Civil defense facts for kids
Civil defense or civil protection is all about keeping people safe from big dangers. These dangers can be things made by humans, like wars, or natural events, like floods or earthquakes. It uses ideas from emergency management to help: stopping problems before they start, making them less harmful, getting ready, responding when something happens, and helping people recover afterward.
People started talking about these programs in the 1920s. Some countries began using them in the 1930s as the risk of war and air attacks grew. Civil defense became very important after people realized how dangerous nuclear weapons were.
After the Cold War ended, civil defense changed its main focus. Instead of just preparing for military attacks, it now helps with all kinds of emergencies and disasters. New terms like crisis management and emergency management describe this wider role.
Some countries see civil defense as a key part of their overall defense. For example, "total defence" means a country uses many of its resources to protect all parts of civilian life.
Contents
How Civil Defense Started
Early Beginnings
Civil Defense in the United Kingdom
Civil defense began because of the bombing of cities during the First World War. German zeppelins started bombing the United Kingdom on January 19, 1915. They dropped bombs near Great Yarmouth, killing six people. German bombers, like the Gotha, were surprisingly effective.
After the war, people thought about how to protect civilians if another war happened. The Air Raid Precautions Committee (ARP) was set up in 1924. Their job was to find ways to keep people safe from air raids.
The Committee predicted that London could have 9,000 casualties in the first two days of an attack. They thought there would be "total chaos and panic" as people tried to leave the city. To control this, some suggested strict measures, like putting London under military control.
A special government group, the Civil Defence Service, was created in 1935. It included the ARP, wardens, firefighters, and first aid teams. Over 1.9 million people worked in civil defense, and nearly 2,400 died helping others during enemy attacks.
Local governments were in charge of organizing civil defense. Volunteers joined different units based on their skills. Wardens, for example, would check areas, report damage, and guide people to safety. They also told survivors where to find food and help.
Rescue Parties searched bombed buildings for injured or dead people. They also turned off gas, electricity, and water, and fixed or pulled down unsafe buildings. Medical teams gave first aid on the spot.
'Report and Control' teams managed all the information during an attack. A local headquarters had an ARP controller who sent rescue and first aid teams to bombing sites. If local help wasn't enough, the controller could ask for help from nearby towns.
Fire Guards watched for incendiary bombs and reported fires. They could put out small magnesium bombs with sand or water. 'Gas Decontamination Teams' wore special gear to clean up areas hit by gas attacks.
Building air-raid shelters was a challenge. People needed to go underground for shelter but stay above ground for gas attacks. In 1936, a committee looked into building shelters. During the Munich crisis, local groups dug trenches for shelter. Later, the British Government made these permanent. They also gave out Anderson shelters for free to poorer families.
During the Second World War, the ARP gave out gas masks and shelters. They also kept public shelters ready and enforced the blackout. ARP workers helped rescue people after air raids. Some women became ARP Ambulance Attendants, giving first aid and recovering bodies.

Germany's air attacks during the "Blitz" did not break the spirit of the British people. This was thanks to strong air defenses, early warning radar, and the brave actions of civil defense units. Even with many civilian losses, the attacks did not stop British production or destroy the Royal Air Force.
Civil Defense in the United States
In the United States, the Office of Civilian Defense was set up in May 1941. It helped organize civilian defense efforts, working with the Department of the Army. One group that still exists today is the Civil Air Patrol. It started on December 1, 1941, to help with search and rescue. The Civil Air Patrol also helped find enemy submarines and watched for ships.
The Coast Guard Auxiliary does similar work for the U.S. Coast Guard. It was also created before World War II. After the war, the Auxiliary focused on boating safety and helping with search and rescue.
A federal civil defense program existed in the U.S. from 1951 to 1994. This program was later changed to cover "all hazards," meaning all types of emergencies. The term "EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS" became more common after these changes.
After World War II

After World War II, especially during the Cold War, many countries prepared for a nuclear war. This included countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, West Germany, and neutral countries like Switzerland and Sweden.
In the United Kingdom, the Civil Defence Service was stopped in 1945. But with rising tensions between East and West, it was brought back in 1949 as the Civil Defence Corps. This volunteer group was meant to take charge after a major national emergency, especially a nuclear attack.
Each part of the Corps had different sections, like Headquarters, Intelligence, Scientific, Warden & Rescue, Ambulance, and Welfare.
In 1954, the Coventry City Council caused a stir when it tried to stop its Civil Defence committee. They believed hydrogen bombs meant there could be no recovery from a nuclear attack. The British government disagreed and held a civil defense exercise in Coventry to show their point.
In the United States, the huge power of nuclear weapons led to a bigger civil defense effort. In 1950, the National Security Resources Board created a 162-page plan for U.S. civil defense. This "Blue Book" guided civil defense for the next 40 years.
A famous part of the Cold War civil defense was the public education. In the film Duck and Cover, Bert the Turtle taught children to "duck and cover" if they saw a bright flash. Books like Survival Under Atomic Attack and Fallout Protection were also common. Radio programs mixed hit music with civil defense tips.
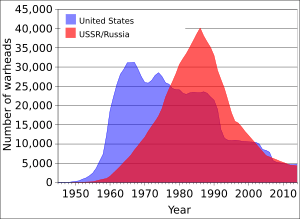
U.S. President Kennedy (1961–63) started a big effort to build fallout shelters across the country. These shelters would not protect against the initial blast of a nuclear weapon. But they would offer some protection from the radiation that would last for weeks. To make these preparations work, people needed some warning. In 1951, CONELRAD was set up. This system would broadcast an alert from a few main radio stations, which other stations would then repeat.
In the Soviet Union, leaders believed a nuclear war could be won. They planned to reduce the effects of nuclear attacks on their land. They spent much more time on civil defense than the U.S. did.
Soviet Civil Defense Troops played a big role after the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear accident. They were called up like in wartime to help clean up. They did dangerous tasks, including removing highly-radioactive debris by hand when robots failed. Many were honored for their work.

In Western countries, strong civil defense plans were not fully put in place. Some thought it went against the idea of "mutual assured destruction" (MAD), which meant no one would survive a nuclear war. Also, a full defense would have been very expensive. Many people felt civil defense efforts were useless against nuclear weapons, even though they were based on scientific research.
The Civil Defence Corps in Great Britain was stopped in 1968 due to money problems. However, the Isle of Man Civil Defence Corps and Civil Defence Ireland continued their work.
In the United States, different civil defense groups were replaced by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) in 1979. In 2002, FEMA became part of the Department of Homeland Security. The focus changed from nuclear war to an "all-hazards" approach, dealing with all kinds of emergencies. Natural disasters and new threats like terrorism have shifted attention to emergency management and homeland security.
Civil Defense Today
Many countries still have a national Civil Defence Corps. These groups usually help with large emergencies like floods, earthquakes, or civil unrest.
After the September 11 attacks in 2001, the idea of civil defense in the United States was revisited. It is now part of homeland security and all-hazards emergency management.
In Europe, the triangle CD logo is still widely used. It was created in 1939 and used during World War II and the Cold War. In the U.S., the old triangle logo was replaced in 2006 with a stylized "EM" for emergency management. However, Hawaii State Civil Defense and Guam Homeland Security/Office of Civil Defense still use the old name and logo.
The term "civil protection" is now common in the European Union. It refers to government systems and resources that protect people, mainly from natural and technological disasters. There's also a focus on preparing for technological disasters from terrorist attacks. Within EU countries, "crisis-management" focuses more on political and security aspects.
In Australia, civil defense is handled by the volunteer-based State Emergency Service. In many former Soviet countries, like Russia, civil defense is managed by government ministries, such as Russia's Ministry of Emergency Situations.
Why Civil Defense Matters
Even small investments in preparing for disasters can speed up recovery by months or years. This can prevent millions of deaths from hunger, cold, and disease. Experts say that a country's people are more valuable than its land or factories. People rebuild a country after it's damaged. So, protecting people is important for a country's economic safety. Also, preparing for uncertain events can help people feel more in control of their lives.
In the United States, the federal civil defense program ran from 1951 to 1994. Parts of it were later included in the Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act. The main change was using "Emergency Preparedness" instead of "Civil Defense."
President Jimmy Carter started a "Crisis Relocation Program." This plan involved moving people during a crisis. However, President Ronald Reagan later stopped this idea.
Understanding Threats
Threats to civilians include NBC (Nuclear, Biological, and Chemical) weapons, or the more modern term CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear). Understanding each threat helps in planning ways to protect people.
- Conventional Attacks: These use regular explosives. A shelter designed only for radiation would be very weak against these.
- Nuclear Attacks: Shelters against nuclear blasts need thick concrete and strong materials. The biggest dangers from a nuclear attack are the blast, fires, and radiation. Switzerland is one of the most prepared countries for a nuclear attack. Almost every building there has a shelter against the initial bomb and fallout. Many people use these shelters to store valuables. Switzerland also has air-raid and nuclear-raid sirens in every village.
- Dirty Bomb: This is a "radiologically enhanced weapon" that uses an explosion to spread radioactive material. This is a theoretical risk and has not been used by terrorists. The dangers might be mostly psychological. Cleanup can be done using standard hazmat methods.
- Biological Attacks: The main threat here is from disease-causing germs like bacteria and viruses.
- Chemical Attacks: Various chemical agents, like nerve gas (VX, Sarin), are a threat.
Steps in Civil Defense
Reducing Harm
Reducing harm means actively trying to prevent war or the use of nuclear weapons. This includes diplomacy, gathering information, and direct actions against terrorist groups. It also involves long-term planning, like designing highways or placing military bases away from cities.
Getting Ready
Getting ready involves building blast shelters and preparing information, supplies, and emergency systems. For example, many large cities in the U.S. have underground emergency centers to help coordinate civil defense. FEMA also has underground facilities for this purpose.
Other preparations include keeping track of grain supplies, having a Strategic National Stockpile of medical supplies, and having a Strategic Petroleum Reserve of oil. It also means having mobile bridges, water purification systems, and temporary housing to help recovery.
For individuals, one way to prepare for nuclear fallout is to have potassium iodide (KI) tablets. These protect the thyroid gland from dangerous radioactive iodine. Another step is to cover your nose, mouth, and eyes to protect against alpha particles.
To help with disaster prevention, those in charge of civil protection need to be ready. This means:
- Creating a way for different civil protection services (police, fire service, healthcare, utilities, volunteers) to work together quickly.
- Setting up training programs for emergency teams and experts, including joint courses.
- Making sure international civil protection efforts work well together.
Preparing also means sharing information:
- Helping to inform the public so people can protect themselves better.
- Collecting and sharing accurate emergency information.
- Sharing information about national civil protection resources, including military and medical help.
- Making sure different authorities share information effectively.
Recovery Efforts
Recovery means rebuilding damaged buildings, roads, and production facilities. This phase is the longest and often the most expensive. After the immediate crisis passes, recovery efforts can sometimes become political.
Planning for recovery can be very helpful. If resources are spread out before an attack, it can prevent many social problems. For example, if a city has a "tourist ferry" on its river, it can help transport people if a bridge is damaged.
Civil Defense Groups
Civil Defense is also the name of many groups worldwide. These groups protect civilians from military attacks and provide rescue services after natural and human-made disasters.
Global protection efforts are managed by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA).
In some countries, like Jordan and Singapore (see Singapore Civil Defence Force), civil defense is basically the same as the fire brigade. But in most countries, civil defense is a government-run, volunteer-staffed group, separate from the fire and ambulance services.
As the Cold War ended, some civil defense groups were stopped or changed their focus. For example, the Royal Observer Corps in the United Kingdom was disbanded. Others, like the State Emergency Service in Australian states, now focus on rescue after natural disasters. However, the ideas of Civil Defense have returned in the United States through FEMA's Citizen Corps and Community Emergency Response Team (CERT).
In the United Kingdom, civil defense work is done by Emergency Responders under the Civil Contingencies Act 2004. They get help from volunteer groups like RAYNET and Search and Rescue Teams. In Ireland, the Civil Defence is still very active. They help with things like flash flooding and provide auxiliary fire and ambulance services.
Civil Defense by Country
More to Explore
- The American Civil Defense Association
- French Civil Protection
- Blast shelter
- Civil-defense Geiger counters
- Civil defense siren
- Collective protection
- Continuity of government
- Critical infrastructure protection
- Effects of nuclear explosions on human health
- Emergency management
- Fallout shelter
- International Civil Defence Organization
- Mass fatality incident
- State Council of Civil Defense
- List of civil defense ranks
General Topics:
- Nuclear warfare
- Nuclear holocaust
- Nuclear terrorism
- Human security
- Industrial antiterrorism
- Infrastructure security
- Survivalism
- Weapon of mass destruction
External Links
- Greece
- Large gallery of Bulgaria's Civil Defense Mechanization(archived link)
- The UK Civil Defence Project – History & Photos
- National Civil Defence College, Nagpur INDIA
- Special Event Amateur Ham Radio Station operated from Bangalore, INDIA
- Protezione Civile Italian Civil Defense
- Dublin Civil Defence Ireland
- SEBEV Search and Rescue (originally a Civil Defence team in the UK)
- Civil Protection (Ministry of Interior, Spain).
- Civil Protection Villena – Spain
- Civil Defense Logo dies at 67, and Some Mourn its Passing, The New York Times, 1 December 2006 by David Dunlap.
- Cold War Era Civil Defense Museum – Features much historical information about Civil Defense history, its equipment and methods, and many historical photographs and posters.
- Annotated bibliography for civil defense from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues
- The American Civil Defense Association
- Civil Defense Caves – Cold War community getaway in case of nuclear war located in Idaho
- Comprehensive Emergency Management Reference Material Repository
- Ready.gov – The official preparedness site of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security
- "Civil Defence" – A site with details of the UK's Civil Defence preparations, including those implemented during the Cold War such as the Burlington Central Government War HQ., at Corsham, Wiltshire.
- Emergency Planning in Lincolnshire
- The official Civil Defence site for the Republic of Ireland: http://www.civildefence.ie/
- The official Civil Defense site of São Paulo State – Brazil: http://www.defesacivil.sp.gov.br/
- Doctors for Disaster Preparedness
- Physicians for Civil Defense
- Dutch civil defense instructions in English
- Emergency Management Portal – online resources for emergency planners and managers
- The Norwegian Civil Defence
- German Federal Agency for Technical Relief – THW Technisches Hilfswerk
nl:Burgerbescherming
See also
 In Spanish: Protección civil para niños
In Spanish: Protección civil para niños









