Viscosity facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Viscosity |
|
|---|---|
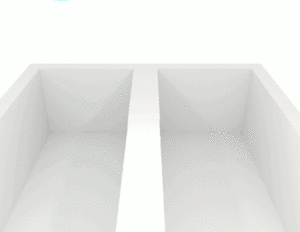
This image shows liquids with different viscosities. The liquid on the left flows more easily than the liquid on the right.
|
|
|
Common symbols
|
η, μ |
|
Derivations from
other quantities |
μ = G·t |
| Dimension | 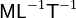 |
Viscosity tells us how much a liquid or gas resists flowing or changing its shape. Think of it as how "thick" a fluid is. For example, syrup is much "thicker" (more viscous) than water. Viscosity measures the internal "stickiness" or friction between different parts of a fluid as they move past each other.
Imagine pushing a fluid through a tube. The fluid in the middle moves faster than the fluid near the walls. This happens because there's friction between the layers of fluid. To keep the fluid flowing, you need to apply a force to overcome this friction. The stronger this force, the higher the fluid's viscosity.
How thick a fluid is can change with its temperature, pressure, and how fast it's being pushed or stirred. For many common fluids, like water, their "thickness" stays pretty much the same no matter how fast you stir them. These are called Newtonian fluids.
Only special "superfluids" at extremely cold temperatures have zero viscosity, meaning they flow without any resistance. Most fluids always have some viscosity.
Contents
- Where Does the Word "Viscosity" Come From?
- Understanding Different Kinds of Viscosity
- How Fluids Behave: Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian
- Viscosity in Solids?
- How Do We Measure Viscosity?
- Units for Viscosity
- What Makes Fluids Viscous? (Molecular Origins)
- Predicting Viscosity
- Examples of Viscosity in Everyday Life
- See also
Where Does the Word "Viscosity" Come From?
The word "viscosity" comes from the Latin word viscum, which means "mistletoe". Mistletoe berries were once used to make a sticky glue, which was also called viscum. This sticky glue gave us the word for how "sticky" or resistant a fluid is.
Understanding Different Kinds of Viscosity
Dynamic Viscosity: How Thick is it?
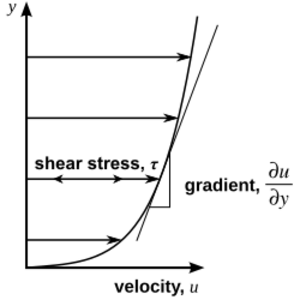
When we talk about how much a material resists changing its shape, we often look at the forces involved. For a fluid, the forces that appear when you try to make it flow depend on how quickly it's changing shape, not just how much it has changed. This property is called viscosity.
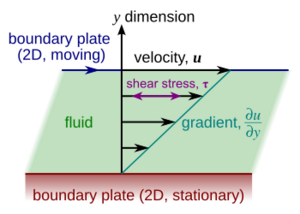
Imagine a fluid trapped between two large, flat plates. One plate is still, and the other moves at a steady speed. If the moving plate goes slowly, the fluid layers slide past each other smoothly. The layer touching the moving plate moves at the same speed as the plate, and the layer touching the still plate doesn't move at all. Each layer in between moves a little faster than the one below it.
Because of friction between these layers, the fluid tries to slow down the moving plate. So, you need to keep pushing the top plate to maintain its speed. The amount of force you need to apply tells you about the fluid's "dynamic viscosity." This is often shown with the Greek letter mu (μ).
The units for dynamic viscosity in the SI system are pascal-seconds (Pa·s). This is like pressure multiplied by time.
Kinematic Viscosity: How Easily Does it Flow?
Sometimes, it's more useful to think about how easily a fluid flows under its own weight. This is where "kinematic viscosity" comes in. It's found by dividing the dynamic viscosity (μ) by the fluid's density (ρ). It's usually shown with the Greek letter nu (ν).
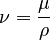
Kinematic viscosity tells us how quickly momentum spreads through a fluid. Its SI unit is square meters per second (m2/s).
How Fluids Behave: Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian
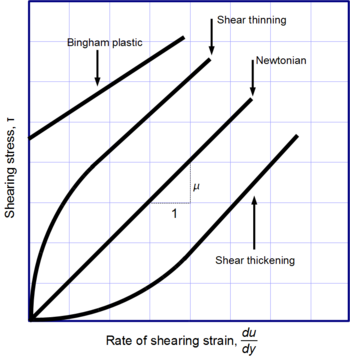
Not all fluids behave the same way. Newton's law of viscosity describes fluids where the viscosity stays constant, no matter how fast you stir or push them. These are called Newtonian fluids. Gases, water, and many common liquids are Newtonian under normal conditions.
However, many fluids are non-Newtonian. Their viscosity changes depending on how much stress or force is applied, or how quickly they are deformed. Here are some examples:
- Shear-thickening liquids: These get thicker when you stir them faster. Think of a mixture of cornstarch and water.
- Shear-thinning liquids: These get thinner when you stir them faster. Paint and ketchup are good examples.
- Thixotropic liquids: These become less viscous over time when shaken or stirred. Some gels and yogurts show this.
