Wood duck facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Wood duck |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Male (above) and female wood ducks, both at the Wissahickon Creek, Philadelphia. |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Aix
|
| Species: |
sponsa
|
 |
|
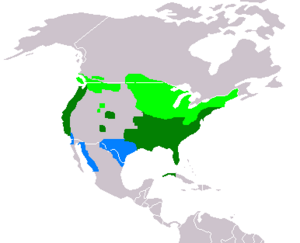
| Range of A. sponsa Breeding range Year-round range Wintering range |
|
| Synonyms | |
| Anas sponsa (Linnaeus, 1758) Lampronessa sponsa | |
The wood duck or Carolina duck (Aix sponsa) is a super colorful duck found in North America. These ducks are special because they can perch in trees, unlike most other ducks! The male wood duck, called a drake, is one of the most vibrant and beautiful waterfowl in North America.
Contents
What Do Wood Ducks Look Like?
The wood duck is a medium-sized duck. An adult is usually about 47 to 54 centimeters (18 to 21 inches) long. Their wings can spread out between 66 and 73 centimeters (26 to 29 inches). A wood duck weighs about 454 to 862 grams (1 to 1.9 pounds). This is about three-quarters the size of a common mallard duck. Wood ducks are related to the beautiful mandarin duck from Asia.
Male and Female Ducks
The adult male wood duck is truly stunning! He has bright, shimmering colors that change in the light. This is called iridescent plumage. He also has striking red eyes and a clear white stripe on his neck.
The female wood duck is not as colorful as the male. She has a white ring around her eye and a whitish throat. Both male and female wood ducks have a cool crest of feathers on their heads. The special feathers on their wings, called speculum feathers, are shiny blue-green with a white edge.
Wood Duck Sounds
Male wood ducks make a rising whistle sound, like jeeeeee. Female wood ducks make a long, rising squeal, like do weep do weep, when they are startled. They also have a sharp alarm call that sounds like cr-r-ek, cr-e-ek.
Where Do Wood Ducks Live?
Wood ducks like to live in wooded swamps, shallow lakes, marshes, ponds, and creeks. You can find them in the eastern and western parts of the United States. They also live in some areas of southern Canada and the west coast of Mexico. They are called "wood ducks" because they are one of the few duck species that can perch and nest in trees.
In recent years, more wood ducks have started nesting in the Great Plains area. Most of them now nest in the Mississippi River valley.
Wood Duck Life Cycle and Behavior
Wood ducks usually build their nests in holes in trees near water. They also use special nesting boxes that people put up in wetland areas. Sometimes, other animals like birds of prey, squirrels, or even other ducks might try to use these nesting spots. Because of this, wood ducks might nest up to a mile away from water.
Female wood ducks line their nests with soft feathers and other materials. Nesting high up in trees helps protect their eggs and babies from predators like raccoons, owls, and hawks. Unlike most other ducks, wood ducks have sharp claws that help them grip tree branches. In warmer areas, a female wood duck can lay eggs and raise two groups of ducklings in one year! This is very rare for North American ducks.
Eggs and Ducklings
Wood ducks usually start laying their eggs between February and April. A female typically lays 7 to 15 eggs. The eggs hatch after about 30 days. Sometimes, if nesting boxes are too close together, female ducks might lay their eggs in a neighbor's nest. This can lead to nests with 30 or more eggs, which can be too many for one mother to care for. This behavior is called "nest dumping."
The day after they hatch, the baby ducklings are ready for adventure! They climb to the opening of the nest hole and bravely jump down from the tree to the ground. Wood duck nests are often built over water, so the ducklings have a soft landing. The mother duck calls her babies to her and guides them to the water. By this time, the ducklings can already swim and find their own food.
What Do Wood Ducks Eat?
Wood ducks find their food by dabbling. This means they feed from the surface of the water or graze on land, rather than diving underwater. They mostly eat berries, acorns, and seeds. They also eat insects, which means they are omnivores (they eat both plants and animals). Wood ducks have a strong part of their stomach called a gizzard that helps them crush acorns after swallowing them whole.
Where Do Wood Ducks Migrate?
Some wood ducks live in the southern parts of their range all year round. But the wood ducks that live in the north fly south for the winter. They spend the winter in the southern United States, especially near the Atlantic Coast. About 75% of the wood ducks in the Pacific Flyway (a migration path) do not migrate at all.
Because they are so beautiful, wood ducks are also kept in collections of waterfowl around the world. Sometimes, they escape in places like Great Britain. There have been some small groups of wood ducks living wild there, but they usually don't last long. In England and Wales, it's actually against the law to release wood ducks into the wild because they are not native to those areas. There is also a small group of wild wood ducks living in Dublin, Ireland.
How Are Wood Ducks Protected?
In the late 1800s, the number of wood ducks dropped a lot. This happened because their homes were being destroyed, and people hunted them for their meat and feathers. By the early 1900s, wood ducks were very rare and almost gone in many places.
To help them, laws like the U.S. Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918 were put in place. These laws helped protect wood ducks, and their numbers started to grow again in the 1920s. Building special nesting boxes for them, starting in the 1930s, also helped a lot. Studies have shown that these artificial nesting sites are very helpful for wood ducks. While natural tree holes are best, nesting boxes still make a big difference.
People who own land, as well as park and wildlife managers, can help wood ducks by building these nesting boxes near water. For example, Fulda, Minnesota, has made the wood duck its unofficial mascot, and you can find many nest boxes there.
Another animal that has helped wood ducks is the North American beaver. As beaver populations have grown, they create more forested wetland areas. These wetlands are perfect homes for wood ducks.
The number of wood ducks has increased a lot in recent years thanks to all these efforts. During hunting season, hunters in the U.S. are allowed to take a certain number of wood ducks. The limit has even been raised in some areas because the population is doing so well. After the mallard, the wood duck is the second most hunted duck in North America.
Images for kids



















