Brachylophosaurus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Brachylophosaurus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Fossil nicknamed Roberta | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: |
Saurolophinae
|
| Tribe: |
Brachylophosaurini
|
| Genus: |
Brachylophosaurus
Sternberg, 1953
|
| Species | |
|
|
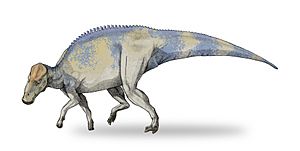
Brachylophosaurus was a type of plant-eating dinosaur. It was a medium-sized member of the hadrosaur family, also known as "duck-billed dinosaurs." These dinosaurs lived about 76.5 million years ago.
Scientists have found many Brachylophosaurus skeletons and large groups of bones. These fossils were discovered in the Judith River Formation in Montana, U.S., and the Oldman Formation in Alberta, Canada.
Contents
What Did Brachylophosaurus Look Like?
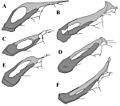
Brachylophosaurus had some unique features. It had a flat, paddle-like bony crest on top of its skull. Some individuals had crests that covered almost their entire skull. Others had shorter, narrower crests.
This dinosaur also had unusually long front limbs. Its upper jaw had a beak that was wider than other hadrosaurs living at the same time.
How Big Was Brachylophosaurus?
An adult Brachylophosaurus could grow to be about 9 meters (30 feet) long. That's about the length of a school bus!
What Did Brachylophosaurus Eat?
Like other hadrosaurs, Brachylophosaurus had cheeks. These helped keep food in its mouth while it chewed. It had hundreds of teeth that fit closely together. These teeth allowed it to chew its food very well. This was a special ability for a reptile, but common for dinosaurs like Brachylophosaurus.
Did Dinosaurs Get Sick?
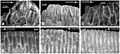
In 2003, scientists found something interesting in Brachylophosaurus fossils. They discovered evidence of tumors, including signs of cancer. Researchers used special scans, like computerized tomography, to check dinosaur vertebrae for these growths.
Other hadrosaurs, such as Edmontosaurus, Gilmoreosaurus, and Bactrosaurus, also showed signs of tumors. Even though more than 10,000 fossils were checked, these growths were mostly found in Brachylophosaurus and its close relatives. Scientists are still trying to understand why this was the case.
Amazing Dinosaur Discoveries
Paleontologists have found some incredibly well-preserved Brachylophosaurus fossils. These discoveries have taught us a lot about these ancient animals.
"Elvis" and "Leonardo"
In 1994, a fossil hunter named Nate Murphy found a complete and perfectly preserved Brachylophosaurus skeleton. He nicknamed it "Elvis."
Even more amazing finds came later. In 2000, Murphy's team discovered "Leonardo." This was a young adult Brachylophosaurus skeleton that was fully connected and partly mummified. It even had some skin impressions! "Leonardo" is considered one of the most spectacular dinosaur finds ever. It was even featured in the Guinness Book of World Records.
Other Important Finds
After "Leonardo," the team found "Roberta." This was an almost complete, slender skeleton. They also found "Peanut," a partially preserved young Brachylophosaurus with some skin impressions. These finds help scientists learn more about how Brachylophosaurus lived and grew.
Images for kids