United States Postal Service facts for kids

Government signature used since 1993
|
|||||||
 USPS Headquarters in Washington, D.C. (2024) |
|||||||
| Independent overview | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formed | July 1, 1971 Washington, D.C., U.S. |
||||||
| Jurisdiction | U.S. federal government | ||||||
| Headquarters | 475 L'Enfant Plaza SW Washington, D.C. 20260-0004 U.S. |
||||||
| Employees | 640,000 (525,377 career personnel, 114,623 pre-career personnel) as of 2024 | ||||||
| Independent executive |
|
||||||
| Key document |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office or U.S. Mail, is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government. Its main job is to deliver mail and packages across the United States, its territories, and some associated states. It is one of the few government agencies mentioned directly in the Constitution of the United States. As of 2024, the USPS has over 640,000 employees.
The USPS has a special role in delivering letters within the U.S. It promises to offer the same price and quality of service everywhere. The Post Office is the only one allowed to use mailboxes marked "U.S. Mail." However, it competes with private companies like United Parcel Service (UPS) and FedEx for package delivery.
Contents
History of U.S. Mail
The first national postal service in the U.S. was called the United States Post Office. It started in Philadelphia on July 26, 1775, during the American Revolution. Benjamin Franklin was the very first Postmaster General.
In 1792, the Post Office Department was officially created. It became a part of the President's Cabinet in 1872. Later, in 1970, it changed into the U.S. Postal Service, becoming an independent agency.
Early Innovations
The Post Office Department once owned and ran the first public telegraph lines in the United States. This started in 1844, connecting Washington to Baltimore.
During World War II (1942-1945), a special "V-Mail" service helped send letters to soldiers. Letters were shrunk onto microfilm and then printed again near their destination. This saved space on transport vehicles for military supplies.
Changes and Challenges
In 1970, postal workers in New York City went on strike. They were unhappy about low pay and poor working conditions. This strike grew to include over 210,000 postal workers across the country.
The strike led to a new law called the Postal Reorganization Act in 1970. This law changed the Post Office Department into the U.S. Postal Service, an independent agency. It also allowed postal worker unions to negotiate contracts.
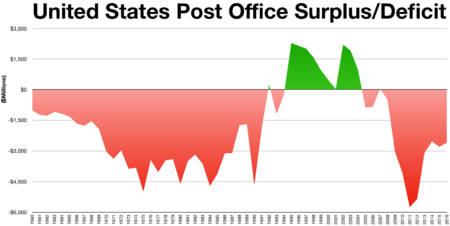
A key part of the 1970 law was that the USPS had to pay for itself. This meant it needed to make enough money from stamps and services to cover its costs. Over the years, mail use declined as people started using email more. This made it harder for the USPS to meet its financial goals.
In 2006, another law, the Postal Accountability and Enhancement Act, added a requirement for the USPS to save money for future retirees' health benefits. This was a huge financial burden. The USPS struggled to make these payments for many years.
Finally, in April 2022, the Postal Service Reform Act of 2022 became law. This act helped the USPS a lot. It removed the requirement to pre-fund future retiree healthcare and forgave a large amount of its debt. This helped the USPS become more financially stable.
How the USPS Works Today
As of 2023, the USPS has over 33,600 Post Office locations. In 2022, it delivered 127.3 billion packages and mail pieces to over 164 million places.
Delivery Schedule
The USPS delivers mail and packages Monday through Saturday. On Sundays, only Priority Express and packages for Amazon.com are delivered in most major cities. Packages are also delivered on most holidays, except for Thanksgiving and Christmas. The busiest time for the Postal Service is between Thanksgiving and Christmas.
USPS Vehicles
The USPS has one of the largest civilian vehicle fleets in the world, with over 235,000 vehicles. Many of these are the well-known Grumman LLV (long-life vehicle) trucks. These older trucks were built between 1987 and 1994 and do not have air conditioning or airbags.
