Canarium indicum facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Canarium indicum |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Burseraceae |
| Genus: | Canarium |
| Species: |
C. indicum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Canarium indicum L.
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The galip nut tree, also known as Canarium indicum, is a special tree from eastern Melanesia. It often grows in rainforests and near villages. People use it for many things. It provides food, wood, and even shade. It's also important in traditional medicine and farming systems.
Contents
What are the Types of Galip Nut?
There are two main types, or varieties, of Canarium indicum. One is called indicum, and the other is platycerioideum. The platycerioideum type is not very common. It grows in Indonesia and West Papua New Guinea. This type has bigger leaves and fruits. In Vanuatu, there are at least five different kinds of galip nut trees. They have different fruit shapes, sizes, colors, and textures.
Where Do Galip Nuts Grow?
The Canarium tree is originally from eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu. Besides Melanesia, people also grow it in Fiji, northern Australia, Taiwan, Hawaii, Honduras, and Trinidad. You can often find it in rainforests, old gardens, and around towns. It's also used to provide shade or block wind on farms.
Galip nuts have been a key food in Papua New Guinea for about 6,000 years! In 2007, about one-third of families there grew Canarium trees. In the Solomon Islands, owning these trees shows how wealthy a family is.
How Does the Galip Nut Tree Grow?
Tree Features and Size
The Canarium indicum is a large, evergreen tree. This means it stays green all year. It has a strong trunk with wide bases called buttresses. Its branches spread out, forming a thick top, or canopy. Grown trees are usually 20 to 30 meters (65 to 98 feet) tall. Some can even reach 40 meters (131 feet)! The trunk can be 1 to 1.5 meters (3 to 5 feet) wide. The canopy can spread up to 30 meters (98 feet) across.
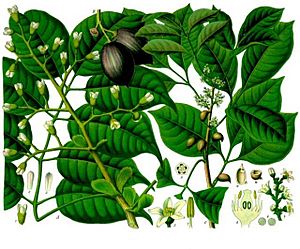
- Leaves: The leaves are bright green and have 3 to 7 pairs of smaller leaflets. Each leaflet is about 7 to 28 cm (3 to 11 inches) long.
- Flowers: The flowers are small, about 1 cm (0.4 inches) wide, and yellowish-white. They grow in clusters.
- Fruits: The fruits are oval-shaped, 3 to 6 cm (1 to 2 inches) long. They start green and turn dark black or blue-black when ripe.
- Nuts: Inside the fruit is a hard, stony nut. The edible part, called the kernel, is usually triangle-shaped.
The tree flowers for only about two weeks. After that, it takes 6 to 9 months for the fruits to grow and ripen.
Tree Life Cycle
In Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands, Canarium trees are usually dioecious. This means a tree is either male or female. In Vanuatu, some trees can have both male and female flowers, or even flowers that are both male and female (hermaphrodite).
Growing Galip Nuts
What Kind of Soil Do They Need?
Canarium trees like medium to heavy soils. These include loams and clay soils that are rich in nutrients. The soil should drain well and have good organic matter. They prefer a pH level between 4.5 and 6.5. Young trees need some shade, but adult trees prefer full sunlight.
Planting Seeds
For the best results, seeds should be planted soon after they are picked. They should be placed about 10 mm (0.4 inches) deep in light soil. When planting trees for their nuts, it's good to space them about 9 to 10 meters (30 to 33 feet) apart.
What Kind of Climate Do They Like?
Canarium trees mostly grow in wet, warm areas near the equator. They prefer average yearly temperatures between 15–28°C (59–82°F). They don't like temperatures below 5–7°C (41–45°F) or frost. These trees usually grow from sea level up to 250 meters (820 feet) high. They need a lot of rain, ideally 2500–3500 mm (98–138 inches) per year. They can handle short dry periods and strong winds.
Taking Care of the Trees
It's important to keep the area around young trees clear of other plants. This helps the seedlings get enough light. Older trees can be planted in forests that are gradually thinned. This allows more light to reach the young trees.
To help the trees grow, farmers can add fertilizer. For the first 10 years, a mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is recommended. After that, the amount should increase as the tree gets bigger.
Pests and Diseases
Canarium trees are quite strong. They don't seem to get many serious pests or diseases. Some types of Canarium have even developed ways to resist pests and diseases naturally. The hard shell of the nut also protects the kernel inside from bugs and germs.
Harvesting and Products
Harvesting Galip Nuts
Harvesting galip nuts is a big event in many communities. The right to pick nuts from certain trees is often passed down through families. Fruits can be picked from the tree or collected from the ground after they fall. In Papua New Guinea, the nuts are ready from May to July. In Vanuatu, it's from October to January. In the Solomon Islands, the busiest time is September to October.
After harvesting, the nuts are usually dried by smoking them. This helps them last for many months. Vacuum-packed nuts can stay fresh for six to nine months. A healthy tree can produce about 100 kg (220 pounds) of nuts each year.
What Can You Do with Galip Nuts?
Many parts of the Canarium tree are useful. The kernels are a very important food in Melanesia. They are full of fat and protein. People eat them raw, baked, or roasted. They can be a snack or added to soups and other dishes. The taste can vary, from a little bitter to a soft, delicate coconut butter flavor.
- Kernel Oil: The oil from the kernel is used for cooking, like coconut oil. It's also used in traditional medicine and in skin care products. In the past, it was used as lamp oil and to help with arthritis.
- Nut Shells: The hard shells can be used for carving jewelry. They can also be burned to make charcoal fuel. In Papua New Guinea, they are even used to make pipes for smoking tobacco.
- Bark: In the western Solomon Islands, the bark is used in traditional medicine for chest pain.
- Wood: The wood is soft and used for building, making canoes, tools, and crafts. It can also be used as firewood.
- Resin: The sticky sap from the trunk is used to seal canoes.
Nutritional Value
Galip nuts are very nutritious! Here's what 100 grams of the edible kernel contains:
| Nutrients | Quantity per 100 g edible portion |
| Fat | 45.9 g |
| Water | 35.4 g |
| Fibre | 10.6 g |
| Protein | 8.2 g |
| Starch | 0.3 g |
| Sugar | 0.2 g |
| Ash | 2.6 g |
| Potassium | 627 mg |
| Magnesium | 284 mg |
| Calcium | 44 mg |
| Sodium | 18 mg |
| Vitamin C | 8 mg |
| Iron | 3.5 mg |
| Zinc | 2.4 mg |
| Niacin | 1.7 mg |
| Copper | 1.6 mg |
| Manganese | 1.1 mg |
| Thiamin | 0.13 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.06 mg |
| ꞵ-carotene equivalent | 165 μg |
A 100-gram serving of raw galip nut kernels provides about 439 calories. They are rich in oil (67-80%), protein (13%), and starch (7%). The oil has a good mix of healthy fats. Galip nuts also contain important antioxidants and vitamin E.
Developing New Varieties
Farmers have been choosing and growing different types of Canarium trees for a long time. They pick trees based on the taste and size of the nut, how much oil it has, and if the shell is thin. Since the 1970s, scientists have been studying these trees to find ones that produce a lot of nuts. They also look for ways to grow them more easily on farms.
Selling Galip Nuts
Commercial sales of Canarium indicum began in the Solomon Islands in 1989. Since the early 1990s, there have been projects to sell more galip nuts. The first commercial products in Papua New Guinea were launched in July 2018. These nuts are now sold in local stores and duty-free shops. You can find them roasted, peeled, or natural.
Prices for nuts in their shells are around 30 US cents per kilogram. Processed kernels can sell for about 3 US dollars per kilogram.
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |

