Connecticut Lakes facts for kids
The Connecticut Lakes are a group of beautiful lakes in northern New Hampshire, United States. They are found in Coos County, right where the Connecticut River begins. You can reach these lakes by taking the northern part of U.S. Route 3, which runs between the village of Pittsburg and the border with Canada. The lakes are located within the town of Pittsburg, but they are quite a distance from the town center. The Connecticut Lakes State Forest is right next to them.
There are four lakes: First, Second, Third, and Fourth Connecticut Lake. They are numbered from south to north. As you go from the First to the Fourth lake, they get smaller in size but higher up in the mountains. The Fourth Connecticut Lake is super special because it's where the mighty Connecticut River actually starts! You can easily see and get to the first three lakes from U.S. Route 3. However, to reach the Fourth Lake, you need to hike on the Fourth Connecticut Lake Trail. This trail even goes into Canada for a bit! All the lakes are north of the 45th parallel, which is an important line of latitude.
Just south of these four lakes is Lake Francis. This is a reservoir (a man-made lake) and the last big lake along the Connecticut River in northern New Hampshire.
Contents
Exploring the Connecticut Lakes
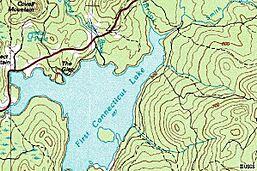
First Connecticut Lake
Quick facts for kids First Connecticut Lake |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Coos County, New Hampshire |
| Coordinates | 45°5′37″N 71°14′52″W / 45.09361°N 71.24778°W |
| Primary inflows | Connecticut River |
| Primary outflows | Connecticut River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 5.3 mi (8.5 km) |
| Max. width | 2.7 mi (4.3 km) |
| Surface area | 3,071 acres (1,243 ha) |
| Average depth | 56 ft (17 m) |
| Max. depth | 163 ft (50 m) |
| Surface elevation | 1,638 ft (499 m) |
| Settlements | Pittsburg |
First Connecticut Lake is located in the town of Pittsburg. It's about 7 miles (11 km) northeast of the village center. This lake covers about 3,071 acres (1,243 ha), making it the eighth-largest lake completely within New Hampshire. It's the lowest in elevation and the biggest in surface area of the four Connecticut Lakes.
You can find fish like landlocked salmon and lake trout here. The lake is about 56 feet (17 m) deep on average, but its deepest point is 163 feet (50 m)! There are three places where you can launch a boat. You can also go ice fishing from January through March. The water flowing out of the lake into the Connecticut River is controlled by the First Lake Dam. This dam is located near U.S. Route 3 on the southwest side of the lake.
A special marker on the southwestern shore remembers Luther Parker. He was an important person from the time of the Republic of Indian Stream in the 1830s.
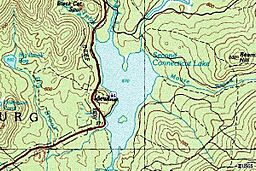
Second Connecticut Lake
| Second Connecticut Lake | |
|---|---|
| Location | Coos County, New Hampshire |
| Coordinates | 45°9′23″N 71°10′14″W / 45.15639°N 71.17056°W |
| Primary inflows | Connecticut River |
| Primary outflows | Connecticut River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 3.1 mi (5.0 km) |
| Max. width | 1.3 mi (2.1 km) |
| Surface area | 1,102 acres (4 km2) |
| Average depth | 20 ft (6.1 m) |
| Max. depth | 63 ft (19 m) |
| Surface elevation | 1,866 ft (569 m) |
| Islands | 3 |
| Settlements | Pittsburg |
Second Connecticut Lake was once called Lake Carmel. It covers about 1,102 acres (446 ha) in Pittsburg. It's about 15 miles (24 km) northeast of the village center. This lake is 228 feet (69 m) higher than the First Lake and is also shallower.
You can find fish like brook trout, landlocked salmon, and lake trout here. There's one public boat launch. Just like the First Lake, you can go ice fishing from January through March. The water flowing out of this lake is controlled by the Second Lake Dam, located near U.S. Route 3.
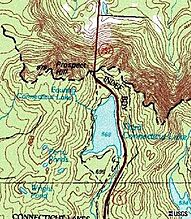
Third Connecticut Lake
| Third Connecticut Lake | |
|---|---|
| Location | Coos County, New Hampshire |
| Coordinates | 45°14′15″N 71°12′0″W / 45.23750°N 71.20000°W |
| Primary inflows | Connecticut River |
| Primary outflows | Connecticut River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 1.1 mi (1.8 km) |
| Max. width | 0.5 mi (0.80 km) |
| Surface area | 231 acres (93 ha) |
| Average depth | 42 ft (13 m) |
| Max. depth | 101 ft (31 m) |
| Surface elevation | 2,188 ft (667 m) |
| Settlements | Pittsburg |
Third Connecticut Lake was once known as Lake St. Sophia. It's a 231-acre (93 ha) lake in Pittsburg. It's about 20 miles (32 km) northeast of the village center. This lake is less than 1 mile (1.6 km) south of the Canadian border. It can be as deep as 100 feet (30 m). It sits 322 feet (98 m) higher in elevation than the Second Lake.
You can find rainbow trout and lake trout here. There's one public boat launch off U.S. Route 3 on the eastern side of the lake. Ice fishing is also allowed from January through March.
Fourth Connecticut Lake
| Fourth Connecticut Lake | |
|---|---|
| Location | Coos County, New Hampshire |
| Coordinates | 45°14′52″N 71°12′52″W / 45.24778°N 71.21444°W |
| Primary outflows | Connecticut River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 0.1 miles (.16 km) |
| Surface area | 1.8 acres (0.73 ha) |
| Surface elevation | 2,670 ft (810 m) |
| Settlements | Pittsburg |
Fourth Connecticut Lake is the northernmost and most difficult to reach of the Connecticut Lakes. It's also the smallest, covering only about 1.8 acres (0.73 ha). This tiny lake is the official source of the Connecticut River! It's located in Pittsburg, about 0.5 miles (0.8 km) upstream and 482 feet (147 m) higher than Third Connecticut Lake. The Fourth Lake is right next to the Third Lake, but a bit to its northwest. You can hike to it using the Fourth Connecticut Lake Trail.
Fourth Connecticut Lake Trail
The Fourth Connecticut Lake Trail is a public hiking path. It's cared for by The Nature Conservancy. This trail crosses the border between New Hampshire and Quebec, Canada, for about 0.6 miles (1 km). It ends with a 0.5-mile (0.8 km) loop around Fourth Connecticut Lake. It's one of the few trails in North America that crosses an international border! The land around the lake is owned by The Nature Conservancy.
The parking area for hikers is at the American border crossing facility for Pittsburg–Chartierville Border Crossing. This is about 22 miles (35 km) north of Pittsburg town center on U.S. Route 3. The trail starts about 50 yards (46 m) to the right of the American building, where you'll see a small sign.
It's important to be prepared for this hike! There's no cell phone service on the trail. You'll need to do some non-technical climbing, and the trail starts at a high elevation. Even in summer, be ready for a good hike. Please remember that pets are not allowed on the trail. Also, no camping, hunting, or fishing is permitted.
If you start hiking from the United States, you don't need a passport. Even though parts of the trail go into Canada, the trail begins and ends on the American side of the border. However, if you were to start from Canada, you would need a passport or other border crossing document to enter the United States at the border facility before hiking the trail.
Climate Around the Lakes
The area around First Connecticut Lake has a type of climate called a warm-summer humid continental climate. This means it has warm summers and cold, snowy winters. The hottest temperature ever recorded at First Connecticut Lake was 93°F (34°C) on July 8, 1921, and again on July 19, 1953. The coldest temperature ever recorded was a very chilly -45°F (-43°C) on February 1, 1920.
| Climate data for First Connecticut Lake, New Hampshire, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1918–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 60 (16) |
64 (18) |
77 (25) |
83 (28) |
91 (33) |
91 (33) |
93 (34) |
92 (33) |
89 (32) |
83 (28) |
72 (22) |
63 (17) |
93 (34) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 45.3 (7.4) |
47.5 (8.6) |
55.0 (12.8) |
70.5 (21.4) |
79.9 (26.6) |
84.5 (29.2) |
85.1 (29.5) |
83.6 (28.7) |
80.6 (27.0) |
71.6 (22.0) |
61.1 (16.2) |
49.4 (9.7) |
87.0 (30.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 22.4 (−5.3) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
34.2 (1.2) |
47.1 (8.4) |
61.5 (16.4) |
70.4 (21.3) |
75.0 (23.9) |
73.6 (23.1) |
66.4 (19.1) |
52.8 (11.6) |
39.9 (4.4) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
49.8 (9.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 11.1 (−11.6) |
12.8 (−10.7) |
21.9 (−5.6) |
36.3 (2.4) |
49.9 (9.9) |
59.3 (15.2) |
64.2 (17.9) |
62.7 (17.1) |
55.1 (12.8) |
43.5 (6.4) |
31.8 (−0.1) |
19.9 (−6.7) |
39.0 (3.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | −0.3 (−17.9) |
0.4 (−17.6) |
9.6 (−12.4) |
25.5 (−3.6) |
38.3 (3.5) |
48.3 (9.1) |
53.4 (11.9) |
51.7 (10.9) |
43.9 (6.6) |
34.1 (1.2) |
23.7 (−4.6) |
11.1 (−11.6) |
28.3 (−2.0) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −27.0 (−32.8) |
−24.6 (−31.4) |
−18.5 (−28.1) |
6.6 (−14.1) |
25.1 (−3.8) |
32.6 (0.3) |
40.7 (4.8) |
38.4 (3.6) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
19.6 (−6.9) |
4.6 (−15.2) |
−14.0 (−25.6) |
−30.0 (−34.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −44 (−42) |
−45 (−43) |
−36 (−38) |
−17 (−27) |
14 (−10) |
25 (−4) |
29 (−2) |
28 (−2) |
18 (−8) |
8 (−13) |
−13 (−25) |
−44 (−42) |
−45 (−43) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.02 (77) |
2.37 (60) |
3.04 (77) |
3.60 (91) |
4.47 (114) |
5.14 (131) |
4.91 (125) |
4.76 (121) |
4.00 (102) |
4.63 (118) |
3.62 (92) |
3.57 (91) |
47.13 (1,199) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 30.3 (77) |
28.4 (72) |
24.6 (62) |
9.7 (25) |
1.0 (2.5) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
2.5 (6.4) |
14.6 (37) |
31.9 (81) |
143.0 (363) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 22.3 (57) |
27.9 (71) |
29.4 (75) |
16.9 (43) |
0.9 (2.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.2 (3.0) |
6.9 (18) |
14.9 (38) |
30.6 (78) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 18.3 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 15.0 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 14.1 | 12.1 | 15.5 | 16.7 | 19.3 | 185.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 16.8 | 13.5 | 11.5 | 5.3 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 8.6 | 15.5 | 73.6 |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service | |||||||||||||
Connecticut Lakes Natural Area

In 2002, a large area of 25,000 acres (10,000 ha) around the lakes was protected. This was done as a land conservation project by the New Hampshire Fish and Game Department. This special protected area is located within the towns of Clarksville and Pittsburg, all the way up to the border with Canada. This helps keep the beautiful natural environment safe for everyone.