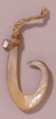Cedros Island facts for kids
| Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 420: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean off Baja California |
| Area | 348 km2 (134 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,205 m (3,953 ft) |
| Administration | |
| State | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1,350 |
Cedros Island (which means "island of cedars" in Spanish) is a dry and rocky island in the Pacific Ocean. It belongs to the state of Baja California, Mexico. In 2005, about 1,350 people lived there.
The island covers an area of 348 square kilometres (134 sq mi). It is very mountainous, with its highest point reaching 1,205 metres (3,953 ft) high. People on Cedros Island mostly earn a living from fishing and making salt. The island has special plants and shows signs of some of the very first humans in the Americas. The ocean around Cedros Island is also a popular spot for sport fishing.
People have lived on Cedros Island for a very long time, about 11,000 years ago! When Spanish explorers first visited in the 1500s, the native people called it Huamalgua, meaning "Island of Fogs." These native people were later moved to the mainland in 1732 and their culture changed.
Contents
Island Location and Features
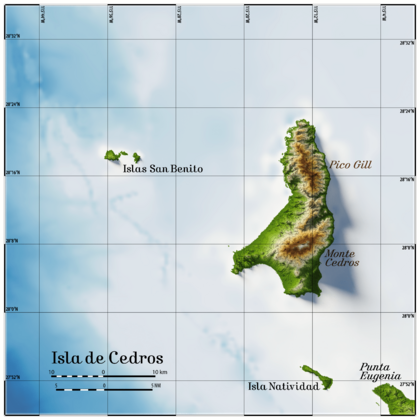
Cedros Island is part of Ensenada Municipality. It sits off the west coast of the Mexican state of Baja California. A wide bay called Sebastián Vizcaíno Bay separates it from the mainland by about 100-kilometre (62 mi).
The island is about 22 km (14 mi) northwest of Punta Eugenia. This point is the westernmost part of Baja California Sur. Cedros Island is also 15 km (9.32 mi) north of Isla Natividad. A channel called Canal de Keller runs between them.
Cedros Island is the fourth-largest island in Mexico. It is about 38 km (24 mi) long and 17 km (11 mi) wide at its widest point. The Islas San Benito, which are smaller islands about 25 km (16 mi) to the west, are also part of Cedros Island's administration.
Early Spanish explorers named the island "Isla de Cedros." They saw lots of driftwood from redwood and cedar trees floating in the ocean. They thought these trees grew on the island, but they were wrong. The island actually has local pine trees. The two main high points on the island are Cedros hill in the south and Pico Gill in the north.
Island Weather
Cedros Island has a desert climate. This means it is very dry, and most of its rain falls during the winter.
| Climate data for Isla Cedros 10 metres (33 ft) above sea level 28°08′N 115°10′W / 28.133°N 115.167°W | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 22.8 (73.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.6 (74.5) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.4 (84.9) |
29.5 (85.1) |
28.6 (83.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
19.1 (66.4) |
19.2 (66.6) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
21.7 (71.1) |
24.0 (75.2) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
23.8 (74.8) |
21.4 (70.5) |
19.0 (66.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.7 (58.5) |
15.7 (60.3) |
16.3 (61.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
17.0 (62.6) |
15.1 (59.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10 (0.4) |
10 (0.4) |
5.1 (0.2) |
2.5 (0.1) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2.5 (0.1) |
5.1 (0.2) |
5.1 (0.2) |
10 (0.4) |
53 (2.1) |
The only weather station is on the southeastern coast. The northern and western parts of the island are cooler. This is because cold ocean waters cause a lot of fog and clouds there. This happens especially during spring and summer. The moisture from the fog helps plants grow, creating "fog oases." Higher parts of the island also get more rain, sometimes up to 200 millimetres (7.9 in) a year.
People and Towns
Cedros Island is divided into 24 smaller areas called delegaciones. In 2005, the island had a total of 1,350 people living there.
The main town is called Cedros, or Pueblo Cedros. It is on the southeast coast. Fishermen founded this town in 1922. By 2010, about 747 people lived there. The town's economy depends on fishing, especially for lobster and abalone. A fishing cooperative helps manage this work.
Another important town is Puerto Morro Redondo, or El Morro. It is a "company town" built by the Mexican Government and Mitsubishi Corporation. Workers for a salt company live there. Salt from the mainland is brought by barge to a special dock at El Morro. From there, it is loaded onto big ships and sent to other countries.
You can fly to Cedros Island from Ensenada on Mondays and Wednesdays. The plane lands at an airstrip near El Morro. A 10 km (6 mi) road connects the airstrip to Pueblo Cedros. You can also take a boat ride from Bahia Tortugas on the mainland. But be ready for possible delays due to bad weather!
There are also smaller settlements on the island:
- Jerusalem is near El Morro and is often considered part of it.
- Lomas Blancas is a mining town between Cedros town and El Morro.
