War in Darfur facts for kids
The War in Darfur was a big armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan. It started in February 2003. Two rebel groups, the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM), began fighting against the government of Sudan. They said the government was unfair to the non-Arab people of Darfur.
The government fought back, and many non-Arab people in Darfur were forced from their homes or killed. This terrible violence led to hundreds of thousands of deaths. Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, was later accused by the International Criminal Court of very serious crimes, including genocide.
Quick facts for kids War in Darfur |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Sudanese Civil Wars | ||||||||
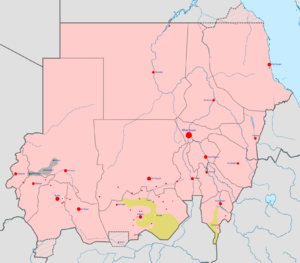 Military situation in Sudan on 6 June 2016. (Darfur on the far left) Under control of the Sudanese Government and allies Under control of the Sudan Revolutionary Front and allies Under control of the Sudanese Awakening Revolutionary Council For a more detailed map of the current military situation in Sudan, see here. |
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
|
Supported by: |
|
|||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Units involved | ||||||||
|
|
No specific units | ||||||
| Strength | ||||||||
|
SRF: 60,000
|
SAF: 109,300
|
UNAMID: 15,845 soldiers and 3,403 police officers |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | 235 killed as of 31 August 2016 | ||||||
|
Total killed: Total displaced: 450,000 (Sudanese government estimate) |
||||||||
Why the Conflict Started
Darfur means "the home of the Fur" in Arabic. It was an independent kingdom for a long time. It became part of Sudan much later.
There are a few reasons why the conflict began in 2003. One big reason was arguments over land. Some people were nomadic herders who moved their animals around. Others were farmers who stayed in one place. They often fought over who owned the land.
Access to water was also a major problem. Water is very important in this dry region. Another reason for the conflict was the long-standing tension between the government and rebel groups in Darfur.
Who Was Involved
One side of the conflict included the Sudanese military and police. They were joined by a group called the Janjaweed. Most Janjaweed members were from Arabized African groups.
The other side was made up of rebel groups. The main ones were the SLM/A and the JEM. These groups were mostly from non-Arab Muslim ethnic groups like the Fur, Zaghawa, and Masalit.
The African Union and the United Nations also sent a joint peacekeeping mission. This mission was called UNAMID. Their goal was to help keep the peace and protect civilians.
Impact of the War
The Sudanese government said it did not support the Janjaweed. However, there was evidence that the government gave them money and weapons. They also worked together on attacks, often against regular people.
Many people died in the conflict, some from fighting, others from hunger and sickness. Millions of people were forced to leave their homes. They had to move to refugee camps or cross borders into other countries. This created a huge humanitarian crisis.
The United States described the situation as very serious violence, like acts of genocide.
Peace Efforts
In February 2010, the Sudanese government and the JEM signed a ceasefire agreement. They hoped to find a way to make lasting peace. However, these talks were stopped. The JEM said the Sudanese army had attacked a village, breaking the agreement.
In August 2019, a new agreement was signed in Sudan. This agreement was part of a plan to move towards a democratic government. It said that a peace agreement must be made in Darfur within six months.
Finally, a big peace agreement was signed on August 31, 2020. This agreement was between the Sudanese government and several rebel groups. It aimed to end the fighting in Darfur.
| List of abbreviations used in this article AU: African Union |
See also
- Banu Hilal
- Bibliography of the Darfur conflict
- Breidjing Camp
- Chadian Civil War (2005–10)
- Command responsibility
- Darfur genocide
- First Sudanese Civil War
- History of Darfur
- History of Sudan
- Human rights in Sudan
- Genocides in history
- Genocide of indigenous peoples
- List of civil wars
- List of conflicts in Africa
- List of ethnic cleansing campaigns
- List of famines
- List of ongoing armed conflicts
- List of wars 2003–present
- Lost Boys of Sudan
- Second Sudanese Civil War
- Slavery in Sudan
- Team Darfur
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |

