Acid–base reaction facts for kids
An acid-base reaction is a special kind of chemical reaction. It happens when an acid mixes with a base. When they react, they usually make something called a salt and water. This type of reaction is also known as a neutralization reaction because the acid and base cancel each other out.
Imagine an acid as something that releases tiny charged particles called hydrogen ions (H+). A base, on the other hand, often releases hydroxide ions (OH−). When these two meet, the H+ and OH− ions combine to form water (H2O). The other parts of the acid and base then join together to form a salt.
For example, when a strong acid like hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with a strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH), they form sodium chloride (NaCl), which is common table salt, and water.
Contents
What Are Acids and Bases?
Acids and bases have different properties that help us identify them.
Understanding Acids
Acids often taste sour, like lemons or vinegar. They can also change the color of certain plant dyes. For example, acids turn litmus paper red. Strong acids can be very dangerous and can burn your skin, so you should never taste them!
Some common acids you might know are:
- Citric acid (found in oranges and lemons)
- Acetic acid (in vinegar)
- Sulfuric acid (used in car batteries)
Understanding Bases
Bases often taste bitter and feel slippery, like soap. They also change the color of plant dyes, but in the opposite way to acids. Bases turn litmus paper blue. Strong bases can also be dangerous and cause burns.
Some common bases include:
- Sodium hydroxide (found in drain cleaners)
- Ammonia (used in cleaning products)
- Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate)
How Acid-Base Reactions Work
The idea of acids and bases has changed over time. Early scientists defined them by their properties, like taste or how they affected dyes.
Early Ideas About Acids and Bases
The first scientific definition of acids and bases was suggested by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier. He thought that acids always contained oxygen. However, later discoveries showed that this was not always true.
The Arrhenius Definition
Later, a Swedish scientist named Svante Arrhenius came up with a more detailed definition. He said:
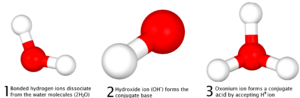
- An Arrhenius acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
- An Arrhenius base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH−) when dissolved in water.
So, in an Arrhenius acid-base reaction, the H+ ions from the acid combine with the OH− ions from the base to form water (H2O). The other parts of the acid and base combine to form a salt.
For example:
- H+(aq) + OH−(aq) → H2O(l)
The other ions present in the solution, which do not take part in the reaction, are called spectator ions. They are just "watching" the reaction happen.
Why Are These Reactions Important?
Acid-base reactions are very common and important in many areas of life:
- In your body: Your stomach uses hydrochloric acid to digest food. Your body also uses acid-base reactions to keep the pH balance of your blood just right.
- In cleaning: Many cleaning products are either acidic or basic. For example, vinegar (acidic) can clean mineral deposits, while ammonia (basic) is good for grease.
- In the environment: Acid rain is caused by acidic gases in the air reacting with water. Scientists use acid-base reactions to understand and fix environmental problems.
- In industry: Many industrial processes, from making fertilizers to producing medicines, involve careful control of acid-base reactions.
Understanding how acids and bases react helps us make new materials, keep our bodies healthy, and protect our environment.
Images for kids
-
Svante Arrhenius was a Swedish scientist who defined acids and bases based on their ions in water.
See also
 In Spanish: Reacción ácido-base para niños
In Spanish: Reacción ácido-base para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |