Bronchopneumonia facts for kids
Bronchopneumonia is a type of pneumonia, which is an infection that causes inflammation in your lungs. It specifically affects the small airways in your lungs called bronchioles and the tiny air sacs around them, known as lobules. Think of it as a common cold or flu that has spread deeper into your lungs, making it hard to breathe.
Bronchopneumonia is often caused by bacteria, but sometimes viruses or fungi can also be responsible. It's different from another type of pneumonia called lobar pneumonia, which affects a larger, single section of the lung.
Contents
What is Bronchopneumonia?
Bronchopneumonia happens when tiny germs, usually bacteria, get into the small tubes (bronchioles) and air sacs (lobules) of your lungs. These germs cause the tissues to swell up and fill with fluid or pus. This makes it difficult for your lungs to do their job, which is to take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
How Your Lungs Work
Your lungs are amazing organs that help you breathe. When you take a breath, air travels down your windpipe (trachea) and into two main tubes called bronchi. These tubes then split into smaller and smaller branches, like a tree, until they become tiny tubes called bronchioles. At the very end of these bronchioles are tiny air sacs called alveoli. These alveoli are where oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your blood, and carbon dioxide leaves your blood.
In bronchopneumonia, the inflammation happens in those small bronchioles and the nearby air sacs. This makes it harder for oxygen to get into your body, which can make you feel very sick.
What Causes It?
Bronchopneumonia is most often caused by bacteria. Some common types of bacteria that can cause it include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. Sometimes, viruses like the influenza virus (the flu) or even fungi can also lead to this type of lung infection.
The germs usually spread through tiny droplets in the air when someone who is sick coughs or sneezes. If you breathe in these droplets, the germs can travel down into your lungs.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of bronchopneumonia can vary, but they often include:
- Coughing: This might be a dry cough or one that brings up mucus.
- Fever: Your body temperature might go up, making you feel hot and sweaty.
- Shortness of breath: You might find it hard to breathe, especially during activity.
- Chest pain: You might feel pain in your chest, especially when you cough or take a deep breath.
- Feeling tired: You might feel very weak and have low energy.
- Chills: You might shiver even if you're warm.
Sometimes, younger children or older adults might not show all these typical symptoms. They might just seem less active or have less appetite.
How Do Doctors Find It?
If a doctor thinks you might have bronchopneumonia, they will usually:
- Ask about your symptoms: They will want to know how you're feeling and what symptoms you have.
- Listen to your lungs: They will use a stethoscope to listen for unusual sounds, like crackling or wheezing.
- Order a chest X-ray: This is a special picture of your lungs that can show if there's inflammation or fluid.
- Do blood tests: These tests can help confirm an infection and see how serious it is.
- Test your mucus: Sometimes, they might ask for a sample of your cough mucus to find out exactly which germ is causing the infection.
How Is It Treated?
The treatment for bronchopneumonia depends on what caused it:
- Antibiotics: If bacteria are the cause, doctors will prescribe antibiotics. It's very important to take all the medicine, even if you start feeling better.
- Antiviral medicines: If a virus is causing it, antiviral medicines might be used, but often the body fights off viral infections on its own.
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest helps your body fight the infection.
- Fluids: Drinking lots of water and other fluids helps thin the mucus in your lungs, making it easier to cough up.
- Pain relievers: Medicines like paracetamol can help with fever and chest pain.
In some serious cases, people might need to go to the hospital to get oxygen or fluids through an IV.
Can You Prevent It?
You can take steps to lower your risk of getting bronchopneumonia:
- Get vaccinated: Vaccines for the flu and pneumonia can help protect you from common causes of lung infections.
- Wash your hands: Washing your hands often with soap and water helps remove germs.
- Avoid sick people: Try to stay away from people who are coughing or sneezing.
- Don't smoke: Smoking damages your lungs and makes them more likely to get infections.
- Stay healthy: Eating healthy food, getting enough sleep, and exercising can boost your immune system.
Who Can Get Bronchopneumonia?
Anyone can get bronchopneumonia, but some people are more at risk. This includes:
- Young children: Their immune systems are still developing.
- Older adults: Their immune systems might be weaker.
- People with other health problems: Conditions like asthma, diabetes, or heart disease can make you more vulnerable.
- People with weakened immune systems: This can be due to certain illnesses or medicines.
Images
-
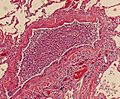
Histopathology of bronchopneumonia, showing neutrophils filling a bronchiole.
See also
 In Spanish: Bronconeumonía para niños
In Spanish: Bronconeumonía para niños