Timber rattlesnake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Timber rattlesnake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A Timber Rattlesnake | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus horridus Linnaeus, 1758
|
|
 |
|
The timber rattlesnake (Crotalus horridus) is a type of venomous pit viper. It lives in the eastern United States. This snake is the second largest venomous snake found in this part of North America. There are no different types (subspecies) of this snake known today.
Contents
What the Timber Rattlesnake Looks Like
Adult timber rattlesnakes usually grow to be about 91 to 152 centimeters (3 to 5 feet) long. The longest one ever found was about 189 centimeters (6.2 feet) long. Large timber rattlesnakes can weigh around 4.5 kilograms (9.9 pounds). However, most of them weigh between 580 and 900 grams (20 to 32 ounces). Their scales are often yellowish-brown or gray. They have dark brown or black stripes on their bodies.
Where Timber Rattlesnakes Live
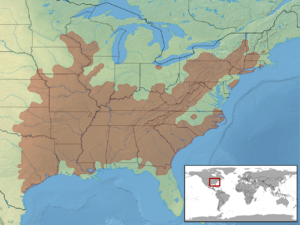
Timber rattlesnakes are found in woodlands and forests across the eastern United States. Their home range stretches from southern Minnesota and southern New Hampshire, all the way south to eastern Texas and northern Florida.
During the summer, pregnant female snakes like to stay in open, rocky areas. These spots are warmer, which helps them get ready to have their babies. Males and females that are not pregnant prefer cooler woodlands. These areas have a thick forest canopy, which is like a roof of leaves.
Females often warm themselves in the sun in open, rocky spots. These places are sometimes called "basking knolls." In the winter, timber rattlesnakes hibernate (sleep deeply) in dens and caves to stay safe from the cold.
What Timber Rattlesnakes Eat
Timber rattlesnakes mainly eat small mammals. But they also hunt and eat birds, frogs, and other snakes. Sometimes, they even eat other rattlesnakes! The most common snake they eat is the garter snake.
Timber Rattlesnake Venom
The timber rattlesnake is one of North America's most dangerous snakes. Before they bite, they usually give a warning. They shake their rattle, which is at the end of their tail. This sound tells others to stay away.
Their venom is a complex mix that can affect the body in different ways. If someone is bitten, there is a special medicine called CroFab antivenom. This medicine helps treat bites from the timber rattlesnake.
How We Protect Timber Rattlesnakes
The timber rattlesnake is listed as "least concern" on the IUCN Red List. This means that, overall, there are enough of them in the world.
However, in some states, their numbers are much lower. The timber rattlesnake is considered endangered (meaning they are at high risk of disappearing) in New Jersey, Vermont, Massachusetts, Virginia, New Hampshire, Indiana, and Ohio. They are listed as threatened (meaning they could become endangered soon) in New York, Connecticut, Illinois, Minnesota, and Texas.
Sadly, timber rattlesnakes are now extinct (meaning they no longer exist) in Maine and Rhode Island. In New Hampshire, only one group of these snakes is left. Even though they are protected in many Appalachian states, their populations are still getting smaller.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cascabel de los bosques para niños
In Spanish: Cascabel de los bosques para niños




