Agate Fossil Beds National Monument facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Agate Fossil Beds National Monument |
|
|---|---|
|
IUCN Category III (Natural Monument)
|
|

University and Carnegie Hills fossil beds
|
|
| Location | Sioux County, Nebraska, United States |
| Nearest city | Harrison, NE |
| Area | 3,057.87 acres (12.3748 km2) |
| Established | June 14, 1997 |
| Visitors | 15,555 (in 2016) |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
| Website | Agate Fossil Beds National Monument |
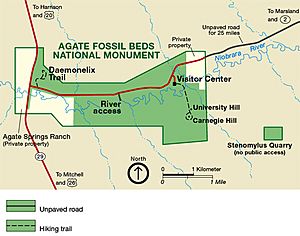
Agate Fossil Beds National Monument is a super cool U.S. National Monument located near Harrison, Nebraska. Imagine a beautiful valley where the Niobrara River flows, surrounded by grassy plains. This place is famous for the incredible fossils found on two special hills: Carnegie Hill and University Hill.
The monument is covered in different kinds of grasses like prairie sandreed and little bluestem. You can also spot pretty wildflowers such as lupin, spiderwort, and bright sunflowers growing there.
Contents
Discovering Ancient Life at Agate Fossil Beds
A Look Back in Time
This land was once a working cattle ranch called Agate Springs Ranch. It was owned by a person named Capt. James Cook. The museum at the monument also has over 500 amazing items from the Cook Collection. These items are artifacts from Plains Indians, showing how they lived long ago.
The idea to make this area a national monument was approved on June 5, 1965. However, it officially became a national monument much later, on June 14, 1997. A historic building called the Harold J. Cook Homestead, also known as the Bone Cabin Complex, was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1977. The National Park Service takes care of Agate Fossil Beds today.
Amazing Ancient Animals
Agate Fossil Beds is best known for its huge collection of very well-preserved Miocene fossils. Many of these fossils were dug up at sites on Carnegie and University Hills. These fossils come from ancient rock layers called the Harrison Formation and Anderson Ranch Formation. They are about 20 to 16.3 million years old! These are some of the best examples of ancient mammals from the Miocene period.
Meet the Fossil Friends
Here are some of the incredible animals whose fossils have been found at Agate:
- Merychippus and Parahippus: These were ancient relatives of the modern-day horse.
- Diceratherium: A type of rhinoceros that had two horns.
- Menoceras: A pony-sized rhinoceros. This is the most common animal found in the fossil beds!
- Daphoenodon and Ysengrinia: These were two kinds of mid-sized animals known as "bear dogs."
- Promerycochoerus: An ancient animal that looked a bit like a hippo and spent time in the water.
- Daeodon: This was the largest of the "entelodonts," which were giant pig-like animals.
- Stenomylus: These were gazelle-like camelids, related to camels.
- Oxydactylus: These were giraffe-like camelids, also related to camels.
- Palaeocastor: These were land beavers that dug huge, corkscrew-shaped burrows. These burrows are called Daemonelix!
- Moropus: An animal called a chalicothere, which are distant relatives of rhinos and horses.
- Merychyus: A sheep-like animal.
- Syndyoceras: An antelope-like mammal that is an extinct relative of animals like deer and cows.
Gallery
|
See also
 In Spanish: Monumento nacional de Yacimientos de Fósiles de Ágata para niños
In Spanish: Monumento nacional de Yacimientos de Fósiles de Ágata para niños