The USPS is replacing its older trucks with new ones. In 2021, a contract was given to Oshkosh Defense to build 165,000 new vehicles over 10 years. These new vehicles, called the Next Generation Delivery Vehicle (NGDV), will come in both gasoline and electric versions.
Electric Vehicles
Starting in 2026, all new delivery truck purchases are planned to be electric vehicles. This is part of a plan to reduce pollution and save money on fuel and maintenance. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provided $3 billion to help the USPS buy these electric vehicles.
By 2028, the USPS plans to add 66,000 electric vehicles to its fleet. This includes vehicles from Ford and Oshkosh. The first new electric vehicles started being used in Kansas in August 2024.
Money and Operations
In 2024, the Postal Service had $79.53 billion in revenue. However, it reported a net loss of $9.5 billion.
Why Revenue Changed
The amount of First-Class mail sent has gone down a lot since 2001. This is because more people use email and the internet for communication. Private companies like FedEx and UPS also compete with USPS for package delivery.
Lower mail volume means less money for the USPS. However, it still has to deliver to every address six days a week. To save money, the USPS has tried to become more efficient.
Changes to Mail Processing
In 2011, the USPS announced it would close many mail processing centers and reduce overnight delivery for some First-Class Mail. This meant that some mail would take two days to arrive instead of one.
Post Office Locations
In 2011, the USPS considered closing many small post offices. However, they changed the plan. Instead, many rural post offices stayed open but with fewer hours. Some services are now offered through "Village Post Offices" in local stores.
The USPS also gets a lot of its money from online purchases and partnerships with stores like Walmart and Staples.
Saturday Delivery
For many years, there were discussions about stopping Saturday mail delivery to save money. In 2013, the USPS announced it would stop Saturday delivery for most mail. However, Congress passed a law that required Saturday delivery to continue. So, Saturday delivery for mail still happens.
Postage Costs
Congress usually limits how much the USPS can raise prices for First-Class Mail. The cost of mailing a 1-ounce First-Class letter increased to 73 cents on July 14, 2024.
How Mail Gets Delivered
Addressing Mail
To send mail, you need to follow rules in the USPS Domestic Mail Manual. This includes things like the size and weight of the mailpiece, how it's sealed, and what can or cannot be mailed (like hazardous materials).
If mail cannot be delivered or returned, it goes to the Mail Recovery Center in Atlanta, Georgia. Here, they try to find an address. If not, items are held for 90 days before being destroyed or auctioned.
The USPS recommends using all capital letters and no punctuation (except for the hyphen in the ZIP+4 code) for addresses. This helps machines read the addresses faster.
Paying for Postage
You can pay for postage in several ways:
- Stamps: Buy them online, at a post office, from a vending machine, or at stores.
- Postage meters: These machines print postage directly onto mail.
- Online labels: Print shipping labels from your computer.
All unused U.S. postage stamps issued since 1861 are still valid. Forever Stamps, sold since 2007, are always valid for First-Class Mail, no matter how much the price changes.
International Mail
The USPS sends letters and packages to almost every country. They use commercial airlines to transport mail. There's a special "M-bag" service for sending large amounts of printed materials internationally.
The Department of Defense and the USPS work together to deliver mail to military personnel. This is called the Army Post Office (for Army and Air Force) and Fleet Post Office (for Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard). Military mail is charged domestic rates from the U.S. and is free when sent by deployed military members.
Some independent countries, like Palau and the Marshall Islands, have a special relationship with the USPS. They use the USPS addressing and ZIP Code system, and mail to and from these countries is treated like domestic mail.
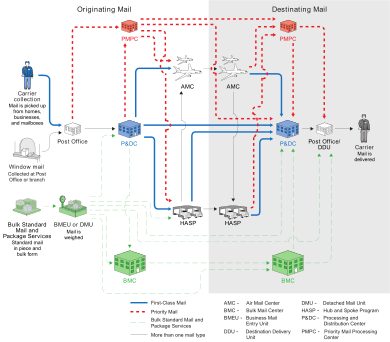
Mail Sorting and Delivery
Mail from customers goes to large Processing and Distribution Centers (P&DCs). These centers sort mail for a specific area and connect to the national mail network.
