, dry day! About 90% of the water a plant takes in is used for transpiration. Most of the rest is used for photosynthesis.
Plants in Dry Places
Desert plants and conifers (like pine trees) have special ways to save water. These are called adaptations. Some examples include thick outer layers called cuticles, smaller leaves, stomata that are sunken into the leaf, and hairs on their leaves. All these features help reduce water loss through transpiration.
Many cacti make their food through photosynthesis in their thick, succulent stems instead of leaves. The surface area of a cactus stem is much smaller than all the leaves on a tree. Also, the stomata of desert plants often close during the day when it's hot and open at night when it's cooler. This helps them save water.
Related topics
Images for kids
-
Some xerophytes (desert plants) can shrink their leaves when there's not enough water (left). When it's cool enough and there's enough water, their leaves expand again (right).
-
The clouds you see in this picture of the Amazon Rainforest are partly formed by water evaporating from plants (evapotranspiration).
See also
 In Spanish: Transpiración vegetal para niños
In Spanish: Transpiración vegetal para niños