- Rheopectic liquids: These become more viscous over time when shaken or stirred. Some lubricants can behave this way.
- Bingham plastics: These act like a solid until a certain amount of force is applied, then they start to flow like a liquid. Toothpaste is a good example.
Viscosity can also depend on other things, like temperature and pressure. For example, a magnetorheological fluid can become much thicker when a magnetic field is applied to it.
Viscosity in Solids?
While we usually talk about viscosity with liquids and gases, some "solids" can also show viscous behavior, meaning they flow very slowly over long periods. Think of granite flowing like a liquid, but over millions of years!
Many materials are actually viscoelastic. This means they have properties of both elastic solids (they bounce back after a quick push) and viscous fluids (they slowly deform over time). For example, pitch looks like a solid, but it flows very, very slowly, as shown in the famous pitch drop experiment.
How Do We Measure Viscosity?
We use special tools called viscometers and rheometers to measure viscosity. It's very important to control the temperature of the fluid during measurement, because even a small change in temperature can greatly affect viscosity.
- Glass capillary viscometers: These are common for measuring kinematic viscosity. You measure how long it takes for a fluid to flow through a narrow tube.
- Cup viscometers: Used in industries like paint and coatings. You measure how long it takes for a certain amount of liquid to flow out of a cup with a small hole at the bottom.
- Vibrating viscometers: These sensors vibrate in the liquid. The more energy the liquid takes away from the vibrating sensor, the higher its viscosity.
For non-Newtonian fluids, which don't have a single viscosity value, rheometers are used to measure how their viscosity changes under different conditions.
Units for Viscosity
The main unit for dynamic viscosity in the SI system is the pascal-second (Pa·s). You might also see it as newton-seconds per square meter (N·s/m2).
Another common unit, especially in older measurements, is the poise (P), named after Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille. One poise is equal to 0.1 Pa·s. Often, you'll see centipoise (cP), which is one-hundredth of a poise. Water at 20 °C has a viscosity of about 1 cP, which is very convenient!
For kinematic viscosity, the SI unit is square meters per second (m2/s). The CGS unit is the stokes (St), named after Sir George Gabriel Stokes. One stokes is 0.0001 m2/s. We often use centistokes (cSt), which is one-hundredth of a stokes. Water at 20 °C has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt.
What Makes Fluids Viscous? (Molecular Origins)
The viscosity of a fluid comes from how its tiny molecules interact with each other.
Viscosity in Gases
In gases, molecules are far apart and move around quickly. Viscosity here comes from these molecules bumping into each other and exchanging momentum. Imagine faster-moving molecules hitting slower-moving ones, transferring some of their speed. This "momentum transfer" creates the internal friction we call viscosity.
Because molecules move faster at higher temperatures, they collide more often and with more energy. This is why the viscosity of gases generally increases as temperature goes up.
Viscosity in Liquids
In liquids, molecules are much closer together and are attracted to each other. Viscosity in liquids is mainly due to these attractive forces. When one layer of liquid tries to slide past another, these attractions resist the movement.
As temperature increases, the molecules in a liquid gain more energy and move around more vigorously. This makes it easier for them to overcome the attractive forces holding them together. So, the viscosity of liquids generally decreases as temperature goes up. Think about how much easier it is to pour cold honey versus warm honey!
Viscosity in Mixtures and Solutions
When you mix different liquids or dissolve something in a liquid, the viscosity can change.
- Liquid blends: Mixing two liquids can result in a viscosity somewhere between the two, or sometimes even higher or lower, depending on how the molecules interact.
- Aqueous solutions: If you dissolve a substance like salt in water, the solution's viscosity can be higher or lower than pure water. For example, a 20% salt solution is thicker than water, but a 20% potassium iodide solution is thinner.
| Solute | 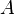 (mol−1/2 L1/2) (mol−1/2 L1/2) |
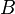 (mol−1 L) (mol−1 L) |
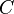 (mol−2 L2) (mol−2 L2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 0.0062 | 0.0793 | 0.0080 |
| Potassium iodide (KI) | 0.0047 | −0.0755 | 0.0000 |
- Suspensions: If you have solid particles floating in a liquid (like sand in water, or cornstarch in water), the mixture's viscosity will usually be higher than the pure liquid. The more particles, the thicker it gets.
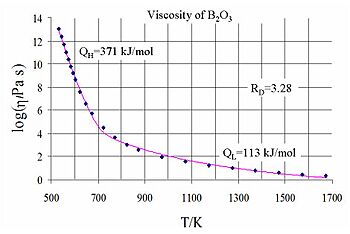
Viscosity in Amorphous Materials (Like Glass)
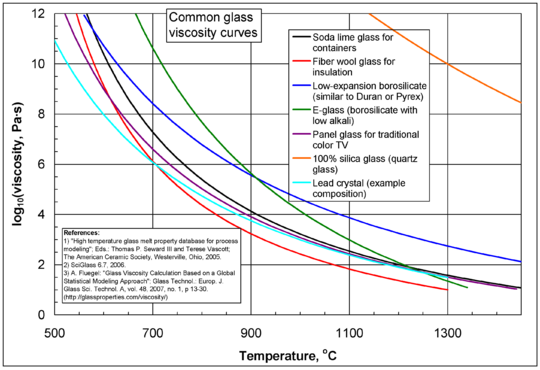
Amorphous materials, like glass or melted plastic, don't have a regular crystal structure. Their viscosity changes a lot with temperature. At very high temperatures, they flow like thick liquids. As they cool down, they become incredibly viscous, eventually becoming solid-like glass. The way their viscosity changes with temperature is often described by special equations.