- San Agustín is a fishing village on the southwest coast.
- La Colorada is another small settlement north of San Agustín.
- Wayle is on the western side of the southern bay.
- Punta Norte is a mining town on the northeast coast.
Ancient Discoveries
For a long time, many scientists thought the first people in the Americas came by walking across a land bridge from Asia. But new discoveries along the Pacific Ocean coastlines are changing this idea. Many now believe the first people arrived by boat. Finds on Cedros Island support this new theory.
Scientists found signs of ancient people on Cedros Island that are older than 10,000 BCE. This is even older than the well-known Clovis culture. Cedros Island was a good place for early humans because it had lots of sea life and more fresh water than other desert coastlines.
The early people on Cedros Island fished, collected shellfish, and hunted seals, sea lions, and seabirds. They used ancient spear points and shell fishhooks. These tools are similar to ones found in other Pacific coastal areas, from Japan to Peru. The shell fishhooks found on Cedros Island are especially important. They show that people were fishing from boats about 6,000 years before similar fishing cultures were known in California.
Oldest Fishhooks in the Americas
In 2017, scientists announced the discovery of the oldest fishhooks in the Americas on Cedros Island. These hooks are about 11,000 years old. The people who made them were fishing for deepwater fish. This means they must have been using boats to go out into the ocean. Similar old fishhooks have also been found on Isla Espíritu Santo in Baja California.
Island History
When Spanish explorers first arrived in 1539, they found several villages on the island. Each village had hundreds of people. Later, in 1732, Jesuit missionaries moved the native people from Cedros Island to the mainland.
Between 1790 and 1850, hunters came to the island to find seals and sea otters.
In the 20th century, people mined for gold and copper near Punta Norte from 1890 to 1914. A fishing village and cannery were set up in Puerto Cedros in 1920. The fishing cooperative was started in 1943. A special dock for loading salt onto ships was built in 1966. Mexican and U.S. geologists made detailed maps of the island in the 1970s.
Nature and Wildlife
Cedros Island is made up of different kinds of rocks. Its highest point, Monte Cedros, is 1,205 metres (3,953 ft) high.
Plants
Most of the island (over 90%) is covered in desert plants. The lower parts of the island get very little rain. However, the northern and western areas often have thick fog. Some plants here have learned to get moisture from this fog. This fog, along with a bit more rain at higher elevations, allows Monterey pine forests to grow. These pine forests are found between 500 metres (1,600 ft) and 800 metres (2,600 ft) high. They only cover a small part of the island (0.46%). The pine trees can grow up to 10 metres (33 ft) tall. California juniper trees also grow at similar heights.
At the very highest parts of the island, you can find chaparral plants. These plants are usually about 3 metres (9.8 ft) tall. They include woody plants like the Cedar Island live oak. Chaparral covers 2.4% of Cedros Island. The most important natural water source on the island is Vargas spring.
Animals
You can find large groups of sea lions on the rocks on the west side of the island. There are also wild goats on Cedros. But unlike on other islands, these goats have not caused much harm to the island's environment. This might be because Cedros Island was once connected to the mainland during the last ice age. So, native animals like the Cedros Island mule deer also live there. They compete with the goats for food and help keep the goat population in check.
The waters around Cedros Island are full of fish! California yellowtail fish are very common here because it's where they breed. They like to live in the kelp beds around the island. Other fish like calico bass and sheepshead are also found in large numbers near the island.
Unique Species
Cedros Island is home to many plants and animals that are found only there or in very few other places. These are called endemic species.
- Animals found only or mostly on Cedros Island
- Cedros side-blotched lizard
- Cedros Island Bewick's wren (a type of bird)
- Cedros Island mule deer
- Cedros Island brush rabbit
- Cedros Island cactus mouse
- Plants found only or mostly on Cedros Island
- Cryptantha maritima var. cedrosensis
- Dudleya cedrosensis
- Dudleya pachyphytum (Cedros Island Liveforever)
- Eriogonum molle (Cedros soft buckwheat)
- Ferocactus chrysacanthus (a type of cactus)
- Harfordia macroptera ssp. fruticosa
- Linanthus veatchii
- Lotus cedrosensis
- Mammillaria goodridgei var. goodridgei (a type of cactus)
- Mammillaria goodridgei var. rectispina (a type of cactus)
- Diplacus stellatus
- Monardella thymifolia
- Penstemon cedrosensis
- Pinus radiata var. binata (Guadalupe Island Monterey pine) — a special type of pine tree.
- Porophyllum cedrense
- Quercus cedrosensis (Cedros Island oak)
- Rhus integrifolia var. cedrosensis
- Salvia cedrosensis (Cedros Island sage)
- Senecio cedrosensis
- Verbesina hastata
- Xylonagra arborea ssp. arborea
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Isla de Cedros para niños
In Spanish: Isla de Cedros para niños