Machines at the P&DCs read addresses and add bar codes to envelopes. If a machine cannot read an address, an image of the mailpiece is sent to a Remote Encoding Center. Here, people manually type in the address so the mail can be sorted.
If someone has moved and filed a change of address, machines can detect the old address and print a new label with the updated address. Mail that cannot be read at all is either returned to the sender or sent to the Mail Recovery Center.
Once mail has a bar code, it is sorted by machines that send it to the correct local post office. For mail going far away, it is flown by commercial airlines to the nearest airport and then taken to the destination P&DC.
The USPS has been creating Sorting and Delivery Centers (S&DCs) to make delivery more efficient. These larger centers combine delivery operations from many smaller post offices.
Types of Postal Facilities


The USPS has different types of facilities:
- Main post office: The main postal building in a community.
- Station or branch: Other postal facilities in or near a community.
- Contract postal unit (CPU): A postal service offered inside another business, like a store.
- Village post office (VPO): A CPU in a small community where other post offices have closed.
- Processing and distribution center (P&DC): Large centers that sort mail for a region.
- International service center (ISC): Processes international mail.
- Self-Service Kiosks (SSKs): Automated machines where you can weigh packages, buy postage, and renew P.O. boxes.
Delivery Methods
Mail was first delivered to post offices, not homes. In 1863, "city delivery" began in urban areas. In 1891, Rural Free Delivery started in less populated areas.
Today, mail is delivered once a day to most homes and businesses.
- City delivery: Carriers often walk and deliver to mailboxes on houses or porches.
- Rural delivery: Carriers usually drive to deliver mail.
- Curbside delivery: Mailboxes are at the end of driveways.
- Central point delivery: Several homes share a group of mailboxes in one spot.
Some people choose to use post office boxes for privacy or convenience. This is a locked box at the post office where mail is delivered. People without a fixed address can use "general delivery" to pick up mail at the post office.
Mail Forwarding and Holds
If you move, you can ask the USPS to forward your mail to your new address. You can also put your mail on "hold" if you are away, like on vacation. The Post Office will store your mail until you return.
Package Services
In July 2023, the USPS introduced USPS Ground Advantage, which replaced First-Class package service. This service helps deliver packages efficiently. The USPS has also installed many new package sorting machines to handle more packages each day.
Law Enforcement and Oversight
Postal Inspection Service
The United States Postal Inspection Service (USPIS) is one of the oldest law enforcement agencies in the U.S. It was founded by Benjamin Franklin in 1775. Its job is to protect the Postal Service, its employees, and customers from crime. They investigate crimes that involve the mail system.
Office of Inspector General
The United States Postal Service Office of Inspector General (OIG) was created in 1996. The OIG's main goal is to prevent and find fraud, waste, and misuse of money. They also work to make the USPS more efficient. The OIG watches over the activities of the Postal Inspection Service.
USPS in Stories
- In the movie Miracle on 34th Street (1947), the court decided that Kris Kringle was the real Santa Claus because the U.S. Post Office delivered mail addressed to Santa to him.
- The novel Post Office (1971) by Charles Bukowski tells about his experiences working as a letter carrier and mail clerk.
- David Brin's novel The Postman (1985) imagines the USPS helping to rebuild the U.S. government after a disaster. It was made into a movie in 1997.
- The Inspectors (2015) is a TV show about postal inspectors solving crimes related to the mail.
See also
 In Spanish: Servicio Postal de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Servicio Postal de los Estados Unidos para niños
 | May Edward Chinn |
 | Rebecca Cole |
 | Alexa Canady |
 | Dorothy Lavinia Brown |