Predicting Viscosity
Since viscosity changes with temperature and pressure, it's impossible to measure it for every single condition. That's why scientists and engineers use formulas and computer models to predict viscosity. These predictions are very important for designing things like engines, pipelines, and even food products, where fluids are constantly changing temperature and pressure.
For simple gases, we can even predict viscosity using basic physics principles. For most other fluids, we rely on formulas that have been carefully matched to experimental measurements.
Examples of Viscosity in Everyday Life
Viscosity values can vary hugely, even for common things. For example, a 70% sugar solution is over 400 times more viscous than water. And pitch, which looks solid, is billions of times thicker than water!
Water's Viscosity
The dynamic viscosity of water at room temperature (25 °C) is about 0.89 mPa·s. As water gets hotter, its viscosity decreases.
| Temperature (°C) |
Viscosity (mPa·s or cP) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 1.305 9 |
| 20 | 1.001 6 |
| 30 | 0.797 22 |
| 50 | 0.546 52 |
| 70 | 0.403 55 |
| 90 | 0.314 17 |
Air's Viscosity
At normal room temperature and pressure, the dynamic viscosity of air is about 18.5 μPa·s. This is roughly 50 times less viscous than water at the same temperature. Unlike liquids, the viscosity of air generally increases with temperature.

Viscosity of Other Common Substances
| Substance | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Temperature (°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 0.604 | 25 | |
| Water | 1.0016 | 20 | |
| Mercury | 1.526 | 25 | |
| Whole milk | 2.12 | 20 | |
| Dark beer | 2.53 | 20 | |
| Olive oil | 56.2 | 26 | |
| Honey |  2,000–10,000 2,000–10,000 |
20 | |
| Ketchup | 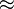 5,000–20,000 5,000–20,000 |
25 | |
| Peanut butter | 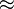 104–106 104–106 |
||
| Pitch | 2.3×1011 | 10–30 (variable) |
How Viscous Are Things? (Order of Magnitude)
This table shows how much viscosity can vary for different substances. Remember, these are estimates and can change based on exact conditions.
| Factor (Pa·s) | Description | Examples | Values (Pa·s) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−6 | Very low viscosity (gases) | Butane | 7.49 × 10−6 | |
| Hydrogen | 8.8 × 10−6 | |||
| 10−5 | Low viscosity (gases) | Krypton | 2.538 × 10−5 | |
| Neon | 3.175 × 10−5 | |||
| 10−4 | Lower range of liquid viscosity | Pentane | 2.24 × 10−4 | |
| Gasoline | 6 × 10−4 | |||
| Water | 8.90 × 10−4 | |||
| 10−3 | Typical for many common liquids | Ethanol | 1.074 × 10−3 | |
| Mercury | 1.526 × 10−3 | |||
| Whole milk (20 °C) | 2.12 × 10−3 | |||
| Blood | 3 × 10−3 to 6 × 10−3 | |||
| Liquid steel (1550 °C) | 6 × 10−3 | |||
| 10−2 – 100 | Oils and thicker liquids | Linseed oil | 0.028 | |
| Oleic acid | 0.036 | |||
| Olive oil | 0.084 | |||
| SAE 10 Motor oil | 0.085 to 0.14 | |||
| Castor oil | 0.1 | |||
| SAE 20 Motor oil | 0.14 to 0.42 | |||
| SAE 30 Motor oil | 0.42 to 0.65 | |||
| SAE 40 Motor oil | 0.65 to 0.90 | |||
| Glycerine | 1.5 | |||
| Pancake syrup | 2.5 | |||
| 101 – 103 | Pastes, gels, and very thick liquids | Ketchup | ≈ 101 | |
| Mustard | ||||
| Sour cream | ≈ 102 | |||
| Peanut butter | ||||
| Lard | ≈ 103 | |||
| ≈108 | Very slow-flowing materials | Pitch | 2.3×108 | |
| ≈1021 | Extremely slow-flowing "solids" | Mantle (geology) | ≈ 1019 to 1024 |
See also
 In Spanish: Viscosidad para niños
In Spanish: Viscosidad para niños
- Dashpot
- Deborah number
- Dilatant
- Herschel–Bulkley fluid
- High viscosity mixer
- Hyperviscosity syndrome
- Intrinsic viscosity
- Inviscid flow
- Joback method (estimation of liquid viscosity from molecular structure)
- Kaye effect
- Microviscosity
- Morton number
- Oil pressure
- Quasi-solid
- Rheology
- Stokes flow
- Superfluid helium-4
- Viscoplasticity
- Viscosity models for mixtures
- Zahn cup