Bending facts for kids
| Mechanics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
This article is about how things bend. For other meanings, see Bending (disambiguation).
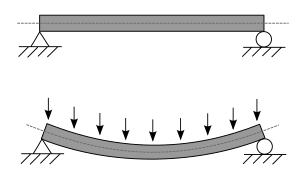
In engineering and mechanics, bending (also called flexure) is what happens when a long object, like a beam, has a force pushing on its side. This force pushes at a right angle to the object's length.
When an object bends, it changes shape. A good example is a closet rod that sags in the middle because of the weight of clothes. That rod is a "beam" that is bending.
Contents
What is Bending?
Bending is a common way that structures react to forces. Imagine a diving board when someone jumps on it. It bends downwards. This is because the force (the person's weight) is pushing down on the board, which is fixed at one end.
How Beams Bend
Objects that are designed to resist bending are often called beams. Beams are usually long and thin. When a force pushes on a beam, one side of the beam gets stretched (pulled longer), and the other side gets squished (pushed shorter).
For example, if you push down on the top of a beam, the top part will get squished, and the bottom part will get stretched. In the middle of the beam, there's a special line where the material doesn't stretch or squish at all. This is called the "neutral axis."
Why is Bending Important?
Understanding bending is super important for engineers. They need to know how much a bridge, a building, or even a tiny part in a machine will bend when forces act on it. If something bends too much, it could break or stop working correctly.
Engineers use math and science to predict how much a beam will bend. They also design beams to be strong enough to handle the forces without bending too much or breaking.
Stiffness and Strength
When we talk about bending, two important ideas are stiffness and strength.
What is Stiffness?
Stiffness is how much an object resists bending. A very stiff object will bend only a little bit, even with a big force. Think of a thick steel beam compared to a thin plastic ruler. The steel beam is much stiffer.
Materials that are stiff are good for things that need to keep their shape, like the frame of a building or a bridge.
What is Strength?
Strength is how much force an object can handle before it breaks. An object can be stiff but not very strong. For example, a piece of glass is very stiff, but it can break easily if you drop it.
Engineers need to make sure structures are both stiff enough (so they don't sag too much) and strong enough (so they don't break).
Examples of Bending in Real Life
Bending is all around us!
- Bridges: When cars drive over a bridge, the bridge deck (the part you drive on) acts like a beam and bends slightly under the weight.
- Buildings: The floors and roofs of buildings are designed to act as beams, bending a little under the weight of people, furniture, and snow.
- Diving Boards: These are designed to bend a lot, storing energy as they bend and then releasing it to push a diver up.
- Tree Branches: When wind blows or snow falls on a tree branch, it bends. If it bends too much, it might break.
Engineers study bending to make sure these everyday structures are safe and work well.
Related pages
- Engineering
- Mechanics
- Deflection
- Shear strength
- Shear stress
- Mechanical Strain
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Flexión mecánica para niños
In Spanish: Flexión mecánica para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |